Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Okamoto, Tomoyuki*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(9), p.3135 - 3140, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:99 Percentile:84.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A crystal structure of the signaling complex between human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF), and a ligand binding region of GCSF receptor (GCSF-R), has been determined to 2.8 resolution. The GCSF:GCSF-R complex formed a 2:2 stoichiometry via a cross-over interaction between the Ig-like domains of GCSF-R and GCSF. The conformation of the complex is quite different to that between human GCSF and the CRH domain of mouse GCSF-R, but similar to that of the interleukin-6 (IL-6)/gp130 signaling complex. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
resolution. The GCSF:GCSF-R complex formed a 2:2 stoichiometry via a cross-over interaction between the Ig-like domains of GCSF-R and GCSF. The conformation of the complex is quite different to that between human GCSF and the CRH domain of mouse GCSF-R, but similar to that of the interleukin-6 (IL-6)/gp130 signaling complex. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
Honjo, Eijiro; Tamada, Taro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Koshiba, Takumi*; Matsukura, Yasuko*; Okamoto, Tomoyuki*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 61(8), p.788 - 790, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.61(Biochemical Research Methods)Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) receptor receives signals for regulating the proliferation and differentiation of the precursor cells of granulocytes. The complex composed of two GCSFs and two GCSF receptors was crystallized. The crystal of the complex was grown in 1.0 M sodium formate and 0.1 M sodium acetate (pH4.6). It belongs to the space group  4
4 2
2 2 (or its enantiomorph
2 (or its enantiomorph  4
4 2
2 2) with unit cell dimensions of
2) with unit cell dimensions of  =
=  = 110.1
= 110.1  ,
,  = 331.8
= 331.8  . However, the diffraction data from the crystal beyond 5
. However, the diffraction data from the crystal beyond 5  resolution could not be collected. Since the heterogeneity of GCSF receptor seems to interrupt growth of good quality crystals, the GCSF receptor was fractionated by achromatography. Crystals of GCSF/fractionated GCSF receptor complex were grown as a new crystal form in 0.2 M ammonium phosphate. The new crystal diffracts beyond 3.0
resolution could not be collected. Since the heterogeneity of GCSF receptor seems to interrupt growth of good quality crystals, the GCSF receptor was fractionated by achromatography. Crystals of GCSF/fractionated GCSF receptor complex were grown as a new crystal form in 0.2 M ammonium phosphate. The new crystal diffracts beyond 3.0  resolution and belongs to space group
resolution and belongs to space group  3
3 21 (or its enantiomorph
21 (or its enantiomorph  3
3 21) with unit-cell parameters
21) with unit-cell parameters  =
=  = 134.8,
= 134.8,  = 105.7
= 105.7  .
.
Maeda, Koji; Koyama, Shinichi; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Kurosawa, Makoto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Arai, Shigeki; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The mouse antibody TN1 recognizes the human thrombopoietin (hTPO) that primarily stimulates megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet production. By the structural comparison between TN1-Fab itselt (hTPO unbound form) and hTPO bound form of TN1-Fab (PDB id 1V7M and 1V7N), we found that the CDR of TN1-Fab need not accompany the large conformational changes of upon TPO recognition. Moreover, the isothermal titration calorimetry showed that the conformational entropy change upon the hTPO binding to the TN1-Fab was  446.4 kJ/mol/K, corresponding to 2,920
446.4 kJ/mol/K, corresponding to 2,920 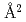 burying upon hTPO binding. This change of accessible surface area is larger than that of the previous result (1,580
burying upon hTPO binding. This change of accessible surface area is larger than that of the previous result (1,580 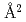 ) estimated from the crystal structure of hTPO / TN1-Fab complex. Since the CDR structure of TN1-Fab did not change, the change in surface area may be from the conformational change of hTPO upon the binding to Fab.
) estimated from the crystal structure of hTPO / TN1-Fab complex. Since the CDR structure of TN1-Fab did not change, the change in surface area may be from the conformational change of hTPO upon the binding to Fab.
