Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fablet, L.*; P drot, M.*; Choueikani, F.*; Kieffer, I.*; Proux, O.*; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.*; Cagniart, V.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Marsac, R.*
drot, M.*; Choueikani, F.*; Kieffer, I.*; Proux, O.*; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.*; Cagniart, V.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Marsac, R.*
Environmental Science; Nano, 12(5), p.2815 - 2827, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nickel is an omnipresent trace element in the environment. Due to its high affinity for iron oxide nanoparticles, its elimination from soils and water by these nanoparticles represents an interesting strategy, specially by magnetites, which is naturally present in the environment. However, the interactions between Ni and magnetite are poorly understood, because of the difficulty to control the stoichiometry (Fe(II)-to-Fe(III) ratio) of magnetite. The behavior of Ni in the presence of magnetite nanoparticles with different stoichiometries, in aqueous solution and inert atmosphere, are probed by adsorption experiments and X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. This study helps predicting the interactions between Ni and magnetite in environmental conditions, which can be used for the development of efficient remediation strategies.
Dronskowski, R.*; Br ckel, T.*; Kohlmann, H.*; Avdeev, M.*; Houben, A.*; Meven, M.*; Hofmann, M.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Zobel, M.*; Schweika, W.*; et al.
ckel, T.*; Kohlmann, H.*; Avdeev, M.*; Houben, A.*; Meven, M.*; Hofmann, M.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Zobel, M.*; Schweika, W.*; et al.
Zeitschrift f r Kristallographie; Crystalline Materials, 239(5-6), p.139 - 166, 2024/06
r Kristallographie; Crystalline Materials, 239(5-6), p.139 - 166, 2024/06
Because of the neutron's special properties, neutron diffraction may be considered one of the most powerful techniques for structure determination of crystalline and related matter. Neutrons can be released from nuclear fission, from spallation processes, and also from low-energy nuclear reactions, and they can then be used in powder, time-of-flight, texture, single crystal, and other techniques, all of which are perfectly suited to clarify crystal and magnetic structures. With high neutron flux and sufficient brilliance, neutron diffraction also excels for diffuse scattering, for in situ and operando studies as well as for high-pressure experiments of today's materials. In this primer, we summarize the current state of neutron diffraction (and how it came to be), but also look at recent advances and new ideas, e.g., the design of new instruments, and what follows from that.
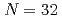
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.81(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
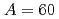
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:76.15(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
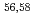 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:85.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 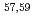 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 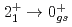 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 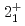 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 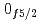 and
and 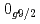 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.46(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
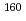 Eu; Quasiparticle configurations of excited states and structure of
Eu; Quasiparticle configurations of excited states and structure of 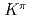 = 4
= 4 bandheads in
bandheads in 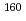 Gd
GdYates, D.*; Kr cken, R.*; Dillmann, I.*; Garrett, P. E.*; Smallcombe, J.; 44 of others*
cken, R.*; Dillmann, I.*; Garrett, P. E.*; Smallcombe, J.; 44 of others*
Physical Review C, 107(6), p.064309_1 - 064309_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Meer, H.*; Wust, S.*; Schmitt, C.*; Herrgen, P.*; Fuhrmann, F.*; Hirtle, S.*; Bednarz, B.*; Rajan, A.*; Ramos, R.*; Ni o, M. A.*; et al.
o, M. A.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 33(21), p.2213536_1 - 2213536_6, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.52(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)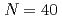 island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in
island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in  V and
V and  V
VElekes, Z.*; Juh sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064321_1 - 064321_10, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.42(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying level structure of  V and
V and  V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for
V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for  V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for
V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for  V. Four and five new transitions were determined for
V. Four and five new transitions were determined for  V and
V and  V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed
V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed  rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2
rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2 and 9/2
and 9/2 levels. The (
levels. The ( ,
,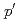 ) excitation cross sections for
) excitation cross sections for  V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,
V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,  V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
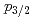 neutron orbital and the
neutron orbital and the 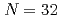 shell closure in
shell closure in  Ca
CaEnciu, M.*; Liu, H. N.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Poves, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 129(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:84.65(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The one-neutron knockout from  Ca was performed at
Ca was performed at  230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt
230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt  spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of
spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of 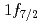 and
and 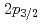 neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number
neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number 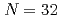 , found as strong as at
, found as strong as at 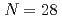 and
and 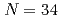 in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron
in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron 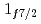 and
and 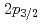 orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the
orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the 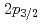 orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
Ramadhan, R. S.*; Glaser, D.*; Soyama, Hitoshi*; Kockelmann, W.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Pirling, T.*; Fitzpatrick, M. E.*; Tremsin, A. S.*
Acta Materialia, 239, p.118259_1 - 118259_12, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Massarczyk, R.*; Schwengner, R.*; Beyer, R.*; Hensel, T.*; Hoffmann, H.*; Junghans, A.*; R mer, K.*; et al.
