Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cl dissociation, CH
Cl dissociation, CH abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH
abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)
Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)Makino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 642, p.158568_1 - 158568_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.63(Chemistry, Physical) O formation on Cu
O formation on Cu Pd(111) and Cu
Pd(111) and Cu Pt(111)
Pt(111)Tsuda, Yasutaka; Gueriba, J. S.*; Makino, Takamasa*; Di o, W. A.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Okada, Michio*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11, p.3906_1 - 3906_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.10(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Au(111)
Au(111)Oka, Kohei*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Okada, Michio*; Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Hideaki*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16(36), p.19702 - 19711, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:43.65(Chemistry, Physical) Au(111) oxidation; Oxygen induced Cu segregation and the protective Au layer profile
Au(111) oxidation; Oxygen induced Cu segregation and the protective Au layer profileTsuda, Yasutaka*; Oka, Kohei*; Makino, Takamasa*; Okada, Michio*; Di o, W. A.*; Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Hideaki*
o, W. A.*; Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Hideaki*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16(8), p.3815 - 3822, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:51.13(Chemistry, Physical) Au(111) surface
Au(111) surfaceTsuda, Yasutaka*; Oka, Kohei*; Makino, Takamasa*; Lehmuskoski, J.*; Okada, Michio*; Di o, W. A.*; Kasai, Hideaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
o, W. A.*; Kasai, Hideaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Au using hyperthermal O
Au using hyperthermal O molecular beam
molecular beamHashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Okada, Michio*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
 Au alloy surface by using hyperthermal molecular beams
Au alloy surface by using hyperthermal molecular beamsTsuda, Yasutaka*; Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Makino, Takamasa*; Okada, Michio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Au(110) using a hyperthermal O
Au(110) using a hyperthermal O molecular molecular beam
molecular molecular beamHashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Okada, Michio*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Au(111) oxidation
Au(111) oxidationTsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Okada, Michio*; Oka, Kohei*; Di o, W. A.*; Kasai, Hideaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
o, W. A.*; Kasai, Hideaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
 Pd(111) surface
Pd(111) surfaceTsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Tsukada, Chie; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
It is well-known that oxidation is an important chemical reactions in corrosion processes. Cu Pd has an attracting material due to its catalytic property and its oxidation is the important subject. In this presentation, initial oxidation processes at the Cu
Pd has an attracting material due to its catalytic property and its oxidation is the important subject. In this presentation, initial oxidation processes at the Cu Pd(111) surface was studied by using molecular beams. In situ photoemission measurements were conducted using surface chemistry apparatus at BL23SU at SPring-8. Single crystal Cu
Pd(111) surface was studied by using molecular beams. In situ photoemission measurements were conducted using surface chemistry apparatus at BL23SU at SPring-8. Single crystal Cu Pd was used after cleaning by means of Ar ion sputtering and annealing. It was found that molecular beams facilitate oxidation compared to that for backfilling condition. Furthermore, diffusion of surface atoms seems to be driven with increasing surface temperature.
Pd was used after cleaning by means of Ar ion sputtering and annealing. It was found that molecular beams facilitate oxidation compared to that for backfilling condition. Furthermore, diffusion of surface atoms seems to be driven with increasing surface temperature.
 H
H on Cu(111) using supersonic C
on Cu(111) using supersonic C H
H molecular beam
molecular beamMakino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Tsukada, Chie; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
Studies on the interaction between ethylene molecule and metal surfaces are the important subject to understand catalyitic reactions such as dehydrogenation. To clarify dissociation adsorption processes of ethylene at metal surfaces, the surface analysis after exposure of ethylene to Cu(111) surface was conducted by using synchrotron radiation XPS. We found the growth of peak intensities and the peak shifted to higher binding energy side when ethylene beams with the kinetic energy of 2 eV were irradiated at the surface temperature of 300 K. The adsorption states and surface temperature dependece of reactions will be discussed.
