Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maruyama, Shuhei
Robutsuri No Kenkyu (Internet), (78), 7 Pages, 2025/03
no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Shuhei; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Maruyama, Shuhei; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 205, p.110591_1 - 110591_13, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Maruyama, Shuhei
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-009, 16 Pages, 2024/08
The Japanese nuclear data processing code FRENDY implements the ACE file perturbation tool based on the random sampling method, which can be used to quantify nuclear data-induced uncertainties. However, it has not been able to evaluate the uncertainty due to the scattering angle distribution, which is not ignored in the uncertainty quantification of fast reactor core analysis and shielding analysis. Recently, a method to quantify the uncertainty based on the maximum entropy method has been proposed by the authors. In this report, a perturbation function for the uncertainty of the elastic scattering angular distribution based on this proposed method has been added to the FRENDY/ACE file perturbation tool.
Endo, Tomohiro*; Maruyama, Shuhei; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(3), p.363 - 374, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Uncertainty quantification (UQ) of the neutron multiplication factor is important to investigate the appropriate safety margin for a target system. Although the random sampling method is a practical and useful UQ method, a large computational cost is required to reduce the statistical error of the estimated uncertainty. Furthermore, if an input variable follows a normal distribution with a large standard deviation, the perturbed input variable by the random sampling method may become a physically inappropriate or negative value. To address these issues for the efficient and robust UQ, a modified deterministic sampling method using the simplex ensemble and the scaling method is proposed. The features of the proposed method are summarized as follows: The sample size is (r+2), where r corresponds to the effective rank of the covariance matrix between the input variables; depending on a situation of target UQ, the amounts of perturbations for the input parameters can be arbitrarily given by the scaling factor method; the scaling factor can be updated to avoid physically inappropriate in the perturbed input variables. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through the UQ of the neutron multiplication factor due to fuel manufacturing uncertainties for a typical PWR pin-cell burnup calculation.
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.31 - 43, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the feasibility of reducing the uncertainty associated with fast-reactor-core design by sharing an experimental database between different fields (e.g., reactor physics and radiation shielding) using data assimilation techniques. As the first step in this study, we focused on the ORNL sodium shielding experiment and investigated the possibility of using the experimental data to reduce the uncertainty in sodium void reactivity (SVR), which is the most important safety parameter for sodium-cooled fast reactors. A sensitivity analysis based on the Generalized Perturbation Theory was performed for the sodium shielding experiment. Using the sensitivity coefficients evaluated here and those of the sodium void reactivity previously evaluated by the JAEA, we showed that sodium shielding experimental data can contribute to the uncertainty reduction of SVR by adopting the cross-section adjustment method. Based on this study, the uncertainty reduction effect is expected to be significant, especially for SVR dominated by neutron-leakage phenomena. Although new reactor physics experimental data on SVR may be difficult to obtain, the results of this study suggest that data from sodium shielding experiments can partially substitute for this role. This study demonstrated the value of the mutual use of integral experimental data in fast reactor designs.
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1372 - 1385, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00008_1 - 00008_9, 2023/03
The applicability of Akaike's Bayesian Information Criterion (ABIC) to covariance modeling in the cross-section adjustment method was investigated. One of the most important things for a reliable cross-section adjustment method is giving a suitable covariance matrix. However, since we cannot know the true covariance matrix in advance, we usually estimate and assume it. To judge the goodness of the covariance matrix modeling, a metric is desirable. As a candidate for this metric, we focus on ABIC which is one of the information criteria in Bayesian inference, because the cross-section adjustment method is often discussed within the framework of Bayesian inference. In the conventional cross-section adjustment method, incorporation of the analysis model uncertainty in a covariance matrix still requires ad hoc treatment. In JAEA, the integral experimental database for fast reactors has been developed and the adjusted cross-section set ADJ2017 has been created based on this database. Many of the core characteristics in the database have been analyzed by a deterministic method. Therefore, the predicted core characteristics have non-negligible uncertainties with correlations due to some numerical approximations. However, the evaluations of the uncertainties and their correlations are still challenging issues. In addition, there would be unknown uncertainties that experimenters and analysts of reactor physics experiments could not recognize. To judge the goodness of the covariance matrix related to these uncertainties, the applicability of ABIC to the cross-section adjustment method was investigated.
