Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,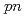 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter
clusters in dilute neutron-rich matterTanaka, Junki*; Yang, Z.*; Typel, S.*; Adachi, Satoshi*; Bai, S.*; van Beek, P.*; Beaumel, D.*; Fujikawa, Yuki*; Han, J.*; Heil, S.*; et al.
Science, 371(6526), p.260 - 264, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.30(Multidisciplinary Sciences)By employing quasi-free  -cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of
-cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of  clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between
clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between  -cluster formation and the neutron skin.
-cluster formation and the neutron skin.
 Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
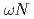 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Physics, Nuclear) F from
F from  O
O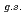 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 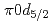 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O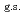 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ozu, Akira; Komeda, Masao; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(7), p.617 - 628, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Mori, Takamasa; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(8), P. 962, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We correct the derivation of equations in the derivation of equations in the paper of "Study of the neutron multiplication effect in an active neutron methods [J Nucl Sci Technol. 2017;54(11):1233-1239]". Although the derivations are not correct, the obtained equations are correct. Therefore, the results and discussions of the paper remain the same.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Toh, Yosuke; Kureta, Masatoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 13(Sp.1), p.2406004_1 - 2406004_4, 2018/02
Recently, it has become important in the field of nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security to quantify nuclear materials (NMs) of uranium and plutonium in nuclear fuel using a non-destructive assay (NDA) technique. Currently, there is no reliable NDA system to apply to nuclear fuels such as spent fuel, fuel debris and next generation fuel for nuclear transmutation. Accordingly, development of NDA techniques for quantification of NMs in those fuels is an urgent issue. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is one candidate that is applicable to the quantification of NMs. Utilizing pulsed neutron beams, NRTA analyzes the content of a sample by measuring neutron beams that are transmitted from the sample. It is one of the reliable NDA methods that are based on a neutron time-of-flight technique for accurately evaluating nuclear data such as total cross sections and resonance parameters. A present NRTA system generally requires a large electron linear accelerator to produce intense neutron beams. Therefore this is not so easy to apply to various facilities that are used to measure NMs. Given this situation, a compact NRTA system would be required for practical applications of a method to quantify NMs in various samples. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we consider two types of system: one uses a D-T neutron generator with pulse width of 10  sec and the other a small electron linac with pulse width of 1
sec and the other a small electron linac with pulse width of 1  sec Assuming each system is applied to measurements of NMs in spent fuel, numerical calculations were carried out and the results showed that the pulse widths of neutron beam largely affect the NRTA measurements. In this presentation, we will talk about the NRTA technique and give a schematic design of a compact NRTA system. Then, comparing calculation results for a D-T tube with those for a small electron linac, we especially discuss how the pulse widths of neutron beams to be used for NRTA affect the measurement of NMs in nuclear fuel.
sec Assuming each system is applied to measurements of NMs in spent fuel, numerical calculations were carried out and the results showed that the pulse widths of neutron beam largely affect the NRTA measurements. In this presentation, we will talk about the NRTA technique and give a schematic design of a compact NRTA system. Then, comparing calculation results for a D-T tube with those for a small electron linac, we especially discuss how the pulse widths of neutron beams to be used for NRTA affect the measurement of NMs in nuclear fuel.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Komeda, Masao; Shiba, Tomooki; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Maeda, Makoto; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
Energy Procedia, 131, p.258 - 263, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:97.40(Energy & Fuels)Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Mori, Takamasa; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(11), p.1233 - 1239, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)The previous active neutron method cannot remove the influence of the multiplication effect of neutrons produced by second- and subsequent fission reactions, and it might overestimate the amount of nuclear material if an item contains large amounts. In this paper, we discussed the correction method for the neutron multiplication effect on the measured data in the fast neutron direct interrogation (FNDI) method, one of the active neutron methods, supposing that the neutron multiplication effect is caused mainly by third-generation neutrons from the second-fission reactions under the condition that the forth-generation neutrons are much fewer. This paper proposed a correction method for the neutron multiplication effect in the measured data. Moreover we have shown a possibility that this correction method gives rough estimates of the effective neutron multiplication factor and the subcriticality.
