Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Oba, Yojiro; Hiroi, Kosuke; Miyatake, Takayuki*; Gautam, R.*; Sepehri-Amin, H.*; Okubo, Tadakatsu*
IEEE Magnetics Letters, 14, p.7100105_1 - 7100105_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:60.2(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Oba, Yojiro; Adachi, Nozomu*; Todaka, Yoshikazu*; Gilbert, E. P.*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(3), p.033473_1 - 033473_6, 2020/11
Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Oba, Yojiro; Oikawa, Kenichi
Shiki, 39, P. 4, 2018/06
no abstracts in English
Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Oba, Yojiro; Terada, Noriki*; Watanabe, Norimichi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.15516_1 - 15516_8, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.1(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 electrons in Ce
electrons in Ce In
In (
( =Rh, Ir)
=Rh, Ir)Fujimori, Shinichi; Okane, Tetsuo; Okamoto, Jun; Mamiya, Kazutoshi; Muramatsu, Yasuji; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Harima, Hisatomo*; Aoki, Dai*; Ikeda, Shugo*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 67(14), p.144507_1 - 144507_5, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:79.9(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have performed angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (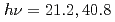 ~eV) and 3
~eV) and 3 -4
-4 resonant photoemission spectroscopy (
resonant photoemission spectroscopy ( ~eV) studies on the layered cerium compounds Ce
~eV) studies on the layered cerium compounds Ce In
In (
( =Rh and Ir), which show competition between superconductivity and antiferromagnetism. The results suggest that the Ce~4
=Rh and Ir), which show competition between superconductivity and antiferromagnetism. The results suggest that the Ce~4 electrons in both compounds are nearly localized. We have found that although the Ce~4
electrons in both compounds are nearly localized. We have found that although the Ce~4 electrons in the superconducting CeIrIn
electrons in the superconducting CeIrIn are more delocalized than those in the antiferromagnetic CeRhIn
are more delocalized than those in the antiferromagnetic CeRhIn , their electronic structures are very similar to each other.
, their electronic structures are very similar to each other.
Hagiya, Hiroyuki; Oku, Takayuki; Kira, Hiroshi; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Nishihara, Yoshikazu*; Oba, Yojiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hagiya, Hiroyuki; Oku, Takayuki; Kira, Hiroshi; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Nishihara, Yoshikazu*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Oba, Yojiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Amamiya, Hiroki; Sasaki, Yoshito; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Yoshito; Asano, Takahiro*; Ise, Kotaro; Sato, Tomofumi; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amamiya, Hiroki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Pd
Pd with a large magnetocaloric effect
with a large magnetocaloric effectKitazawa, Hideaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Terada, Noriki*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Doenni, A.*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Igawa, Naoki
no journal, ,
We have performed neutron powder diffraction experiments at JRR-3 using polycrystalline Ho Pd
Pd . The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing below about 100 K. The peak width is significantly broader than an experimental resolution even temperature is 5 K. These results indicate that Ho
. The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing below about 100 K. The peak width is significantly broader than an experimental resolution even temperature is 5 K. These results indicate that Ho Pd
Pd is a short-range ordered antiferromagnet with a long wave length.
is a short-range ordered antiferromagnet with a long wave length.
Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Terada, Noriki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Tsujii, Naohito*; Doenni, A.*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
no journal, ,
In this paper, we will demonstrate some application of neutron scattering for magnetic refrigerant materials Ho Pd
Pd and dilute spinel ferrites. In order to determine the magnetic structure, we have performed neutron powder diffraction experiments at JRR-3. The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing. The peak width is significantly broader even 5 K, indicating a short-range order with a long wave length.
and dilute spinel ferrites. In order to determine the magnetic structure, we have performed neutron powder diffraction experiments at JRR-3. The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing. The peak width is significantly broader even 5 K, indicating a short-range order with a long wave length.
Kirishima, Akira*; Kuno, Atsushi*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kubota, Takumi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*
no journal, ,
For understanding of the migration behavior of minor actinides (MA) in groundwater, the interaction of rare earth elements and suspended matters contained in Horonobe deep groundwater was studied. From this chemical analog study, it is suggested that the migration behavior of MA in the Horonobe groundwater system seems to be regulated by the formation of phosphate precipitation and small percentage of MA would be carried in the groundwater as pseudo colloids like MA-humic substance complex.
