Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi*; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Morishita, Kazuki; Watanabe, Masashi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Yano, Yasuhide; Oki, Shigeo
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113755_1 - 113755_17, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ac and its uncertainty through the
Ac and its uncertainty through the  Ra(n,2n) reaction in the experimental fast reactor Joyo
Ra(n,2n) reaction in the experimental fast reactor JoyoSasaki, Yuto*; Sano, Aaru; Sasaki, Shinji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Ouchi, Kazuki; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Takaki, Naoyuki*; Maeda, Shigetaka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.509 - 520, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:73.39(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ac is attracting attention as an alpha-emitting medical radioisotope. Since its demand is expected to increase, domestic production of
Ac is attracting attention as an alpha-emitting medical radioisotope. Since its demand is expected to increase, domestic production of  Ac is required from the viewpoint of Japan's medical research and economic security. To establish the technical bases for the
Ac is required from the viewpoint of Japan's medical research and economic security. To establish the technical bases for the  Ac production, JAEA has evaluated the radioactivity that can be produced in the experimental fast reactor Joyo and designed the concept that upgrades the existing facilities for transporting the irradiated target from Joyo to a neighboring PIE facility rapidly. Efficient
Ac production, JAEA has evaluated the radioactivity that can be produced in the experimental fast reactor Joyo and designed the concept that upgrades the existing facilities for transporting the irradiated target from Joyo to a neighboring PIE facility rapidly. Efficient  Ac Separation from
Ac Separation from  Ra irradiated in a fast reactor was studied. Ba and La were used as alternatives to Ra and Ac, respectively. By using DGA resin as an adsorbent, it can be expected that Ra and impurities generated by irradiation will be removed and Ac will be isolated. This study has revealed that Joyo can sufficiently produce
Ra irradiated in a fast reactor was studied. Ba and La were used as alternatives to Ra and Ac, respectively. By using DGA resin as an adsorbent, it can be expected that Ra and impurities generated by irradiation will be removed and Ac will be isolated. This study has revealed that Joyo can sufficiently produce  Ac as a raw material for pharmaceuticals.
Ac as a raw material for pharmaceuticals.
Maeda, Shigetaka
Hoshasen Kagaku Furonteia, (5), P. 17, 2024/02
Regarding Actinium-225, which is one of the medical radioisotopes and has been attracting attention today, we will report on the domestic movement toward domestic production, the research and development plan and progress for production of Actinium-225 using the experimental fast reactor Joyo.
 Ra nuclear data library and its impact on the production amount of
Ra nuclear data library and its impact on the production amount of  Ac via the
Ac via the  Ra (n,2n) reaction
Ra (n,2n) reactionSasaki, Yuto; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Takaki, Naoyuki*; Maeda, Shigetaka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.251 - 260, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ac is a promising alpha emitter for targeted alpha therapy. However, the current capability of
Ac is a promising alpha emitter for targeted alpha therapy. However, the current capability of  Ac supply is limited to approximately 63 GBq/y, primarily relying on the natural source of
Ac supply is limited to approximately 63 GBq/y, primarily relying on the natural source of  Th stocked at a few institutes. Therefore, alternative
Th stocked at a few institutes. Therefore, alternative  Ac production methods are highly desired. The research and development of
Ac production methods are highly desired. The research and development of  Ac and its parent nuclide production methods using accelerators and reactors to target
Ac and its parent nuclide production methods using accelerators and reactors to target  Ra and
Ra and  Th are actively pursued worldwide. Hence, the authors focused on the
Th are actively pursued worldwide. Hence, the authors focused on the  Ra(n,2n)
Ra(n,2n)  Ra method using fast neutron spectra as an application of the experimental fast reactor Joyo. This study investigated the status of nuclear data libraries for
Ra method using fast neutron spectra as an application of the experimental fast reactor Joyo. This study investigated the status of nuclear data libraries for  Ra, an essential target for
Ra, an essential target for  Ac production, and evaluated the impact of different nuclear data libraries on the amount of
Ac production, and evaluated the impact of different nuclear data libraries on the amount of  Ac produced. Consequently, cross-sections with covariance data were stored in TENDL-2021, JEFF-3.3, and EAF-2010 but not in ENDF or JENDL, the major nuclear data libraries. Furthermore, no consistency occurred among the respective nuclear data, and the
Ac produced. Consequently, cross-sections with covariance data were stored in TENDL-2021, JEFF-3.3, and EAF-2010 but not in ENDF or JENDL, the major nuclear data libraries. Furthermore, no consistency occurred among the respective nuclear data, and the  Ra production amount varied.
