Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A.*; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science VII, p.225 - 240, 2011/05
 http://www.springer.com/physics/atomic,+molecular,+optical+%26+plasma+physics/book/978-3-642-18326-3
http://www.springer.com/physics/atomic,+molecular,+optical+%26+plasma+physics/book/978-3-642-18326-3We present substantial enhancement of the accelerated ion energies up to 10-20 MeV per nucleon by utilizing the unique properties of the cluster-gas target irradiated with 40-fs laser pulses of only 150 mJ energy, corresponding to approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using thin foil targets. A particle-in-cell simulation infers that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in sub-critical density plasmas. The demonstrated method can be important in the development of efficient laser ion accelerators for hadron therapy and other applications.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(16), p.165002_1 - 165002_4, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:171 Percentile:96.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A new approach for accelerating ions, based on the use of a cluster-gas target and a compact ultrashort pulse laser, is presented. It is shown that ions with energy 10-20 MeV per nucleon having a small divergence (full angle) of 3.4 are generated, corresponding to an approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell code simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in near-critical density plasmas.
are generated, corresponding to an approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell code simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in near-critical density plasmas.
Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; Kameshima, Takashi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 95(10), p.101107_1 - 101107_3, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:76.96(Physics, Applied)Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1153, p.85 - 93, 2009/07
When the target consists of solid-density clusters embedded in the background gas, its irradiation by high intensity laser light renders ion acceleration a truly unique property. We present that the cluster-gas target, which consists of submicron-sized clusters and background gases, irradiated by a few TW laser pulse produces high energy ions upward of the order of 10-20 MeV/n in the forward direction.
Faenov, A. Y.; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Gasilov, S. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Palchan, T.*; Zigler, A.*; Henis, Z.*
Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 107(3), p.351 - 355, 2008/09
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J.*; Csanak, G.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
High-Power Laser Ablation VII (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.7005), p.70051R_1 - 70051R_11, 2008/06
Palchan, T.*; Henis, Z.*; Faenov, A. Y.; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Gasilov, S. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Zigler, A.*
Applied Physics Letters, 91(25), p.251501_1 - 251501_3, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:48.13(Physics, Applied)Faenov, A. Y.; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Giulietti, D.*; Betti, S.*; Galimberti, M.*; Gamucci, A.*; Giulietti, A.*; Gizzi, L. A.*; et al.
JETP Letters, 86(3), p.178 - 183, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Physical Review E, 73(6), p.066404_1 - 066404_6, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:74.43(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A model that solves simultaneously both the electron and atomic kinetics was used to generate synthetic He X-ray spectra to characterize a high intensity ultrashort laser driven Ar cluster target experiment. In particular, level populations were obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collisional rates were computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero dimensional Boltzmann equation. In addition, aparticle-in-cell simulation was used to model the laser interaction with the cluster target and provided the initial electron energy distribution function (EEDF) for the Boltzmann solver. This study suggests that the high density plasma contribution to the time-integrated He
X-ray spectra to characterize a high intensity ultrashort laser driven Ar cluster target experiment. In particular, level populations were obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collisional rates were computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero dimensional Boltzmann equation. In addition, aparticle-in-cell simulation was used to model the laser interaction with the cluster target and provided the initial electron energy distribution function (EEDF) for the Boltzmann solver. This study suggests that the high density plasma contribution to the time-integrated He spectrum was in a highly non-equilibrium state in both the EEDF and the ion level populations and provides a prediction of 5.7 ps for the average cluster integrity time for this high density state.
spectrum was in a highly non-equilibrium state in both the EEDF and the ion level populations and provides a prediction of 5.7 ps for the average cluster integrity time for this high density state.
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Kilcrease, D. P.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; et al.
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 99(1-3), p.584 - 594, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.92(Optics)In this work, we present a model that solves self-consistently the electron and atomic kinetics to characterize highly non-equilibrium plasmas, in particular for those systems where both the electron distribution function is far from Maxwellian and the evolution of the ion level populations are dominated by time dependent atomic kinetics. In this model, level populations are obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collision rates are computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero-dimensional Boltzmann equation. The Boltzmann collision term includes the effects of electron-electron collisions, electron collisional ionization, excitation and de-excitation. An application for He spectra from a short pulse laser irradiated argon cluster target will be shown to illustrate the results of our model.
spectra from a short pulse laser irradiated argon cluster target will be shown to illustrate the results of our model.
