Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oki, Shigeo; Maruyama, Shuhei; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Ohtaki, Akira; Kubo, Shigenobu; Hibi, Koki*; Kan, Taro*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/04
Yoshida, Fumiko; Nagashima, Keisuke; Tsubouchi, Masaaki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Maruyama, Momoko; Sugiyama, Akira
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(1), p.012201_1 - 012201_5, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.52(Physics, Applied)Ochi, Yoshihiro; Nagashima, Keisuke; Maruyama, Momoko; Tsubouchi, Masaaki; Yoshida, Fumiko; Kono, Nanase; Mori, Michiaki; Sugiyama, Akira
Optics Express (Internet), 23(11), p.15057 - 15064, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:81.62(Optics)We have developed a 1 kHz repetition picosecond laser system dedicated for intense terahertz (THz) pulse generation. The system comprises a chirped pulse amplification laser equipped with a Yb:YAG thin-disk amplifier. At room temperature, the Yb:YAG thin-disk regenerative amplifier provides pulses having energy of over 10 mJ and spectral bandwidth of 1.2 nm. The pulse duration achieved after passage through a diffraction grating pair compressor was 1.3 ps. By employing this picosecond laser as a pump source, THz pulses having a peak frequency of 0.3 THz and 4  J of energy were generated by means of optical rectification in an Mg-doped LiNbO
J of energy were generated by means of optical rectification in an Mg-doped LiNbO crystal.
crystal.
Satou, Akira; Watanabe, Tadashi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.120 - 124, 2011/10
In the BWR subjected to an earthquake, the oscillating acceleration attribute to the seismic wave may cause the variation of the coolant flow rate and void fraction in the core, which might result in the core instability due to the void-reactivity feedback. In the present study, the numerical code analyzing the behavior of nuclear power plant under the seismic acceleration is developed based on the 3-D neutron-coupled thermal hydraulic code. The coolant flow in the core is simulated with introducing the oscillating acceleration attributed to the earthquake motion into the motion equation force terms. The analyses are performed on a real BWR4-type nuclear power plant with the sinusoidal acceleration and the acceleration obtained from a real earthquake. The behaviors of the core and coolant are calculated in the various parameters of acceleration. The effects of the frequency, amplitude and direction of the oscillating acceleration are discussed.
Satou, Akira; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 5(3), p.263 - 278, 2011/04
A new model for the occurrence of the net vapor generation was developed to improve the predictive capability of best-estimate thermal hydraulic codes for transient void behavior under fast transient condition such as reactivity initiated accidents (RIA). It was clarified that the concept of vapor condensation in the model needed to be improved by analyzing the RIA simulation experiments, thus, the new model for the net vapor generation was developed by using the thickness of thermal boundary layer as a characteristic length of vapor condensation. The new model was introduced into TRAC-BF1 code and was applied to the analyses for the high pressure experiments, confirming that the predictive capability of the modified code was improved.
Satou, Akira; Watanabe, Tadashi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2010/10
In the BWR subjected to an earthquake, the oscillating acceleration attribute to the seismic wave may cause the variation of the coolant flow rate and void fraction in the core, which might result in the core instability due to the void-reactivity feedback. Therefore, it is important to properly evaluate the effect of the seismic acceleration on the core stability from a viewpoint of plant integrity estimation. In the present study the numerical code analyzing the behavior of nuclear power plant under the seismic acceleration is developed based on the 3-D neutron-coupled thermal hydraulic code, TRAC/SKETCH. The coolant flow is simulated with introducing the acceleration attributed to the earthquake into the motion equation of the flow as external force terms. The analyses are performed on a real BWR4-type nuclear power plant with the sinusoidal acceleration and the acceleration obtained from the response analysis to an actual earthquake. The behaviors of the core and coolant are calculated in the various parameters of acceleration. The effects of the frequency, amplitude and direction of the oscillating acceleration are discussed.
Satou, Akira; Maruyama, Yu; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 1(2), p.154 - 165, 2007/00
Series of out-of-pile experiments to obtain the knowledge on the transient void behavior during reactivity initiated accidents are in progress at JAEA. In the present series of experiments, the transient void behavior in a test section of 2 2 bundle geometry under atmospheric pressure condition was measured using an impedance technique. The measuring areas and the arrangement of electrodes for the impedance technique were defined on the basis of numerical analyses and scaled model experiments. The comparison was made between the impedance and differential pressure techniques for steady boiling experiments to estimate the accuracy of the impedance technique. The impedance technique showed a good agreement with the void fraction estimated from the differential pressure. The transient void behavior in the bundle geometry was measured using the impedance technique. It was clarified that the transient void behavior depends on both the subcooling of inlet water and the heat generation rate of simulated fuel rod. Local void fraction was influenced by the ratio of flow area to heat transfer area of the simulated fuel rod.
