Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD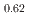 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 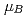 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD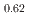 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 35(1), p.4 - 11, 2025/03
Iron reacts with hydrogen to form solid solutions with body-centered cubic, face-centered cubic, hexagonal close packed, and double hexagonal close packed structures at high temperatures and high pressures. Neutron diffraction is the most powerful tool for determining the occupation sites and occupancies of hydrogen atoms dissolved in a metal lattice. Structural parameters, including hydrogen occupation sites and occupancies, are refined via Rietveld analysis for neutron diffraction data. We present our expertise in Rietveld refinement of iron hydrides accumulated over 10 years.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 80(6), p.695 - 705, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)So far, the odd hydration number has been missing in the water-rich magnesium chloride hydrate series (MgCl

 H
H O). In this study, we have identified magnesium chloride heptahydrate, MgCl
O). In this study, we have identified magnesium chloride heptahydrate, MgCl
 7H
7H O (or MgCl
O (or MgCl
 7D
7D O) which forms at high pressures and high temperatures of above 2 GPa and above 300 K, respectively. Its structure has been determined by a combination of
O) which forms at high pressures and high temperatures of above 2 GPa and above 300 K, respectively. Its structure has been determined by a combination of  single crystal X-ray diffraction at 2.5 GPa and 298 K and powder neutron diffraction at 3.1 GPa and 300 K. The results showed an orientational disorder of water molecules, which was also examined by the density-functional-theory calculations. The disorder involves the reconnection of hydrogen bonds, which differs from those in water ice phases and known disordered salt hydrates. The shrinkage by compression occurs mainly in one direction. In the plane perpendicular to this most compressible direction, oxygen and chlorine atoms are in a hexagonal-like arrangement.
single crystal X-ray diffraction at 2.5 GPa and 298 K and powder neutron diffraction at 3.1 GPa and 300 K. The results showed an orientational disorder of water molecules, which was also examined by the density-functional-theory calculations. The disorder involves the reconnection of hydrogen bonds, which differs from those in water ice phases and known disordered salt hydrates. The shrinkage by compression occurs mainly in one direction. In the plane perpendicular to this most compressible direction, oxygen and chlorine atoms are in a hexagonal-like arrangement.
Fujisawa, Yuita*; Krishnadas, A*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Hsu, C.-H.*; Smith, B. R. M.*; Pardo-Almanza, M*; Hiyane, Hoshu*; Nagai, Yuki; Machida, Tadashi*; Okada, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 110(22), p.224511_1 - 224511_5, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Understanding the nature of vortices in type-II superconductors has been vital for deepening the physics of exotic superconductors and applying superconducting materials to future electronic devices. A recent study has shown that the LiTi O
O (111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi
(111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi O
O (111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
(111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 19(11), p.1888 - 1894, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In our previous article (Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014)), the site occupancies of D atoms dissolved in an fcc Fe metal lattice were investigated via Rietveld refinement of neutron powder diffraction patterns collected at 988 K and 6.3 GPa. The fcc metal lattice has two interstitial sites available for accommodating D atoms: octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The Rietveld refinement revealed that D atoms occupied mainly the octahedral sites with occupancy of 0.532 and slightly the tetrahedral sites with occupancy of 0.056. Subsequent density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations by Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019)) showed that the occupation energy on the tetrahedral site was significantly higher than that on the octahedral site; the tetrahedral site occupation was unlikely to occur even at temperatures as high as 988 K. We reexamined the site occupancies of D-atom by Rietveld refinement including extinction correction. As a result, the octahedral occupancy was increased to 0.60 and the tetrahedral occupancy was reduced to zero. The occupation of only the octahedral site for D atom is consistent with the DFT calculation, although in contrast to the previous results.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)High-pressure responses of the O-D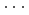 F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)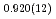 F
F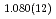 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2776, p.012009_1 - 012009_9, 2024/06
 O ice observed by neutron diffraction
O ice observed by neutron diffractionKomatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Klotz, S.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Yamashita, Keishiro*; Ito, Hayate*; Kobayashi, Hiroki*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5100_1 - 5100_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:67.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hydrogen bond symmetrisation is the phenomenon where a hydrogen atom is located at the centre of a hydrogen bond. Theoretical studies predict that hydrogen bonds in ice VII eventually undergo symmetrisation upon increasing pressure, involving nuclear quantum effect with significant isotope effect and drastic changes in the elastic properties through several intermediate states with varying hydrogen distribution. Despite numerous experimental studies conducted, the location of hydrogen and hence the transition pressures reported up to date remain inconsistent. Here we report the atomic distribution of deuterium in D O ice using neutron diffraction above 100 GPa and observe for the first time the transition from a bimodal to a unimodal distribution of deuterium at around 80 GPa. At the transition pressure, a significant narrowing of the peak widths of 110 was also observed, attributed to the structural relaxation by the change of elastic properties.
O ice using neutron diffraction above 100 GPa and observe for the first time the transition from a bimodal to a unimodal distribution of deuterium at around 80 GPa. At the transition pressure, a significant narrowing of the peak widths of 110 was also observed, attributed to the structural relaxation by the change of elastic properties.
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.38(Materials Science, Ceramics)Kim, M.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.*; Abe, Tomohisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Machida, Masahiko; Saito, Kimiaki
Kankyo Hoshano Josen Gakkai-Shi, 12(2), p.39 - 53, 2024/04
More than ten years have passed since the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. But with the progress of decontamination, the evacuation order has been lifted and the return of residents is still ongoing. Under these circumstances, in order to quantitatively evaluate the effect of decontamination activities and cultivation on air dose rate reduction, a detailed environmental model was constructed using 3D-ADRES for a real area located in the Okuma town, Fukushima prefecture. Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the model to calculate realistic distributions of radioactive Cs based on measurement results and air dose rates reflecting changes over time. As a result, the distribution of air dose rates at 100 cm above ground level in the target area according to decontamination and cultivation activities was calculated. The calculated air dose rates reproduced the measured values well, and were confirmed to be appropriate as a method for evaluating the effects of decontamination and cultivation activities. This method is expected to serve as a reference for further decontamination management measures to reduce the air dose rate in the difficult-to-return zone, where entry is still restricted.
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied) neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionKobayashi, Hiroki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ito, Hayate*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(47), p.10664 - 10669, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.29(Chemistry, Physical)Ice IV is a metastable high-pressure phase of ice in which the water molecules exhibit orientational disorder. Although orientational ordering is commonly observed for other ice phases, it has not been reported for ice IV. We conducted  powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D
powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
 Sr (
Sr (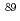 Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areas
Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areasMachida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.119 - 139, 2023/11
We estimate monthly discharged inventory of  Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of
Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of  Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 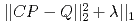 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
 H behavior in the Fukushima coastal region; Comparison of influences of discharges from the Fukushima Daiichi and rivers
H behavior in the Fukushima coastal region; Comparison of influences of discharges from the Fukushima Daiichi and riversSakuma, Kazuyuki; Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Iijima, Kazuki
Marine Pollution Bulletin, 192, p.115054_1 - 115054_10, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:59.95(Environmental Sciences)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)