Arai, Shigeki; Tamada, Taro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The mouse antibody TN1 recognizes the human thrombopoietin (hTPO) that primarily stimulates megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet production. In order to clarify the mechanism of the neutralizing activity of the TN1 antibody, the crystal structure of TN1-Fab was determined to 2.0 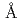 resolution and was compared with that of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (PDB id 1V7M and 1V7N). The relative angle of the variable- and constant-regions of the hTPO unbound form of TN1-Fab was slightly shifted from those of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (rms deviation = 2.4
resolution and was compared with that of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (PDB id 1V7M and 1V7N). The relative angle of the variable- and constant-regions of the hTPO unbound form of TN1-Fab was slightly shifted from those of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (rms deviation = 2.4 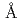 for all C
for all C atoms of Fab). On the other hand, only the slight shift of the side chain of CDR was observed (rmsd
atoms of Fab). On the other hand, only the slight shift of the side chain of CDR was observed (rmsd  1.5
1.5 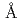 for atoms of side chain of each CDR) upon recognition of the epitope of hTPO. This structural shift of side chain of paratope did not accompany the
for atoms of side chain of each CDR) upon recognition of the epitope of hTPO. This structural shift of side chain of paratope did not accompany the  -angle rotation, but the parallel shift. These results indicate that the CDR of TN1-Fab need not accompany the large conformational changes of upon TPO recognition.
-angle rotation, but the parallel shift. These results indicate that the CDR of TN1-Fab need not accompany the large conformational changes of upon TPO recognition.
Kuroki, Ryota; Honjo, Eijiro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
We have succeeded in preparation and crystallization of 2:2 complex between human GCSF (hGCSF) and the Ig-like and CRH domains of human GCSF-R (hGCSF-R) and determined its tertiary structure by X-ray crystallography at 2.8 A resolution. The signaling 2:2 complex is formed via cross-over interactions between the Ig-like domain of hGCSF-R and the neighboring hGCSF, forming a two-fold axis of crystallographic symmetry. This conformation is quite different from that of the heterogeneous mGCSF-R complex, and more closely resembles the 2:2:2 active assembly of human interleukin-6 (IL-6), human IL-6  -receptor and human gp130 (which is a shared signal transducing receptor for several cytokines), and the 2:2 assembly of viral IL-6 and human gp130. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
-receptor and human gp130 (which is a shared signal transducing receptor for several cytokines), and the 2:2 assembly of viral IL-6 and human gp130. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Okamoto, Tomoyuki*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
We have succeeded in crystallization of 2:2 complex between human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (hGCSF) and the Ig-like and CRH domains of human GCSF-R (hGCSF-R) and determined its tertiary structure by X-ray crystallography at 2.8  resolution. The signaling 2:2 complex is formed via cross-over interactions between the Ig-like domain of hGCSF-R and the neighboring hGCSF, forming a two-fold axis of crystallographic symmetry. This conformation is quite different from that of the heterogeneous mGCSF-R complex, and more closely resembles the 2:2:2 active assembly of human interleukin-6 (IL-6), human IL-6
resolution. The signaling 2:2 complex is formed via cross-over interactions between the Ig-like domain of hGCSF-R and the neighboring hGCSF, forming a two-fold axis of crystallographic symmetry. This conformation is quite different from that of the heterogeneous mGCSF-R complex, and more closely resembles the 2:2:2 active assembly of human interleukin-6 (IL-6), human IL-6  -receptor and human gp130 (which is a shared signal transducing receptor for several cytokines), and the 2:2 assembly of viral IL-6 and human gp130. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
-receptor and human gp130 (which is a shared signal transducing receptor for several cytokines), and the 2:2 assembly of viral IL-6 and human gp130. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
Arai, Shigeki; Tamada, Taro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The mouse antibody TN1 recognizes the human thrombopoietin (hTPO) that primarily stimulates megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet production. In order to clarify the mechanism of the neutralizing activity of the TN1 antibody, the crystal structure of TN1-Fab was determined to 2.1  resolution and was compared with that of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (PDB id 1V7M and 1V7N). It was found that only side chain level "Induced-fit" upon the antigen binding was enough for TN1 to recognize hTPO. On the other hand, the relative angle of the variable- and constant-regions of the hTPO unbound form of TN1-Fab was slightly shifted from those of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (rms deviation = 2.4
resolution and was compared with that of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (PDB id 1V7M and 1V7N). It was found that only side chain level "Induced-fit" upon the antigen binding was enough for TN1 to recognize hTPO. On the other hand, the relative angle of the variable- and constant-regions of the hTPO unbound form of TN1-Fab was slightly shifted from those of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (rms deviation = 2.4  for all C
for all C atoms of Fab). In this presentation, we will explain the details of the conformational change of the crystal structure of TN1-Fab fragment with and without binding of hTPO.
atoms of Fab). In this presentation, we will explain the details of the conformational change of the crystal structure of TN1-Fab fragment with and without binding of hTPO.
Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) has become an important cytokine for medical treatment of patients suffering from granulopoenia. Here, we report the crystal structure of a complex between human GCSF (hGCSF) and the Ig-like and CRH domains of human GCSF-R (hGCSF-R) at 2.8 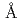 resolution. The signaling 2:2 complex is formed via cross-over interactions between the Ig-like domain of hGCSF-R and the neighboring hGCSF, forming a two-fold axis of crystallographic symmetry. This conformation is quite different from that of the heterogeneous mGCSF-R complex, and more closely resembles the 2:2:2 active assembly of human interleukin-6 (IL-6), human IL-6 alpha-receptor and human gp130 (which is a shared signal transducing receptor for several cytokines), and the 2:2 assembly of viral IL-6 and human gp130. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
resolution. The signaling 2:2 complex is formed via cross-over interactions between the Ig-like domain of hGCSF-R and the neighboring hGCSF, forming a two-fold axis of crystallographic symmetry. This conformation is quite different from that of the heterogeneous mGCSF-R complex, and more closely resembles the 2:2:2 active assembly of human interleukin-6 (IL-6), human IL-6 alpha-receptor and human gp130 (which is a shared signal transducing receptor for several cytokines), and the 2:2 assembly of viral IL-6 and human gp130. The Ig-like domain cross-over structure necessary for GCSF-R activation is consistent with previously reported thermodynamic and mutational analyses.
Kuroki, Ryota; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Maeda, Yoshitake*
no journal, ,
Receptor proteins expressed in the surface of the cell are known to be important drug targets for several diseases. The receptor transfer the signal originated from the binding of ligand proteins in to the signal cascades located inside of the cell. The signal transduction usually induced by the association of plural receptor molecules, thus the ligand molecules that help association of receptors are considered to be drug candidates. There are several association schemes are known. For example, the erythropoietin receptors associate with its ligand in 2:1 manner, the granulocyte colony stimulating factor receptor active complex with its ligand in 2:2 manners, and so on. Therefore, it is quite important to investigate the active scheme of receptor-ligand complex to understand how the receptor molecule start signal transduction. In this symposium, we show several examples of the measurements aimed to understand the activation scheme of drug target receptors.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Maeda, Koji; Kaito, Takeji; Inoue, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
JAEA evaluate an applicable prospect of the high Ni steel as the ODS steel which will be used core materials of the fast reactor. As a part of the applicable prospect evaluation, the high Ni steel was irradiated a high dose and high temperature. The result of 600  C, the resistance of swelling in high Ni-based steel was good.
C, the resistance of swelling in high Ni-based steel was good.
Arai, Shigeki; Tamada, Taro; Maeda, Yoshitake*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The mouse antibody TN1 recognizes the human thrombopoietin (hTPO) that primarily stimulates megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet production. The TN1 neutralize the TPO activity preventing from the homo-dimerization of its receptor. In order to investigate the structural change of the TN1 upon antigen binding, the crystal structure of TN-1 Fab was determined to 2.1 resolution and was compared with that of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (1V7M). It was found that each domain comprising TN1-Fab was strikingly similar (rmsd
resolution and was compared with that of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex (1V7M). It was found that each domain comprising TN1-Fab was strikingly similar (rmsd  0.6
0.6 ) between the antigen bound and unbound forms of TN1-Fab including three complementarity determining regions. The relative locations of the variable- and constant-regions of the TPO unbound form of TN1-Fab was slightly shifted from those of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex, which may be caused by difference of their crystal packing. These results indicate that the TN1-Fab need not accompany the conformational changes upon antigen binding.
) between the antigen bound and unbound forms of TN1-Fab including three complementarity determining regions. The relative locations of the variable- and constant-regions of the TPO unbound form of TN1-Fab was slightly shifted from those of TN1-Fab / hTPO complex, which may be caused by difference of their crystal packing. These results indicate that the TN1-Fab need not accompany the conformational changes upon antigen binding.