2 bundle geometry under atmospheric pressure condition was measured using an impedance technique. The measuring areas and the arrangement of electrodes for the impedance technique were defined on the basis of numerical analyses and scaled model experiments. The comparison was made between the impedance and differential pressure techniques for steady boiling experiments to estimate the accuracy of the impedance technique. The impedance technique showed a good agreement with the void fraction estimated from the differential pressure. The transient void behavior in the bundle geometry was measured using the impedance technique. It was clarified that the transient void behavior depends on both the subcooling of inlet water and the heat generation rate of simulated fuel rod. Local void fraction was influenced by the ratio of flow area to heat transfer area of the simulated fuel rod.
Satou, Akira; Maruyama, Yu; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/07
Series of out-of-pile experiments to obtain the knowledge on the transient void behavior during reactivity initiated accidents are in progress at JAEA. In the present series of experiments, the transient void behavior in a test section of 2 2 bundle geometry under atmospheric pressure condition was measured using an impedance technique. The measuring areas and the arrangement of electrodes for the impedance technique were defined on the basis of numerical analyses and scaled model experiments. The comparison was made between the impedance and differential pressure techniques for steady boiling experiments to estimate the accuracy of the impedance technique. The impedance technique showed a good agreement with the void fraction estimated from the differential pressure. The transient void behavior in the bundle geometry was measured using the impedance technique. It was clarified that the transient void behavior depends on both the subcooling of inlet water and the heat generation rate of simulated fuel rod. Local void fraction was influenced by the ratio of flow area to heat transfer area of the simulated fuel rod.
2 bundle geometry under atmospheric pressure condition was measured using an impedance technique. The measuring areas and the arrangement of electrodes for the impedance technique were defined on the basis of numerical analyses and scaled model experiments. The comparison was made between the impedance and differential pressure techniques for steady boiling experiments to estimate the accuracy of the impedance technique. The impedance technique showed a good agreement with the void fraction estimated from the differential pressure. The transient void behavior in the bundle geometry was measured using the impedance technique. It was clarified that the transient void behavior depends on both the subcooling of inlet water and the heat generation rate of simulated fuel rod. Local void fraction was influenced by the ratio of flow area to heat transfer area of the simulated fuel rod.
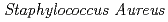
Cui, L.*; Iwamoto, Akira; Lian, J.-Q.*; Neoh, H.*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Horikawa, Yataro*; Hiramatsu, Keiichi*
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 50(2), p.428 - 438, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:173 Percentile:97.49(Microbiology)no abstracts in English
Hirata, Yuichi*; Onishi, Akira*; Nara, Yasushi*; Kido, Toshihiko; Maruyama, Toshiki; Otsuka, Naohiko*; Niita, Koji*; Takada, Hiroshi; Chiba, Satoshi
Nuclear Physics A, 707(1-2), p.193 - 212, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:50.64(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Yasuo; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Yamamoto, Shin; Maruyama, So; Mizoguchi, Tadanori*; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Kitamura, Kazunori*; Ioki, Kimihiro*; Inoue, Takashi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(Suppl.), 224 Pages, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Chikazumi, Shimpei*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Chiba, Satoshi; Niita, Koji*; Iwamoto, Akira
Physical Review C, 63(2), p.024602_1 - 024602_10, 2001/02
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:73.35(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Yoichiro; Kato, Masaaki; Ozu, Akira
Optical Pulse and Beam Propagation III (Proceedings of SPIE Vol.4271), p.335 - 338, 2001/01
no abstracts in English
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro; Kamo, Hideki*; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
Dai-7-Kai Doryoku Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (00-11), p.451 - 456, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Kato, Masaaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 39(9A), p.5118 - 5123, 2000/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.41(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Kato, Masaaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
Review of Scientific Instruments, 71(6), p.2288 - 2291, 2000/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Kato, Masaaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
Applied Physics Letters, 76(21), p.2979 - 2981, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.94(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Suzuki, Yoji; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Arisawa, Takashi
Applied Physics Letters, 76(14), p.1822 - 1824, 2000/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.90(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Kato, Masaaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
Optics Communications, 177(1-6), p.355 - 361, 2000/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.29(Optics)no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Kato, Masaaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro
Optics & Laser Technology, 32(2), p.101 - 105, 2000/03
no abstracts in English