Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Okamoto, Koji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 184, p.105710_1 - 105710_10, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Very recently, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) has been proposed as a scheme capable to inversely estimate radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms from air dose rate measurements together with the predicted lower bound of the measurement numbers for successful reconstructions. However, no one has ever analyzed how the uncertainty of input data including the measurement errors influences the accuracy of the inverse estimation results. In this paper, we therefore perform uncertainty analysis of the LASSO scheme and suggest an uncertainty estimation function derived based on the theory of Candes. We actually demonstrate in two types of numerical tests with different input uncertainties obtained by using Monte Carlo code, Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) that the calculated errors obey the proposed uncertainty estimation function. Thus, the LASSO scheme allows to successfully estimate radioactive distributions within the predicted uncertainty.
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 19(11), p.1888 - 1894, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2024/11
Efficiency and safety improvements in nuclear fuel development demand a comprehensive understanding of the thermal properties of PuO . Because of difficulty of experiments at high temperatures, they have been supplemented by numerical simulations, such as density functional theory (DFT). While DFT struggles to replicate the nonmagnetic insulating ground state of PuO
. Because of difficulty of experiments at high temperatures, they have been supplemented by numerical simulations, such as density functional theory (DFT). While DFT struggles to replicate the nonmagnetic insulating ground state of PuO , DFT+U can reproduce nonmagnetic insulating state. However, the obtained state remains less stable than magnetic states and is not the ground state. Adiabatic connection fluctuation-dissipation theory (ACFDT) is expected to be a promising solution, addressing higher-order correlations and exact exchange energies. In this study, we evaluate the ground state energy using ACFDT and find that the nonmagnetic state can be the ground state. This result successfully reproduces the observed nonmagnetic ground state of PuO
, DFT+U can reproduce nonmagnetic insulating state. However, the obtained state remains less stable than magnetic states and is not the ground state. Adiabatic connection fluctuation-dissipation theory (ACFDT) is expected to be a promising solution, addressing higher-order correlations and exact exchange energies. In this study, we evaluate the ground state energy using ACFDT and find that the nonmagnetic state can be the ground state. This result successfully reproduces the observed nonmagnetic ground state of PuO and has the potential to improve predictions of the thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials.
and has the potential to improve predictions of the thermal properties of nuclear fuel materials.
Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Tanimura, Naoki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.16004_1 - 16004_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)When we decommission a reactor building, it is desirable to identify the radiation source distribution for safety. It has been reported that the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates at appropriate observation points by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). However, it is difficult to decide on suitable points in advance. Therefore, we estimate the posterior distribution from the prior distribution of the source amounts, which are calculated by the standard LASSO, using the Bayesian LASSO, and evaluate the predictive distribution of the evaluated air dose rates at the candidate observation points from the posterior distribution. We select the additional observation point based on the variances of the predictive distributions. We confirmed that the method can estimate the source distribution with fewer additional observation points than when adding ones randomly in most cases.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2776, p.012009_1 - 012009_9, 2024/06
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.38(Materials Science, Ceramics)Kim, M.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.*; Abe, Tomohisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Machida, Masahiko; Saito, Kimiaki
Kankyo Hoshano Josen Gakkai-Shi, 12(2), p.39 - 53, 2024/04
More than ten years have passed since the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. But with the progress of decontamination, the evacuation order has been lifted and the return of residents is still ongoing. Under these circumstances, in order to quantitatively evaluate the effect of decontamination activities and cultivation on air dose rate reduction, a detailed environmental model was constructed using 3D-ADRES for a real area located in the Okuma town, Fukushima prefecture. Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the model to calculate realistic distributions of radioactive Cs based on measurement results and air dose rates reflecting changes over time. As a result, the distribution of air dose rates at 100 cm above ground level in the target area according to decontamination and cultivation activities was calculated. The calculated air dose rates reproduced the measured values well, and were confirmed to be appropriate as a method for evaluating the effects of decontamination and cultivation activities. This method is expected to serve as a reference for further decontamination management measures to reduce the air dose rate in the difficult-to-return zone, where entry is still restricted.
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)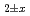 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dohi, Terumi; Iijima, Kazuki; Machida, Masahiko; Suno, Hiroya*; Omura, Yoshihito*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kimura, Shigeru*; Kanno, Futoshi*
Environmental Radiochemical Analysis VII, p.50 - 57, 2023/12
Kim, M.; Malins, A.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshida, Hiroko*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.156 - 169, 2023/11
Dose reduction factor of a Japanese house is important information in the external exposure estimation of returning residents. In 2019, a total of 19 wooden houses were surveyed in Iitate Village and Namie Town using a gamma plotter that can continuously measure the air dose rate. In addition, the characteristics of the reduction factor were investigated from the measured air dose rate. In the vicinity of houses, uncontaminated areas exist underneath houses and, the ratio of paved surfaces such as asphalt roads is relatively high; furthermore, the pavement has a tendency for the radiation source to decay quickly. Therefore, the air dose rate near the house showed a relatively low value in common at all sites. Air dose rates above unpaved surfaces showed higher values and larger variations than those above paved surfaces within a radius of 50 m form the center of a house. The reduction factor was widely distributed even for one house, if the ratio of every air dose rate observed inside and outside the house is considered. It is suggested that a realistic reduction factor may not be obtained when the reduction factor is obtained based on the measured values at a small number of points that do not have the representativeness of the radiation field to be measured.
 Sr (
Sr (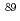 Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areas
Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areasMachida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.119 - 139, 2023/11
We estimate monthly discharged inventory of  Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of
Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of  Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:75.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 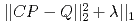 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
 H behavior in the Fukushima coastal region; Comparison of influences of discharges from the Fukushima Daiichi and rivers
H behavior in the Fukushima coastal region; Comparison of influences of discharges from the Fukushima Daiichi and riversSakuma, Kazuyuki; Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Iijima, Kazuki
Marine Pollution Bulletin, 192, p.115054_1 - 115054_10, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:59.95(Environmental Sciences)Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Arikawa, Taro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(2), p.73 - 86, 2023/06
no abstracts in English
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)