Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Xu, Z.*; Litzinger, A.*; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Arora, B.*; Hazenberg, P.*; Wang, L.*; Gonzalez Raymat, H.*; Fabricatore, E.*; Wainwright, Haruko*; Eddy-Dilek, C.*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2024/03
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Kaneda-Nakashima, Kazuko*; Shirakami, Yoshifumi*; Kadonaga, Yuichiro*; Watabe, Tadashi*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Yin, X.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Internet), 25(2), p.933_1 - 933_14, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)R hm, W.*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Chen, J.*; Li, C.*; Dobynde, M.*; Durante, M.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Ozasa, Kotaro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
hm, W.*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Chen, J.*; Li, C.*; Dobynde, M.*; Durante, M.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Ozasa, Kotaro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
Journal of Medical Physics - Zeitschrift f r medizinische Physik -, 10 Pages, 2024/00
r medizinische Physik -, 10 Pages, 2024/00
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) provides independent recommendations on radiological protection for the public benefit. For more than 90 years, the ICRP System of Radiological Protection has been guiding the development and implementation of national and international standards and regulations on radiological protection. In 2019, ICRP established Task Group (TG) 115 to address a broader range of topics related to dose and risk assessment for radiological protection of astronauts. This paper gives an overview of the System of Radiological Protection and a brief summary of ICRP's work on radiological protection of astronauts.
Taniguchi, Takeshi*; Isobe, Kazuo*; Imada, Shogo*; Eltayeb, M. M.*; Akaji, Yasuaki*; Nakayama, Masataka; Allen, M. F.*; Aronson, E. L.*
Science of the Total Environment, 899, p.165524_1 - 165524_13, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:84.15(Environmental Sciences)Dryland ecosystems experience seasonal cycles of severe drought and moderate precipitation. Desert plants typically have patchy distributions, and many may develop symbiotic relationships with root endophytic microbes to survive under the repeated wet and extremely dry conditions. Although community coalescence has been found in many systems, the colonization by functional microbes and its relationship to seasonal transitions in arid regions are not well understood. Here we examined root endophytic microbial taxa, and their traits in relation to their root colonization, during the dry and wet seasons in a hot desert of the southwestern United States. We used high-throughput DNA sequencing of 16S rRNA and ITS gene profiling of five desert shrubs, and analyzed the seasonal change in endophytic microbial lineages. In summer, Actinobacteria increased, although this was not genus-specific. For fungi, Glomeraceae selectively increased in summer. In winter, Gram-negative bacterial genera, including those capable of nitrogen fixation and plant growth promotion, increased. Neutral model analysis revealed a strong stochastic influence on endophytic bacteria but a weak effect for fungi, especially in summer. The taxa with higher frequency than that predicted by the neutral model shared environmental adaptability and symbiotic traits, whereas the frequency of pathogenic fungi was at or under the predicted value. These results suggest that community assembly of bacteria and fungi is regulated differently. The bacterial community was affected by stochastic and deterministic processes via the bacterial response to drought (response trait) and beneficial effect on plants (effect trait). For fungi, mycorrhizal fungi were selected by plants in summer. The regulation of beneficial microbes by plants in both dry and wet seasons suggests the presence of plant-soil positive feedback in this natural desert ecosystem.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Lind, T.*; Kalilainen, J.*; Marchetto, C.*; Beck, S.*; Nakamura, Koichi*; Kino, Chiaki*; Maruyama, Yu; Kido, Kentaro; Kim, S. I.*; Lee, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4796 - 4809, 2023/08
Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki*; Shimada, Asako; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
Shavers, M. R.*; Semones, E. J.*; Shurshakov, V.*; Dobynde, M.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Tomi, L.*; Chen, J.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Straube, U.*; et al.