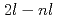 ' X-ray transitions from
' X-ray transitions from  1
1  m Kr clusters irradiated by high-intensity femtosecond laser pulses
m Kr clusters irradiated by high-intensity femtosecond laser pulsesHansen, S. B.*; Fournier, K. B.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; et al.
Physical Review E, 71(1), p.016408_1 - 016408_9, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:56.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)X-ray line emission from 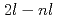 ' transitions in Ne-like Kr and nearby ions has been observed from
' transitions in Ne-like Kr and nearby ions has been observed from  1
1  m Kr clusters irradiated by fs-scale laser pulses at the JAERI facility in Kyoto, Japan. The dependence of X-ray spectral features and intensity on the incident laser intensity is rather weak, indicating that the 1-2 ps cluster lifetimes limit the number of ions beyond Ne-like Kr that can be produced by collisional ionization. A collisional-radiative model based on the relativistic multiconfigured FAC code has been constructed and used to determine that the cluster plasma has electron densities near 10
m Kr clusters irradiated by fs-scale laser pulses at the JAERI facility in Kyoto, Japan. The dependence of X-ray spectral features and intensity on the incident laser intensity is rather weak, indicating that the 1-2 ps cluster lifetimes limit the number of ions beyond Ne-like Kr that can be produced by collisional ionization. A collisional-radiative model based on the relativistic multiconfigured FAC code has been constructed and used to determine that the cluster plasma has electron densities near 10 cm
cm , temperature of a few hundred eV and hot electron fraction of a few percent.
, temperature of a few hundred eV and hot electron fraction of a few percent.
Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Yamakawa, Koichi; Faenov, A. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 22(3), p.215 - 220, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:78.80(Physics, Applied)High resolution K-shell spectra of a plasma created by superintense laser irradiation of micron-sized Ar clusters have been measured with an intensity above 10 W/cm
W/cm and a pulse duration of 30 fs. The total photon flux of 2
and a pulse duration of 30 fs. The total photon flux of 2 10
10 photons/pulse was achieved for He
photons/pulse was achieved for He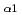 resonant line of Ar (
resonant line of Ar ( =3.9491 AA , 3.14 keV). In parallel with X-ray measurements, energy distributions of emitted ions have been measured. The multiply-charged ions with kinetic energies up to 800 keV were observed. It is found that hot electrons produced by high contrast laser pulses allow the isochoric heating of clusters and shift the ion balance towards the higher charge states, which enhances both the X-ray line yield of the He-like argon ion and the ion kinetic energy.
=3.9491 AA , 3.14 keV). In parallel with X-ray measurements, energy distributions of emitted ions have been measured. The multiply-charged ions with kinetic energies up to 800 keV were observed. It is found that hot electrons produced by high contrast laser pulses allow the isochoric heating of clusters and shift the ion balance towards the higher charge states, which enhances both the X-ray line yield of the He-like argon ion and the ion kinetic energy.
Smirnov, M. B.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Yamakawa, Koichi; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; et al.
Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 98(6), p.1123 - 1132, 2004/06
Interaction between high-power ultrashort laser pulse and giant clusters (microdroplets) consisting of 10 to 10
to 10 atoms is considered. The microdroplet size is comparable to the laser wavelength. A model of the evolution of a microdroplet plasma induced by a high-power laser pulse is developed, and the processes taking place after interaction with the pulse are analyzed. It is shown theoretically that the plasma is superheated: its temperature is approximately equal to the ionization potential of an ion having a typical charge. The microdroplet plasma parameters are independent of the pulse shape and duration. The theoretical conclusions are supported by experimental studies of X-ray spectra conducted at JAERI, where a 100-terawatt Ti-sapphire lasersystem was used to irradiate krypton and xenon microdroplets by laser pulses with pulse widths of 30 to 500 fs and intensities of 6
atoms is considered. The microdroplet size is comparable to the laser wavelength. A model of the evolution of a microdroplet plasma induced by a high-power laser pulse is developed, and the processes taking place after interaction with the pulse are analyzed. It is shown theoretically that the plasma is superheated: its temperature is approximately equal to the ionization potential of an ion having a typical charge. The microdroplet plasma parameters are independent of the pulse shape and duration. The theoretical conclusions are supported by experimental studies of X-ray spectra conducted at JAERI, where a 100-terawatt Ti-sapphire lasersystem was used to irradiate krypton and xenon microdroplets by laser pulses with pulse widths of 30 to 500 fs and intensities of 6 10
10 to 2
to 2 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Yamakawa, Koichi; Faenov, A. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; et al.