Ra production amount varied.
 Ra purity as a target for
Ra purity as a target for  Ac production using a fast reactor
Ac production using a fast reactorSasaki, Yuto; Maeda, Shigetaka
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333, p.5987 - 5996, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Researchers are seeking alternative  Ac production methods because of the scarcity of
Ac production methods because of the scarcity of  Ac for targeted alpha therapy. Although
Ac for targeted alpha therapy. Although  Ra from waste sources has been considered, obtaining
Ra from waste sources has been considered, obtaining  Ra is challenging. Therefore, the authors focused on the contamination of minerals with
Ra is challenging. Therefore, the authors focused on the contamination of minerals with  Th-derived
Th-derived 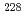 Ra while investigating methods to recover
Ra while investigating methods to recover  Ra from uranium ores. The effect of 228Ra contamination on
Ra from uranium ores. The effect of 228Ra contamination on  Ac production by
Ac production by  Ra transmutation using fast reactors was evaluated. Consequently, toxic
Ra transmutation using fast reactors was evaluated. Consequently, toxic 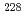 Ac contaminates
Ac contaminates  Ac. However, using the different half-lives of
Ac. However, using the different half-lives of  Ac and
Ac and 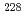 Ac, pure
Ac, pure  Ac can be obtained from the chemical separation of actinium after cooling for 5-8 days.
Ac can be obtained from the chemical separation of actinium after cooling for 5-8 days.
Arai, Masaji; Maeda, Shigetaka
Rinsho Hoshasen, 68(10), p.963 - 970, 2023/10
Ac-225 is attracting attention as an alpha-emitting medical radioisotope. Since its demand is expected to increase, domestic production of Ac-225 is required from the viewpoint of Japan's medical research and economic security. To establish the technical bases for the Ac-225 production, JAEA has evaluated the radioactivity that can be produced in the experimental fast reactor Joyo and designed the concept that upgrades the existing facilities for transporting the irradiated target from Joyo to a neighboring PIE facility rapidly. Efficient Actinium-225 Separation from Ra-226 irradiated in a fast reactor was studied. This study has revealed that Joyo can sufficiently produce Ac-225 as a raw material for pharmaceuticals.
 Ac for Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) using the experimental fast reactor Joyo
Ac for Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) using the experimental fast reactor JoyoMaeda, Shigetaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Enerugi Rebyu, 42(10), p.19 - 22, 2022/09
Ac-225 is attracting attention as an alpha-emitting medical radioisotope. Since its demand is expected to increase, domestic production of Ac-225 is required from the viewpoint of Japan's medical research and economic security. To establish the technical bases for the Ac-225 production, JAEA has evaluated the radioactivity that can be produced in the experimental fast reactor Joyo and designed the concept that upgrades the existing facilities for transporting the irradiated target from Joyo to a neighboring PIE facility rapidly. Efficient Actinium-225 Separation from Ra-226 irradiated in a fast reactor was studied. Ba and La were used as alternatives to Ra and Ac, respectively. By using DGA resin as an adsorbent, it can be expected that Ra and impurities generated by irradiation will be removed and Ac will be isolated. This study has revealed that Joyo can sufficiently produce Ac-225 as a raw material for pharmaceuticals.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Ito, Chikara; Maeda, Shigetaka; Inoue, Toshihiko; Tomita, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Radiation Protection, 40(6), p.491 - 495, 2020/11
A highly accurate and precise technique for measurement of the  Nb(n,n')
Nb(n,n') Nb reaction rate was established for the material surveillance tests, etc. in fast reactors. The self-absorption effect on the measurement of the characteristic X-rays emitted by
Nb reaction rate was established for the material surveillance tests, etc. in fast reactors. The self-absorption effect on the measurement of the characteristic X-rays emitted by  Nb was decreased by the solution and evaporation to dryness of niobium dosimeter. A highly precise count of the number of