mer, K.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(4), p.044326_1 - 044326_11, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.16(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:80.70(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
 No
NoBronis, A.*; He berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Andel, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Antalic, S.*; Andel, B.*; Ackermann, D.*; Heinz, S.*; Hofmann, S.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kindler, B.*; Kojouharov, I.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(1), p.014602_1 - 014602_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:67.20(Physics, Nuclear)Tregoning, R.*; Wallace, J.*; Bouydo, A.*; Costa-Garrido, O.*; Dillstr m, P.*; Duan, X.*; Heckmann, K.*; Kim, Y.-B.*; Kim, Y.*; Kurth-Twombly, E.*; et al.
m, P.*; Duan, X.*; Heckmann, K.*; Kim, Y.-B.*; Kim, Y.*; Kurth-Twombly, E.*; et al.
Transactions of the 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/07
Fourteen organizations, representing eleven countries, participated in a leak-before-break (LBB) benchmark exercise that compared results from analyses among participating countries and identified the effects of weld residual stress (WRS) and crack morphology on crack opening displacement (COD), critical bending moment (CBM), and leak rate (LR) results. The participants determined whether the initial problem would meet their country's LBB acceptance criteria and then evaluated the effects of crack morphology and WRS for a prescribed crack size, geometry and loading. Six out of fourteen participants indicated that the initial problem met their LBB requirements. In the follow-on tasks, differences among the participant's CBM predictions were principally due to the material properties used in the analysis while the type of failure model chosen contributed much less. Most of the differences in the LR predictions were directly attributable to differences among the COD models, but a portion was attributable to the treatment of crack face pressure (CFP). The benchmark identified several aspects of an LBB analysis that could support a more realistic evaluation.
Busi, M.*; Polatidis, E.*; Malamud, F.*; Kockelmann, W.*; Morgano, M.*; Kaestner, A.*; Tremsin, A.*; Kalentics, N.*; Log , R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; et al.
, R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(5), p.053602_1 - 053602_8, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:65.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:67.20(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Bi
BiDoherty, D. T.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seweryniak, D.*; Woods, P. J.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Auranen, K.*; Ayangeakaa, A. D.*; Back, B. B.*; Bottoni, S.*; Canete, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(20), p.202501_1 - 202501_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary) RuO
RuO
Fittipaldi, R.*; Hartmann, R.*; Mercaldo, M. T.*; Komori, Sachio*; Bj rlig, A.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Maeno, Yoshiteru*; Di Bernardo, A.*; 18 of others*
rlig, A.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Maeno, Yoshiteru*; Di Bernardo, A.*; 18 of others*
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.5792_1 - 5792_9, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:75.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The layered oxide perovskite Sr RuO
RuO , which has been intensively investigated due to its unusual properties. Whilst the debate on the symmetry of the superconducting state in Sr
, which has been intensively investigated due to its unusual properties. Whilst the debate on the symmetry of the superconducting state in Sr RuO
RuO is still ongoing, a deeper understanding of the Sr
is still ongoing, a deeper understanding of the Sr RuO
RuO normal state appears crucial as this is the background in which electron pairing occurs. Here, by using low-energy muon spin spectroscopy we discover the existence of surface magnetism in Sr
normal state appears crucial as this is the background in which electron pairing occurs. Here, by using low-energy muon spin spectroscopy we discover the existence of surface magnetism in Sr RuO
RuO at an onset temperature higher than 50 K. Our observations set a reference for the discovery of the same magnetic phase in other materials.
at an onset temperature higher than 50 K. Our observations set a reference for the discovery of the same magnetic phase in other materials.