Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kei; Maekawa, Sadamichi*
Annalen der Physik, 536(5), p.2300395_1 - 2300395_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Lyons, T. P.*; Puebla, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Deacon, R. S.*; Hwang, Y.*; Ishibashi, Koji*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Otani, Yoshichika*
Physical Review Letters, 131(19), p.196701_1 - 196701_6, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.40(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Liao, L.*; Puebla, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Kim, J.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Hwang, Y.*; Ba, Y.*; Otani, Yoshichika*
Physical Review Letters, 131(17), p.176701_1 - 176701_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.40(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Ma, J.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:91.88(Physics, Applied)Mori, Michiyasu; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Applied Physics Letters, 122(4), p.042202_1 - 042202_5, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.44(Physics, Applied)Maekawa, Sadamichi; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 133(2), p.020902_1 - 020902_24, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:96.40(Physics, Applied)Fujimoto, Junji*; Funaki, Hiroshi*; Koshibae, Wataru*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi*
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1500407_1 - 1500407_7, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Puebla, J.*; Hwang, Y.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Otani, Yoshichika*
Applied Physics Letters, 120(22), p.220502_1 - 220502_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:93.70(Physics, Applied)Yamamoto, Kei; Xu, M.*; Puebla, J.*; Otani, Yoshichika*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 545, p.168672_1 - 168672_10, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:65.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) /La
/La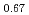 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO heterostructures
heterostructuresZhang, J.*; Chen, M.*; Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Wang, H.*; Hamdi, M.*; Sun, Y.*; Wagner, K.*; He, W.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.7258_1 - 7258_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:79.57(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -Josephson junction
-Josephson junctionMori, Michiyasu; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Applied Physics Express, 14(10), p.103001_1 - 103001_4, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.12(Physics, Applied)Yao, Y.*; Cai, R.*; Yang, S.-H.*; Xing, W.*; Ma, Y.*; Mori, Michiyasu; Ji, Y.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Xie, X.-C.*; Han, W.*
Physical Review B, 104(10), p.104414_1 - 104414_6, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Imai, Masaki; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(8), p.081003_1 - 081003_11, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fujimoto, Junji*; Koshibae, Wataru*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review B, 103(22), p.L220402_1 - L220402_5, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 103(17), p.174308_1 - 174308_10, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsuoka, Hideki*; Barnes, S. E.*; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Bahramy, M. S.*; Saika, B. K.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Wang, Y.*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(4), p.1807 - 1814, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:77.78(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Kei; Yu, W.*; Yu, T.*; Puebla, J.*; Xu, M.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Bauer, G.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(11), p.113702_1 - 113702_5, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:71.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kurimune, Yuki*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Nozaki, Yukio*
Physical Review B, 102(17), p.174413_1 - 174413_7, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:71.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Harii, Kazuya*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Express, 13(10), p.109102_1 - 109102_2, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:52.38(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English