Laser-Generated & Other Lab. X-Ray & EUV Sources (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.5196), p.234 - 243, 2004/00
High resolution X-ray emission spectra of plasma created by laser irradiation of rare-gas (Ar, Kr, Xe) clusters have been measured at laser intensities over 10 W/cm
W/cm and 30-fs pulse duration. To make these measurements possible, in addition to the effort to decrease a prepulse intensity using Pockels cell switches, micron-size clusters were produced using a specially designed conical nozzle. The Boltzmann equation and a detailed collisional radiative model are solved simultaneously as a function of time to model the time integrated X-ray spectra of the transient plasma. The results are quantitatively in good agreement with the experimentally observed X-ray emission spectra of Ar clusters.
and 30-fs pulse duration. To make these measurements possible, in addition to the effort to decrease a prepulse intensity using Pockels cell switches, micron-size clusters were produced using a specially designed conical nozzle. The Boltzmann equation and a detailed collisional radiative model are solved simultaneously as a function of time to model the time integrated X-ray spectra of the transient plasma. The results are quantitatively in good agreement with the experimentally observed X-ray emission spectra of Ar clusters.
Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Yamakawa, Koichi; Faenov, A. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; et al.
Physical Review A, 68(6), p.063201_1 - 063201_8, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:86.59(Optics)The Boltzmann Equation and a detailed collisional radiative model are solved simultaneously as a function of time to model the time integrated X-ray spectra of the transient plasma produced by a high intensity ultrafast laser source. The results are in agreement with highly resolved F-like to He-like K-shell emission spectra recorded recently during ultrashort laser experiments with argon cluster targets in Japan.
Fukuda, Yuji; Yamakawa, Koichi; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Magunov, A. I.*; et al.
JETP Letters, 78(3), p.115 - 118, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:76.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have measured the X-ray emission spectra of a plasma generated by laser radiation with an intensity above 10 W/cm
W/cm and a pulse duration of 30 fs acting uon an argon jet target with a large aboundance of micron-sized clusters. The time variation of the X-ray yeild from various multiplicities, calculated within the framework of a nonstationary kinetic model, shows a good qualitative agreement with the experimental time-integrated spectrum.
and a pulse duration of 30 fs acting uon an argon jet target with a large aboundance of micron-sized clusters. The time variation of the X-ray yeild from various multiplicities, calculated within the framework of a nonstationary kinetic model, shows a good qualitative agreement with the experimental time-integrated spectrum.
Auguste, T.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Fukumoto, Ichiro; Hulin, S.*; Magunov, A. I.*; Monot, P.*; D'Oliveira, P.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Sasaki, Akira; Sharkov, B. Y.*; et al.
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 71(2-6), p.147 - 156, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:57.34(Optics)no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; Yogo, Akifumi; et al.
no journal, ,
We demonstrate generation of 10-20 MeV/u ions with a compact 4 TW laser using a gas target mixed with submicron clusters, corresponding to tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments with solid targets. It is inferred that the high energy ions are generated due to formation of a strong dipole vortex structure.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; Kotaki, Hideyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
An approach for accelerating ions, with the use of a cluster-gas target and an ultrashort pulse laser of 150-mJ energy and 40-fs duration, is presented. Ions with energy 10-20 MeV per nucleon having a small divergence (full angle) of 3.4 are generated in the forward direction, corresponding to approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in subcritical density plasmas.
are generated in the forward direction, corresponding to approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in subcritical density plasmas.