Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085015_1 - 085015_11, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:87.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Key parts of the ITER scenarios are determined by the capability of the proposed poloidal field (PF) coil set. They include the plasma breakdown at low loop voltage, the current rise phase, the performance during the flat top (FT) phase and a ramp down of the plasma. The ITER discharge evolution has been verified in dedicated experiments. New data are obtained from C-Mod, ASDEX Upgrade, DIII-D, JT-60U and JET. Results show that breakdown for 
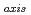
 0.23-0.33 V m
0.23-0.33 V m is possible unassisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in devices with a capability of using ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. This allows optimization of the flux usage from the PF set. Additional heating keeps
is possible unassisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in devices with a capability of using ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. This allows optimization of the flux usage from the PF set. Additional heating keeps 
 (3)
(3)  0.85 during the ramp up to
0.85 during the ramp up to 
 = 3. A rise phase with an H-mode transition is capable of achieving
= 3. A rise phase with an H-mode transition is capable of achieving 
 (3)
(3)  0.7 at the start of the FT. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at
0.7 at the start of the FT. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at 

 3 and the hybrid scenario at
3 and the hybrid scenario at 
 = 4-4.5 during the FT phase is documented, providing data for the
= 4-4.5 during the FT phase is documented, providing data for the 
 (3) evolution after the H-mode transition and the
(3) evolution after the H-mode transition and the 
 (3) evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation. The inductance could be kept
(3) evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation. The inductance could be kept  1.2 during the first half of the current decay, using a slow
1.2 during the first half of the current decay, using a slow 
 ramp down, but still consuming flux from the transformer. Alternatively, the discharges can be kept in H-mode during most of the ramp down, requiring significant amounts of additional heating.
ramp down, but still consuming flux from the transformer. Alternatively, the discharges can be kept in H-mode during most of the ramp down, requiring significant amounts of additional heating.
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T. A.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The ITER discharge evolution has been verified in dedicated experiments. Results show that breakdown at E 0.23-0.32 V/m is possible un-assisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in all devices with ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at q
0.23-0.32 V/m is possible un-assisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in all devices with ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at q = 3 and the hybrid scenario at q95=4-4.5 during the flat top phase was documented. Specific studies during the flat top phase provide data for the li evolution after the H-mode transition and the li evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation.
= 3 and the hybrid scenario at q95=4-4.5 during the flat top phase was documented. Specific studies during the flat top phase provide data for the li evolution after the H-mode transition and the li evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation.
Rice, J. E.*; Ince-Cushman, A.*; de Grassie, J. S.*; Eriksson, L.-G.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Scarabosio, A.*; Bortolon, A.*; Burrell, K. H.*; Fenzi-Bonizec, C.*; Greenwald, M. J.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Parametric scalings of the intrinsic (spontaneous, with no external momentum input) toroidal rotation observed on a large number of tokamaks have been combined with an eye toward revealing the underlying mechanism(s) and extrapolation to future devices. The intrinsic rotation velocity has been found to increase with plasma stored energy or pressure in JET, Alcator C-Mod, Tore Supra, DIII- D, JT-60U and TCV, and to decrease with increasing plasma current in some of these cases. Use of dimensionless parameters has led to a roughly unified scaling with Mach number in proportion to normalized beta, although a variety of Mach numbers works fairly well; scalings of the intrinsic rotation velocity with normalized gyro-radius or collisionality show no correlation. Whether this suggests the predominant role of MHD phenomena such as ballooning transport over turbulent processes in driving the rotation remains an open question. For an ITER discharge with 
 =2.6, an intrinsic rotation Alfv
=2.6, an intrinsic rotation Alfv n Mach number of M
n Mach number of M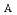
 0.02 may be expected from the above deduced scaling, possibly high enough to stabilize resistive wall modes without external momentum input.
0.02 may be expected from the above deduced scaling, possibly high enough to stabilize resistive wall modes without external momentum input.