Nb was decreased by the solution and evaporation to dryness of niobium dosimeter. A highly precise count of the number of  Nb atoms was obtained by measuring the niobium solution concentration using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. X-rays of
Nb atoms was obtained by measuring the niobium solution concentration using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. X-rays of  Nb were measured accurately by means of comparing the X-ray intensity of irradiated niobium solution with that of the solution in which stable
Nb were measured accurately by means of comparing the X-ray intensity of irradiated niobium solution with that of the solution in which stable  Nb was added. The difference between both intensities indicates the effect of
Nb was added. The difference between both intensities indicates the effect of 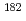 Ta, which is generated from an impurity tantalum, and the intensity of X-rays from
Ta, which is generated from an impurity tantalum, and the intensity of X-rays from  Nb was evaluated. Measurement error of the
Nb was evaluated. Measurement error of the  Nb(n,n')
Nb(n,n') Nb reaction rate was reduced to be less than 4%, which was equivalent to the other reaction rate errors of dosimeters used for Joyo dosimetry. In addition, an advanced technique using Resonance Ionization Mass Spectrometry was proposed for the precise measurement of
Nb reaction rate was reduced to be less than 4%, which was equivalent to the other reaction rate errors of dosimeters used for Joyo dosimetry. In addition, an advanced technique using Resonance Ionization Mass Spectrometry was proposed for the precise measurement of  Nb yield, and
Nb yield, and  Nb will be resonance-ionized selectively by discriminating the hyperfine splitting of the atomic energy levels between
Nb will be resonance-ionized selectively by discriminating the hyperfine splitting of the atomic energy levels between  Nb and
Nb and  Nb at high resolution.
Nb at high resolution.
Usami, Shin; Kishimoto, Yasufumi*; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Maeda, Shigetaka
JAEA-Technology 2018-003, 97 Pages, 2018/07
The decay heat used for effectiveness evaluation of the prevention measures against severe accidents in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated by applying the updated nuclear data libraries based on JENDL-4.0, reflecting the realistic core operation pattern, and setting the rational extent of uncertainty. The decay heats of fission products, the actinide nuclides such as Cm-242, and radioactive structural materials were calculated by FPGS code. The decay heat of U-239 and Np-239 was evaluated based on ANSI/ANS-5.1-1994. The calculation uncertainty of each decay heat was evaluated based on summation of uncertainty factors, C/E values of reaction rates obtained in Monju system startup test, and so on. Furthermore, the decay heat evaluation method based on the FPGS90 was verified by the comparison of the results of the decay heat measurement of the two spent MOX fuel subassemblies in the experimental fast reactor Joyo MK-II core.
Yamamoto, Takahiro; Ito, Chikara; Maeda, Shigetaka; Ito, Hideaki; Sekine, Takashi
JAEA-Technology 2017-036, 41 Pages, 2018/02
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, the damaged upper core structure (UCS) was retrieved into the cask in May 2014 The dose rate on UCS surface was quite high due to the activation for over 30 years operation. In order to attain the optimum safety design, manufacture and operation of equipment for UCS replacement, the method to evaluate UCS surface dose rate was developed on the basis of C/E obtained by the in-vessel dose rate measurement in Joyo. In order to verify the evaluation method, the axial gamma-ray distribution measurement on the surface of the cask, which contained UCS, was conducted using a plastic scintillating optical fiber (PSF) detector. This paper describes the comparison results between calculation and measurement as follows. (1) The measured axial gamma-ray distribution on the cask surface had a peak on proper location with considering the cask shielding structure and agree well with the calculated distribution. (2) The C/E of axial gamma-ray distribution on the cask surface was ranged from 1.1 to 1.7. It was confirmed that the calculation for UCS replacement equipment design had a margin conservatively. Then, the results showed that the developed evaluation method for UCS replacement equipment design was sufficiently reliable.