Amano, Yuki; Amamiya, Hiroki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Terashima, Motoki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kirishima, Akira*; Kuno, Atsushi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kubota, Takumi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kirishima, Akira*; Kuno, Atsushi*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kubota, Takumi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kokami, Takayuki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kubota, Takumi*; Kirishima, Akira*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Pd
Pd (R=Tb, Ho)
(R=Tb, Ho)Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Keller, L.*; Toyoizumi, Saori*; Terada, Noriki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Doenni, A.*; Lee, S.*; Metoki, Naoto; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron Scattering study has been carried out in order to reveal the magnetic structure of the antiferromagnet Ho Pd
Pd , which shows giant magnetocaloric effect. We observed short rage magnetic order at k=0.18, 0.18, 0.18 above the antiferromagnetic transition temperature
, which shows giant magnetocaloric effect. We observed short rage magnetic order at k=0.18, 0.18, 0.18 above the antiferromagnetic transition temperature 
 . Tb
. Tb Pd
Pd also showed magnetic short range correlation above the temperature higher than 2
also showed magnetic short range correlation above the temperature higher than 2

 .
.
Amamiya, Hiroki; Mizuno, Takashi; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yuguchi, Takashi; Murakami, Hiroaki; Kokubu, Yoko
no journal, ,
The long-term evolution of geochemical environment in deep underground is indispensable research subject for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Many researchers have made efforts previously to elucidate the geochemical environment within the groundwater residence time based on the analysis of the actual groundwater. However, it is impossible to estimate the geochemical environment for the longer time scale than the groundwater residence time in this method. In this case, analysis of the chemical properties of secondary minerals are one of useful method to estimate the past hydrochemical characteristics (temperature, salinity, pH and redox potential). We reviewed the previous studies on carbonate minerals and geochemical conditions in deep underground and estimated the hydrochemical characteristics of past groundwater by using carbonate minerals in crystalline rock at Tono area, Japan. As a result, it is found that temperature and salinity of the groundwater during crystallization of carbonate minerals were evaluated quantitatively. On the other hand, pH and redox potential can only be understood qualitatively. However, it is suggested that the content of heavy metal elements such as manganese, iron and uranium, and rare earth elements in the carbonate minerals are useful indicators for estimating redox potential.
Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kokami, Takayuki*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kirishima, Akira*
no journal, ,
For thermodynamic analysis of the trace metals in groundwater, concentrations of Th, U, and rare earth elements (REEs) were investigated at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. Groundwater was sampled in anaerobic condition directly from a packed section in the boreholes drilled to 140 m and 250 m depth in drift. The colloidal distribution was checked by an on-site batch ultrafiltration unit using 0.2  m or 10 kDa membranes. As the result, both Th and U concentrations could be estimated by thermodynamic calculations, assuming that the soluble solid phases are restricted to ThO
m or 10 kDa membranes. As the result, both Th and U concentrations could be estimated by thermodynamic calculations, assuming that the soluble solid phases are restricted to ThO (cr) and UO
(cr) and UO (cr), respectively. Meanwhile, the concentrations of REEs were also very low, and significant colloidal distribution for lighter REEs was observed. In the thermodynamic analysis where the lanthanide phosphate was assumed to be a solid phase, the experimental plots matched better with the calculated one, even though the changing trend differs from each other.
(cr), respectively. Meanwhile, the concentrations of REEs were also very low, and significant colloidal distribution for lighter REEs was observed. In the thermodynamic analysis where the lanthanide phosphate was assumed to be a solid phase, the experimental plots matched better with the calculated one, even though the changing trend differs from each other.
Watanabe, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Hiroaki; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Amamiya, Hiroki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kubota, Mitsuru; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
Chronological and geochemical studies of fracture filling calcite in rocks provide the information for changes in geochemical condition, such as redox potential and pH in geological environments. Because the calcite can be found as common filling minerals in the natural samples, age zoning and spatial distribution of chemical composition in the calcite could be a wide-use indicator to reconstruct the past environmental changes. Radiometric (U-Pb) dating in a micro scale area (less than 10 micrometer) on the filling mineral surface by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasm mass spectrometry system (LA-ICPMS) has been applied to geological samples. Additionally, past redox potential has been estimated by Fe contents in the carbonates, which is based on the distribution coefficient of Fe between calcite deposit and groundwater. In this study, we evaluated the possibility of in-situ radiometric dating for the filling minerals by LA-ICPMS and redox potential reconstruction by the theoretical calculation using the distribution coefficient.
Oba, Yojiro; Adachi, Nozomu*; Todaka, Yoshikazu*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English