Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyYamashita, Takayuki*; Koga, Norimitsu*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Fujii, Hidetoshi*; Umezawa, Osamu*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*; Ito, Tatsuya; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steelIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Harjo, S.; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.205 - 208, 2024/11
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ito, Tatsuya; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gao, S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The yield stress of Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) metastable austenitic steel increased 3.5 times (158  551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35
551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35  m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5
m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5  m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87
m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87  0.82).
0.82).  neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the
neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the  111
111 //LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the
//LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the  111
111 //LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
//LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
Mao, W.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; 8 of others*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 50(Part D), p.969 - 978, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.43(Chemistry, Physical) -Ti alloy
-Ti alloyZhang, B.*; Xin, S.*; Huang, M.*; Mao, W.; Jia, W.*; Li, Q.*; Li, S.*; Zhang, S.*; Mao, C.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 890, p.145898_1 - 145898_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A significant increase in the recovery strain of a high-Zr  -Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the
-Ti alloy from 2.25 % to 5.5 % when decreasing the deformation temperature from 300 K to 77 K is reported in this study. It is found that the super-elasticity of this alloy is independent of the  -grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
-grain size at 77 K. The results reveal that a coarse-grained specimen exhibited approximately the same super-elasticity as its ultra-fine grain counterpart at 77 K. The relative easiness of deformation-induced martensitic transformation and dislocation slip was substantially changed at 77 K, with a strong suppression of dislocation slip, which overshadowed the effect of grain refinement on the super-elasticity.
 ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining
ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysis
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysisMao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Scripta Materialia, 235, p.115642_1 - 115642_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:86.78(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In the present study, a hybrid  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation measurement was performed on tensile deformation of an ultrafine grain (UFG) stainless steel exhibiting a huge L
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation measurement was performed on tensile deformation of an ultrafine grain (UFG) stainless steel exhibiting a huge L ders band deformation to evaluate the individual contribution of the austenite matrix and the deformation-induced martensite to the strain hardening during the propagation of the band. Quantitative analysis revealed that the strain hardening of the austenite matrix was insufficient to maintain a uniform deformation when the flow stress was greatly enhanced by the UFG structure. The strain hardening required for the L
ders band deformation to evaluate the individual contribution of the austenite matrix and the deformation-induced martensite to the strain hardening during the propagation of the band. Quantitative analysis revealed that the strain hardening of the austenite matrix was insufficient to maintain a uniform deformation when the flow stress was greatly enhanced by the UFG structure. The strain hardening required for the L ders band to propagate was mostly provided by the formation of martensite and the high internal stress within it.
ders band to propagate was mostly provided by the formation of martensite and the high internal stress within it.
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Bai, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 256, p.119139_1 - 119139_16, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:98.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP)-assisted steels exhibit an excellent combination of strength and ductility due to enhanced strain hardening rate associated with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT). Quantitative evaluation on the role of DIMT in strain hardening behavior of TRIP-assisted steels and alloys can provide guidance for designing advanced materials with strength and ductility synergy, which is, however, difficult since the phase composition keeps changing and both stress and plastic strain are dynamically partitioned among constituent phases during deformation. In the present study, tensile deformation with  neutron diffraction measurement was performed on an Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) TRIP-assisted austenitic steel. The analysis method based on stress partitioning and phase fractions measured by neutron diffraction was proposed, by which the tensile flow stress and the strain hardening rate of the specimen were resolved into factors associated with each phase, i.e., the austenite matrix, deformation-induced martensite, and the transformation rate of DIMT after differentiation, and then the role of each factor in the global strain hardening behavior was discussed. In addition, the plastic strain partitioning between austenite and martensite was indirectly estimated using the dislocation density measured by diffraction profile analysis, which constructed the full picture of stress and strain partitioning between austenite and martensite in the material. The results suggested that both the transformation rate and the phase stress borne by the deformation-induced martensite played important roles in the global tensile properties of the material. The proposed decomposition analysis method could be widely applied to investigating mechanical behavior of multi-phase alloys exhibiting the TRIP phenomenon.