Shiba, Tomooki; Maeda, Shigetaka; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Ishimi, Akihiro; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Energy Procedia, 131, p.250 - 257, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)In the present paper, the  ray source data was developed for the debris composition based on "best estimates", and the subsequent photon transportation calculation was performed to evaluate the leakage
ray source data was developed for the debris composition based on "best estimates", and the subsequent photon transportation calculation was performed to evaluate the leakage  ray spectra according to the fuel debris. Since the creation of the line spectrum source requires a great deal, we have developed the relatively simple but accurate enough method to build up
ray spectra according to the fuel debris. Since the creation of the line spectrum source requires a great deal, we have developed the relatively simple but accurate enough method to build up  ray source, coupling of baseline spectra evaluated by ORIGEN2 code and several line spectra of interest. One of the advantages of the method is taking bremsstrahlung X rays into consideration by utilizing the bremsstrahlung libraries of ORIGEN2. The new
ray source, coupling of baseline spectra evaluated by ORIGEN2 code and several line spectra of interest. One of the advantages of the method is taking bremsstrahlung X rays into consideration by utilizing the bremsstrahlung libraries of ORIGEN2. The new  ray source was used to calculate the detector response of HPGe detector and the results was compared as a benchmark with experimental measurement results of irradiated fuel pins. As the result, the simulated
ray source was used to calculate the detector response of HPGe detector and the results was compared as a benchmark with experimental measurement results of irradiated fuel pins. As the result, the simulated  ray spectrum shape agreed well with the shape of
ray spectrum shape agreed well with the shape of  ray spectrum obtained by the experiment.
ray spectrum obtained by the experiment.
Usami, Shin; Kishimoto, Yasufumi; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Maeda, Shigetaka
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Unifying Theory and Experiments in the 21st Century (PHYSOR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.3263 - 3274, 2016/05
The present paper describes the validation of the new decay heat evaluation method using FPGS90 code with both the updated nuclear data library and the rational extent of uncertainty, by comparing the results of the decay heat measurement of the spent fuel subassemblies in Joyo MK-II core and by comparing with the calculation results of ORIGEN2.2 code. The calculated values of decay heat (C) by FPGS90 based on the JENDL-4.0 library were coincident with the measured ones (E) within the calculation uncertainties, and the C/E ranged from 1.01 to 0.93. FPGS90 evaluated the decay heat almost 3% larger than ORIGEN2.2, and it improved the C/E in comparison with the ORIGEN2.2 code. Furthermore, The C/E by FPGS90 based on the JENDL-4.0 library was improved than that based on the JENDL-3.2 library, and the contribution of the revision of reaction cross section library to the improvement was dominant rather than that of the decay data and fission yield data libraries.
Takahashi, Naoki; Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Harada, Akio; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Ueno, Takashi; Kurihara, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Soju; Takamatsu, Misao; Maeda, Shigetaka; Iseki, Atsushi; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Homu Peji (Internet), 64 Pages, 2016/00
no abstracts in English
Ota, Katsu; Ushiki, Hiroshi*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Kawahara, Hirotaka; Takamatsu, Misao; Kobayashi, Tetsuhiko; Kikuchi, Yuki; Tobita, Shigeharu; Nagai, Akinori
JAEA-Technology 2015-026, 180 Pages, 2015/11
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, it was confirmed that the top of the irradiation test sub-assembly of "MARICO-2" (material testing rig with temperature control) had bent onto the in-vessel storage rack as an obstacle and had damaged the upper core structure (UCS). The replacement of the UCS was conducted from May to December 2014. The design and manufacture of UCS was started from 2008, and the installation of UCS was completed successfully in November 21th 2014. The major results gained during the design and manufacture of UCS is as follows.