 Pt(111) surface with hyperthermal oxygen molecule
Pt(111) surface with hyperthermal oxygen moleculeTsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Tsukada, Chie; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
Oxidation is a main reaction in corrosion processes and its understabding is important to develop anticorrosion materials. In this study, initial oxidation at Cu Pt(111) surface was investigated by using surface analysis apparatus at BL23SU of SPring-8. The surface oxidized by 2.3 eV molecular beams was analzyed by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. We confirmed that Cu L
Pt(111) surface was investigated by using surface analysis apparatus at BL23SU of SPring-8. The surface oxidized by 2.3 eV molecular beams was analzyed by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. We confirmed that Cu L M
M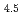 M
M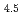 AES spectrum and Cu-2p XPS spectrum show the only growth of Cu oxide whereas Pt oxide was not formed from the results of Pt-4f XPS. It was also found that the reactivity of Cu
AES spectrum and Cu-2p XPS spectrum show the only growth of Cu oxide whereas Pt oxide was not formed from the results of Pt-4f XPS. It was also found that the reactivity of Cu Pd(111) surface is lower than that of Cu
Pd(111) surface is lower than that of Cu Au(111) surface.
Au(111) surface.
Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
Initial stage of corrosion is one of the central topics in material science. In the present study, we report the results of oxidation on Cu Pd(111) and Cu
Pd(111) and Cu Pt(111) with a hyperthermal O
Pt(111) with a hyperthermal O molecular beam (HOMB) with variable incident energies, using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. All experiments were performed using the Surface Reaction Analysis Apparatus constructed in BL23SU at SPring-8. The Cu
molecular beam (HOMB) with variable incident energies, using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. All experiments were performed using the Surface Reaction Analysis Apparatus constructed in BL23SU at SPring-8. The Cu Pd(111) and Cu
Pd(111) and Cu Pt(111) samples were cleaned by Ar+ sputtering and annealing. The kinetic energy of the HOMB was set to be 2.3 eV. From the uptake curves, it was found that the oxidation of Cu
Pt(111) samples were cleaned by Ar+ sputtering and annealing. The kinetic energy of the HOMB was set to be 2.3 eV. From the uptake curves, it was found that the oxidation of Cu Pt is less effective than that on Cu
Pt is less effective than that on Cu Au and Cu
Au and Cu Pd. This suppression of the surface reactivity may be caused by the Pt-rich subsurface layer.
Pd. This suppression of the surface reactivity may be caused by the Pt-rich subsurface layer.
 Au(110) surface
Au(110) surfaceHashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Okada, Michio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Okada, Michio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
Oxidation processes of alloy materials are important chemical reactions for the fabrication of protective layers used in various industrial applications. In this study, surface temperature dependence of oxidation of Cu Au(111) was studied using synchrotron radiation XPS and molecular beams. It was found that no dependence among uptake curves was observed from 300 to 500 K in low oxygen dosage because a direct dissociative adsorption takes place in this incident energy region. In contrast, clear difference between 400 and 500 K due to Cu
Au(111) was studied using synchrotron radiation XPS and molecular beams. It was found that no dependence among uptake curves was observed from 300 to 500 K in low oxygen dosage because a direct dissociative adsorption takes place in this incident energy region. In contrast, clear difference between 400 and 500 K due to Cu O formation was observed. This result suggests that thermal-driven diffusion of Au atoms into bulk depress the protective function for oxidation.
O formation was observed. This result suggests that thermal-driven diffusion of Au atoms into bulk depress the protective function for oxidation.
 H
H on Cu(410)
on Cu(410)Makino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
The de-hydrogenation reaction of hydrocarbon molecules at metal surface is important as an elementary process of graphene generation and various catalytic reactions. In order to investigate C H
H reactions at Cu(410) surface, C
reactions at Cu(410) surface, C H
H molecular beams and synchrotron radiation X-rays photoelectron spectroscopy was used. We found that the chemical species which became dehydrogenation adsorbs at the surface when C
molecular beams and synchrotron radiation X-rays photoelectron spectroscopy was used. We found that the chemical species which became dehydrogenation adsorbs at the surface when C H
H molecule has kinetic energy of 2 eV.
molecule has kinetic energy of 2 eV.
 Pt(111)
Pt(111)Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
The oxidation with oxygen molecules is important in a metal corrosion process. In order to develop high noncorrosive materials, the understanding of oxidation processes is significant. In this study, the influence on oxidation reaction due to alloy ingredient difference was investigated by the comparison between Cu Au(111) and Cu
Au(111) and Cu Pt(111) surfaces. It was found that the Cu
Pt(111) surfaces. It was found that the Cu Pt(111) surface has lower reactivity than the Cu
Pt(111) surface has lower reactivity than the Cu Au(111) surface.
Au(111) surface.