 -ray Spectrometry of Environmental Samples Collected in Fukushima
-ray Spectrometry of Environmental Samples Collected in FukushimaSaegusa, Jun; Yoda, Tomoyuki; Maeda, Satoshi; Okazaki, Tsutomu; Otani, Shuichi; Yamaguchi, Toshio; Kurita, Yoshiyuki; Hasumi, Atsushi; Yonezawa, Chushiro*; Takeishi, Minoru
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1078 - 1085, 2017/11
After the nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in March 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has newly set up a laboratory for radioactivity analysis in Fukushima. At the laboratory, radioactivity concentrations of environmental samples such as soil, water, dust filter, plant, etc., approximately 1,000 samples in a month, are measured with high-resolution  -ray spectrometry systems. The systems employ n-type HPGe detectors from Ortec. Since September 2012, characterization and upgrade of the systems have been performed aimed at enhancing reliability of analysis and convenience of customers. Resolving both systematic and technical issues, the laboratory has been accredited the ISO/IEC 17025 standard as a testing laboratory for radioactivity analysis.
-ray spectrometry systems. The systems employ n-type HPGe detectors from Ortec. Since September 2012, characterization and upgrade of the systems have been performed aimed at enhancing reliability of analysis and convenience of customers. Resolving both systematic and technical issues, the laboratory has been accredited the ISO/IEC 17025 standard as a testing laboratory for radioactivity analysis.
Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference (GLOBAL 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2017/09
We have developed a special Nuclear Material Accountancy (NMA) technique using the Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method which is one of active neutron techniques. A measurement system, for fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, implemented in the simulation was designed as follows. This system has a neutron generator, which can produce neutron yield of 1 10
10 per pulse in 1 kHz repetition rate. The length of the system is 140 cm, and the outer diameter is 80cm. Sixteen He-3 detectors, 100 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter, are installed. Simulations were carried out using the Monte Carlo code MVP developed at JAEA. This work provides simulation results and the applicable range of the FNDI method for fuel debris, using various debris model parameters for example, burn-up composition and heterogeneous materials.
per pulse in 1 kHz repetition rate. The length of the system is 140 cm, and the outer diameter is 80cm. Sixteen He-3 detectors, 100 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter, are installed. Simulations were carried out using the Monte Carlo code MVP developed at JAEA. This work provides simulation results and the applicable range of the FNDI method for fuel debris, using various debris model parameters for example, burn-up composition and heterogeneous materials.
Maeda, Seiichiro; Oki, Shigeo; Otsuka, Satoshi; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ozawa, Takayuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
The next generation fast reactor is being investigated in Japan, aiming at several targets such as "safety", "reduction of environmental burden" and "economic competitiveness". As for the safety aspect, FAIDUS concept is adopted to avoid re-criticality in core destructive accidents. The uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuel, in which minor actinide elements are included, will be applied to reduce the amount and potential radio-toxicity of radioactive wastes. The high burn-up fuel is pursued to reduce fuel cycle cost. The candidate concept of the core and fuel design, which could satisfy various design criteria by design devisals, has been established. In addition, JAEA is investigating material properties and irradiation behavior of MA-MOX fuel. JAEA is developing the fuel design code especially for the fuel pin with annular pellets of MA-bearing MOX. Furthermore, JAEA is developing oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel cladding for the high burnup fuel.
Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Tobita, Hiroshi; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J. M.*; Varasano, G.*; Pedersen, B.*
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/02
JAEA and EC/JRC are carrying out collaborative research to develop NDA techniques that can be utilized for quantification of high radioactive special nuclear materials such as spent fuel and next generation minor actinide fuels. In the research, reliability of neutron transport codes is important because it is utilized for design and development of a demonstration system of next-generation Differential Die-away (DDA) technique in JAEA. In order to evaluate the reliability, actual neutron flux distribution in a sample cavity was examined in PUNITA device using JRC type DDA technique and JAWAS-T device using JAEA type DDA technique, and then the measurement results were compared with the simulation results obtained by the neutron transport codes. The neutron flux distribution in the target matrix was also examined in the PUNITA and compared with the simulation results. We report on the measurement and simulation results of the neutron flux distribution and evaluation results of the reliability of the neutron transport codes.
Ozu, Akira; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Tobita, Hiroshi; Kureta, Masatoshi
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/02
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Toh, Yosuke; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J. M.*; Varasano, G.*; Pedersen, B.*
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.694 - 701, 2017/00