Konno, Chikara; Maeda, Shigetaka; Kosako, Kazuaki*
Energy Procedia, 71, p.213 - 218, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)We report a problem on multigroup cross section data MATXS files with multiple temperatures. This problem was newly found out through neutron and  flux calculations in a simple model of experimental fast reactor Joyo with DORT and MATXSLIB-J40, which is a multigroup cross section data file (300, 600, 900, 1200, 1800 K) of the latest Japanese Nuclear Data Library version 4.0 (JENDL-4.0) processed with the NJOY99 code. The calculated total neutron fluxes were almost the same both in 300 K and 600 K, while the total
flux calculations in a simple model of experimental fast reactor Joyo with DORT and MATXSLIB-J40, which is a multigroup cross section data file (300, 600, 900, 1200, 1800 K) of the latest Japanese Nuclear Data Library version 4.0 (JENDL-4.0) processed with the NJOY99 code. The calculated total neutron fluxes were almost the same both in 300 K and 600 K, while the total  fluxes in 600 K were by 10% higher those that in 300 K. Through our detailed investigation, it was found out that the MATXS data format processed with NJOY was not consistent to that assumed in TRANSX for
fluxes in 600 K were by 10% higher those that in 300 K. Through our detailed investigation, it was found out that the MATXS data format processed with NJOY was not consistent to that assumed in TRANSX for  production data. In order to solve this problem, we made a simple program for modifying MATXS files to ones suitable to TRANSX. MATXSLIB-J40 will be revised with this program.
production data. In order to solve this problem, we made a simple program for modifying MATXS files to ones suitable to TRANSX. MATXSLIB-J40 will be revised with this program.
Maeda, Shigetaka; Naito, Hiroyuki; Soga, Tomonori; Aoyama, Takafumi
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.494 - 497, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.39(Physics, Nuclear)The evaluation of the spatial distribution of  heating in fast reactors requires consideration of all the
heating in fast reactors requires consideration of all the  intensity components. However, the delayed
intensity components. However, the delayed  ray yield data of all actinides are not prepared in evaluated nuclear data files such as ENDF or JEDNL. In this study, new neutron/
ray yield data of all actinides are not prepared in evaluated nuclear data files such as ENDF or JEDNL. In this study, new neutron/ cross section constants based on JENDL-3.2 and -4 were developed. The delayed
cross section constants based on JENDL-3.2 and -4 were developed. The delayed  yields were added to JENDL-3.2 and JENDL-4. Based on these modified JENDL-3.2 and -4, MATXSLIB-type library for conventional discrete ordinate multi-group transport code were generated. Neutron and
yields were added to JENDL-3.2 and JENDL-4. Based on these modified JENDL-3.2 and -4, MATXSLIB-type library for conventional discrete ordinate multi-group transport code were generated. Neutron and  ray coupling calculations for the experimental fast reactor Joyo core, based on transport theory as a fixed source problem, revealed that the
ray coupling calculations for the experimental fast reactor Joyo core, based on transport theory as a fixed source problem, revealed that the  flux increased by approximately 40% when the delayed
flux increased by approximately 40% when the delayed  intensity in both JENDL-3.2 and -4 were considered. The calculated
intensity in both JENDL-3.2 and -4 were considered. The calculated  heat rates were verified by comparison with the measured data obtained by on-line irradiation rigs. It was confirmed that the calculated
heat rates were verified by comparison with the measured data obtained by on-line irradiation rigs. It was confirmed that the calculated  heat rates agreed with the measurements within 3-12%.
heat rates agreed with the measurements within 3-12%.
Maeda, Shigetaka; Ito, Chikara; Ishihara, Kohei*; Takagi, Keisuke*; Minato, Haruna*; Sakai, Yosuke*; Kawarabayashi, Jun*; Tomita, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.665 - 669, 2014/04
In order to realize neutron spectroscopy in high-intensity  ray fields, an advanced nuclear emulsion based on a non-sensitized OPERA film with AgBr grain sizes of 60 nm has been developed together with a neutron spectrum unfolding method. The response functions were evaluated in the neutron energy range between 0.1 and 4.5 MeV by Monte Carlo calculations. To realize a highly reliable unfolding method that does not require an initial guess spectrum, an algorithm was formulized based on the maximum entropy principle and the maximum likelihood method, and the new unfolding code MEALU was developed. Through analyses of mock-up data, its performance was checked. The neutron spectrum from fresh fuel from the experimental fast reactor Joyo was estimated and track lengths were simulated using the calculated response function and the estimated spectrum. Comparison between the assumed neutron spectrum and the unfolded one confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed technique.