Journal of Medical Physics - Zeitschrift f r medizinische Physik -, 13 Pages, 2023/00
r medizinische Physik -, 13 Pages, 2023/00
The Partner Agencies of the International Space Station (ISS) present an intracomparison of the ionizing radiation absorbed dose and risk quantities used to characterize example mission lunar space. The results and the work itself provide insights to the level of agreement with which space agencies can perform organ dosimetry and calculate effective dose. This work was performed in collaboration with the advisory and guidance efforts of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) Task Group 115 and will be presented in an ICRP Report
Takano, Kazuya; Oki, Shigeo; Ozawa, Takayuki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Ogura, Masashi*; Yamada, Yumi*; Koyama, Kazuya*; Kurita, Koichi*; Costes, L.*; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 8, p.35_1 - 35_9, 2022/12
The France and Japan teams have carried out collaborative works to have common technical views regarding a sodium-cooled fast reactor concept. Japan has studied the feasibility of an enhanced high burnup low-void effect (CFV) core and fuel using oxide dispersion-strengthened steel cladding in ASTRID 600. Regarding passive shutdown capabilities, Japan team has performed a preliminary numerical analysis for ASTRID 600 using a complementary safety device, called a self-actuated shutdown system (SASS), one of the safety approaches of Japan. The mitigation measures of ASTRID 600 against a severe accident, such as a core catcher, molten corium discharge assembly, and the sodium void reactivity features of the CFV core, are promising to achieve in-vessel retention for both countries. The common design concept based on ASTRID 600 is feasible to demonstrate the SFR core and safety technologies for both countries.
Maurer, C.*; Galmarini, S.*; Solazzo, E.*; Ku mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar
mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar , J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
, J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.106968_1 - 106968_27, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.8(Environmental Sciences)After performing multi-model exercises in 2015 and 2016, a comprehensive Xe-133 atmospheric transport modeling challenge was organized in 2019. For evaluation measured samples for the same time frame were gathered from four International Monitoring System stations located in Europe and North America with overall considerable influence of IRE and/or CNL emissions. As a lesion learnt from the 2nd ATM-Challenge participants were prompted to work with controlled and harmonized model set ups to make runs more comparable, but also to increase diversity. Effects of transport errors, not properly characterized remaining emitters and long IMS sampling times (12 to 24 hours) undoubtedly interfere with the effect of high-quality IRE and CNL stack data. An ensemble based on a few arbitrary submissions is good enough to forecast the Xe-133 background at the stations investigated. The effective ensemble size is below five.
Iida, Kazuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chang, L.-J.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.20663_1 - 20663_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Spin excitation of an ilmenite FeTiO powder sample is measured by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamic magnetic pair-density function
powder sample is measured by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamic magnetic pair-density function 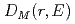 is obtained from the dynamic magnetic structure factor
is obtained from the dynamic magnetic structure factor 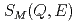 by the Fourier transformation.
by the Fourier transformation.
Xu, X.*; Odaira, Takumi*; Xu, S.*; Hirata, Kenji*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Ueki, Kosuke*; Ueda, Kyosuke*; Narushima, Takayuki*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*; et al.
Advanced Materials & Processes, 180(7), p.35 - 37, 2022/10
 ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; Kaneko, Tatsuya*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
 decay of the 8
decay of the 8 isomer in
isomer in  U
UZhang, M. M.*; Tian, Y. L.*; Wang, Y. S.*; Zhang, Z. Y.*; Gan, Z. G.*; Yang, H. B.*; Huang, M. H.*; Ma, L.*; Yang, C. L.*; Wang, J. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024305_1 - 024305_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)Odaira, Takumi*; Xu, S.*; Hirata, Kenji*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Ueki, Kosuke*; Ueda, Kyosuke*; Narushima, Takayuki*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Harjo, S.; et al.
Advanced Materials, 34(27), p.2202305_1 - 2202305_11, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:87.73(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Geng, R. L.*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.323 - 325, 2022/05
In order to evaluate the performance of a superconducting cavity, we are developing a mapping system to measure the distribution of cavity temperature, field emission X-rays, and trapped magnetic flux with high positional resolution. In order to construct a system with high positional resolution, a large number of sensors are required. However, as the number of sensors increases, so does the amount of wiring, which increases the complexity of the wiring in the cryogenic apparatus, and also increases the heat transfer through the wiring, which disturb efficient operation of cavity tests. We are developing an efficient mapping system with a multiplexer that scans the readout signal on the same circuit as the sensor in the cryogenic dewar where the cavity test is conducted. In this presentation, we report the outline and test results of the mapping system under development
Arai, Yosuke*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Tin, Z. H.*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Bareille, C.*; Akebi, Shuntaro*; Kurokawa, Kifu*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Zhang, W.-L.*; et al.
Nature Materials, 21(4), p.410 - 415, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:77.62(Chemistry, Physical)