neutron diffraction measurement was performed on an Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) TRIP-assisted austenitic steel. The analysis method based on stress partitioning and phase fractions measured by neutron diffraction was proposed, by which the tensile flow stress and the strain hardening rate of the specimen were resolved into factors associated with each phase, i.e., the austenite matrix, deformation-induced martensite, and the transformation rate of DIMT after differentiation, and then the role of each factor in the global strain hardening behavior was discussed. In addition, the plastic strain partitioning between austenite and martensite was indirectly estimated using the dislocation density measured by diffraction profile analysis, which constructed the full picture of stress and strain partitioning between austenite and martensite in the material. The results suggested that both the transformation rate and the phase stress borne by the deformation-induced martensite played important roles in the global tensile properties of the material. The proposed decomposition analysis method could be widely applied to investigating mechanical behavior of multi-phase alloys exhibiting the TRIP phenomenon.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:68.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Bai, Y.*; Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 17, p.2690 - 2700, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:80.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable austenitic steels having ultrafine grained (UFG) microstructures can be fabricated by conventional cold rolling and annealing processes by utilizing the deformation-induced martensitic transformation during cold rolling and its reverse transformation to austenite upon annealing. However, such processes are not applicable when the austenite has high mechanical stability against deformation-induced martensitic transformation, since there is no sufficient amount of martensite formed during cold rolling. In the present study, a two-step cold rolling and annealing process was applied to an Fe-24Ni-0.3C metastable austenitic steel having high mechanical stability. Prior to the cold rolling, a repetitive subzero treatment and reverse annealing treatment were applied. Such a treatment dramatically decreased the mechanical stability of the austenite and greatly accelerated the formation of deformation-induced martensite during the following cold rolling processes. As a result, the grain refinement was significantly promoted, and a fully recrystallized specimen with a mean austenite grain size of 0.5 mm was successfully fabricated, which exhibited both high strength and high ductility.
Mao, W.; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 837, p.142758_1 - 142758_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.81(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Kimata, Tetsuya*; Kakitani, Kenta*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Iwase, Akihiro*; Mao, W.*; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Terai, Takayuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(3), p.035801_1 - 035801_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kong, L.*; Gong, J.*; Hu, Q.*; Capitani, F.*; Celeste, A.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Li, N.*; Yang, W.*; Liu, G.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 31(9), p.2009131_1 - 2009131_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:82.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The soft nature of organic-inorganic halide perovskites renders their lattice particularly tunable to external stimuli such as pressure, undoubtedly offering an effective way to modify their structure for extraordinary optoelectronic properties. However, these soft materials meanwhile feature a general characteristic that even a very mild pressure will lead to detrimental lattice distortion and weaken the critical light-matter interaction, thereby triggering the performance degradation. Here, using the methylammonium lead iodide as a representative exploratory platform, we observed the pressure-driven lattice disorder can be significantly suppressed via hydrogen isotope effect, which is crucial for better optical and mechanical properties previously unattainable.
 Fe(CN)
Fe(CN) accompanied with enhanced conductivity
accompanied with enhanced conductivityLi, K.*; Zheng, H.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Tulk, C. A.*; Molaison, J.*; Feygenson, M.*; Ivanov, I. N.*; Yang, W.*; Mao, H.-K.*
Inorganic Chemistry, 54(23), p.11276 - 11282, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.46(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Pressure-induced polymerization of triple bonds would produce conductive conjugated double bonds. To find a metal cyanide with a low polymerization pressure, anhydrous Li Fe(CN)
Fe(CN) is synthesized and its crystal structure is determined. The irreversible bonding between the CN
is synthesized and its crystal structure is determined. The irreversible bonding between the CN can be realized by use of the industrial apparatus. The conductivity is enhanced by more than 3 orders of magnitude, which makes the polymerized Li
can be realized by use of the industrial apparatus. The conductivity is enhanced by more than 3 orders of magnitude, which makes the polymerized Li Fe(CN)
Fe(CN) a potential cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries.
a potential cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries.
 O
O thin films on Si (100) by ion beam sputter deposition
thin films on Si (100) by ion beam sputter depositionMao, W.*; Fujita, Masaya*; Chikada, Takumi*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Surface & Coatings Technology, 283, p.241 - 246, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.82(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Single-phase nanocrystalline thin films of Er O
O (440) has been first prepared using Si (100) substrates by ion beam sputter deposition at 973 K at a pressure of
(440) has been first prepared using Si (100) substrates by ion beam sputter deposition at 973 K at a pressure of  10
10 Pa and
Pa and 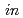 -
-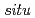 annealing at 1023 K at a pressure of
annealing at 1023 K at a pressure of  10
10 Pa. Er silicides formed during the deposition are eliminated via the annealing, which results in the single phase and the smooth surface of the Er
Pa. Er silicides formed during the deposition are eliminated via the annealing, which results in the single phase and the smooth surface of the Er O
O thin films. The epitaxial relationship between Si (100) and Er
thin films. The epitaxial relationship between Si (100) and Er O
O (110) is clarified by X-ray diffraction and reflection high energy electron diffraction.
(110) is clarified by X-ray diffraction and reflection high energy electron diffraction.
Ding, F.*; Luo, G.-N.*; Pitts, R.*; Litnovsky, A.*; Gong, X.*; Ding, R.*; Mao, H.*; Zhou, H.*; Wampler, W. R.*; Stangeby, P. C.*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 455(1-3), p.710 - 716, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:88.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)