ray fields, an advanced nuclear emulsion based on a non-sensitized OPERA film with AgBr grain sizes of 60 nm has been developed together with a neutron spectrum unfolding method. The response functions were evaluated in the neutron energy range between 0.1 and 4.5 MeV by Monte Carlo calculations. To realize a highly reliable unfolding method that does not require an initial guess spectrum, an algorithm was formulized based on the maximum entropy principle and the maximum likelihood method, and the new unfolding code MEALU was developed. Through analyses of mock-up data, its performance was checked. The neutron spectrum from fresh fuel from the experimental fast reactor Joyo was estimated and track lengths were simulated using the calculated response function and the estimated spectrum. Comparison between the assumed neutron spectrum and the unfolded one confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed technique.
Ishihara, Kohei*; Kawarabayashi, Jun*; Tomita, Hideki*; Naka, Tatsuhiro*; Asada, Takashi*; Morishima, Kunihiro*; Nakamura, Mitsuhiro*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.661 - 664, 2014/04
Spent fuel emits not only neutrons but also lots of  -rays by its included fission products (for example, neutron/
-rays by its included fission products (for example, neutron/ ratio is in the order of 10
ratio is in the order of 10 ). For its safety handling, it is important to investigate the neutron characteristics such as an emission rate, emission profile and energy spectrum. But it is difficult to measure the neutron characteristics with high precision because of lots of
). For its safety handling, it is important to investigate the neutron characteristics such as an emission rate, emission profile and energy spectrum. But it is difficult to measure the neutron characteristics with high precision because of lots of  -rays. So the neutron characteristics are estimated by an evaluation based on its burning history. It is necessary to measure them for estimate of adequacy of the simulated result. Also, a direct measurement of the neutron characteristics is essential in the case that each spent fuel has different burning history and is mixed (for example the accident of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant). Therefore, we develop a new nuclear emulsion in order to measure neutrons under high
-rays. So the neutron characteristics are estimated by an evaluation based on its burning history. It is necessary to measure them for estimate of adequacy of the simulated result. Also, a direct measurement of the neutron characteristics is essential in the case that each spent fuel has different burning history and is mixed (for example the accident of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant). Therefore, we develop a new nuclear emulsion in order to measure neutrons under high  -rays field in our study.
-rays field in our study.
 -ray fields with novel nuclear emulsion technique
-ray fields with novel nuclear emulsion techniqueIshihara, Kohei*; Takagi, Keisuke*; Minato, Haruna*; Kawarabayashi, Jun*; Tomita, Hideki*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Naka, Tatsuhiro*; Morishima, Kunihiro*; Nakano, Toshiyuki*; Nakamura, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 55, p.79 - 82, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to measure the neutron under a condition of high intensity of  -ray background, we made new nuclear emulsion based on non-sensitized OPERA emulsion which had small AgBr grain size (AgBr grain size of 60, 90 and 160 nm). The sensitivity of this new emulsion, which was a correlation between stopping power and grain density, was estimated experimentally by irradiating neutrons with several energies. We also simulated the response to
-ray background, we made new nuclear emulsion based on non-sensitized OPERA emulsion which had small AgBr grain size (AgBr grain size of 60, 90 and 160 nm). The sensitivity of this new emulsion, which was a correlation between stopping power and grain density, was estimated experimentally by irradiating neutrons with several energies. We also simulated the response to  -ray induced electrons and compared with some experimental results by using
-ray induced electrons and compared with some experimental results by using  Co
Co  source. The results showed that there might be a threshold energy deposited in one AgBr grain under which it was impossible to develop. We estimated efficiency to the
source. The results showed that there might be a threshold energy deposited in one AgBr grain under which it was impossible to develop. We estimated efficiency to the  -ray and the neutron with this obtained response of the new emulsion.
-ray and the neutron with this obtained response of the new emulsion.