Fukui, Yuhei*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Maruyama, Shuhei
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00006_1 - 00006_9, 2023/03
We developed a new nuclear data adjustment method for experimental data containing outliers. This method mitigates the effect of outliers by applying M-estimation, a type of robust estimation, to the conventional nuclear data adjustment method using sensitivity coefficients. Based on the M-estimation, we derived a weighted nuclear data adjustment formula and developed a weight calculation method. The weighted nuclear data adjustment formula was derived by weighting the function to take the extremum of the conventional nuclear data adjustment. The weighting of each nuclear characteristic is calculated from the difference between the measured and calculated values of the nuclear characteristic. This weight calculation method can evaluate the validity of each nuclear characteristic by considering correlations between nuclear characteristics using singular value decomposition. The proposed method and the conventional method were compared and verified by twin experiments. In the twin experiments, the nuclear data were adjusted using experimental data that intentionally included outliers. As a result of twin experiments, it was confirmed that the nuclear data were adjusted robustly and appropriately even with the experimental data containing outliers.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Maruyama, Shuhei
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors 2022 (PHYSOR 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/05
This paper proposes a new homogenization method, "Boundary Condition Free Homogenization (BCFH)". The traditional homogenization method separates the core calculation and the cell (assembly) calculation by assuming a specific boundary condition or a peripheral region in the cell calculation. Nevertheless, there are ambiguities and approximation in these assumptions, and they can also cause a decline in accuracy. BCFH aims to avoid these problems and improve the accuracy in the cell calculation such as homogenization. We imposed the conditions that the physical quantities in the cell related to the reaction rate preservation is preserved for any incoming partial current, during the homogenization. That is, the response matrices of cell average (or total) flux and outgoing partial current, to be the same form between heterogeneous and homogeneous system. As a result, homogenized parameters, such as cross-sections, superhomgenization factors, and discontinuity factors, are no longer dependent on a specific boundary condition. The new homogenized parameters obtained in this way are extended from the conventional vector form to the matrix form in BCFH. To investigate the performance of BCFH, numerical tests are done for the simplified models which originates in 750MW-class sodium-cooled fast reactor with MOX fuel core in Japan. It is found that BCFH is particularly effective in evaluating control rod reactivity worth and reaction rate distribution, compared to the traditional method. We conclude that the BCFH can be a promising homogenization concept for core neutronic analysis.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Maruyama, Shuhei; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Oki, Shigeo
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-019, 115 Pages, 2022/03
In JAEA, several versions of unified cross-section set for fast reactors have been developed so far; we have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017R, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section setADJ2017 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses in reactor core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design. In the methodology, the cross-section set is adjusted by integrating the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. ADJ2017R basically has the same performance as ADJ2017, but we conducted an additional investigation on ADJ2017 and revised the following two points. The first is to unify the evaluation method of the correlation coefficient of uncertainty caused by experiments (hereinafter referred to as the experimental correlation coefficient). Because it was found that the common uncertainty used in the evaluation of the experimental correlation coefficient was evaluated by two different methods, the experimental correlation coefficients were revised for all experimental data, and the evaluation method was unified. The second is the review of the integral experiment data used for the cross-section adjustment calculation. It was found that one of the experimental values of composition ratio after irradiation of the Am-243 sample has a problem in uncertainty evaluation because its experimental uncertainty is extremely small compared to the others. The cross-section adjustment calculation was, therefore, redone by excluding the experimental value. In the creation of ADJ2017, a total of 719 data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets. In contrast, a total of 61
Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ishikawa, Makoto; Maruyama, Shuhei; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*
JAEA-Research 2018-011, 556 Pages, 2019/03
We have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section set ADJ2010 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology, which integrates with the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. The ADJ2017 is based on Japan's latest nuclear data library JENDL-4.0 as in the previous version of ADJ2010, and it incorporates more information on integral experimental data sets related to minor actinides (MAs) and degraded plutonium (Pu). In the creation of ADJ2010, a total of 643 integral experimental data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and 488 of the integral experimental data sets were finally selected to be used for the cross-section adjustment. In contrast, we have evaluated a total of 719 data sets, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets to create ADJ2017. ADJ2017 shows almost the same performance as ADJ2010 for the main neutronic characteristics of conventional sodium-cooled MOX-fuel fast reactors. In addition, for the neutronic characteristics related to MA and degraded Pu, ADJ2017 improves the C/E values of the integral experimental data sets, and reduces the uncertainty induced by the nuclear data. ADJ2017 is expected to be widely used in the analysis and design research of fast reactors. Moreover, it is expected that the integral experimental data sets used for ADJ2017 can be utilized as a standard database of FBR core design.
Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kimura, Junichi*; Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Danhara, Toru*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Iwano, Hideki*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Chang, Q.*; Miyazaki, Takashi*; et al.
Geochemical Journal, 52(6), p.531 - 540, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.35(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Takano, Kazuya; Maruyama, Shuhei; Hazama, Taira; Usami, Shin
Proceedings of Reactor Physics Paving the Way Towards More Efficient Systems (PHYSOR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), p.1725 - 1735, 2018/04
Irradiation dependence of the core excess reactivity was investigated for the Monju system startup tests at zero-power carried out in 2010. The excess reactivity basically decreases with the  decay of
decay of  Pu in zero-power operation. However, the excess reactivity little changed in the two month period of the startup tests, which suggests a positive reactivity insertion during the period. The investigated irradiation dependence shows that the positive reactivity increases with reactor operation and mostly saturates by the fission-dose attained during the Monju zero-power operation in a month (
Pu in zero-power operation. However, the excess reactivity little changed in the two month period of the startup tests, which suggests a positive reactivity insertion during the period. The investigated irradiation dependence shows that the positive reactivity increases with reactor operation and mostly saturates by the fission-dose attained during the Monju zero-power operation in a month ( 10
10 fissions/cm
fissions/cm ). The saturated positive reactivity is equivalent to approximately 47% of the initially accumulated self-irradiation damage recovery assuming the defects were recovered by the fission-fragment irradiation in the reactor operation.
). The saturated positive reactivity is equivalent to approximately 47% of the initially accumulated self-irradiation damage recovery assuming the defects were recovered by the fission-fragment irradiation in the reactor operation.
Oki, Shigeo; Maruyama, Shuhei; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Ohtaki, Akira; Kubo, Shigenobu; Hibi, Koki*; Kan, Taro*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/04
Kan, Taro*; Ogura, Masashi*; Hibi, Koki*; Oki, Shigeo; Maeda, Seiichiro; Maruyama, Shuhei; Ohgama, Kazuya
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/04
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ikeda, Kazumi*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kan, Taro*; Maruyama, Shuhei; Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Oki, Shigeo
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/04
Yokoyama, Kenji; Maruyama, Shuhei; Numata, Kazuyuki; Ishikawa, Makoto; Takeda, Toshikazu*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Unifying Theory and Experiments in the 21st Century (PHYSOR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.1906 - 1915, 2016/05
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C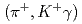 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 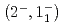 was measured to be
was measured to be 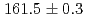 (stat)
(stat)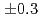 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 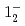 and
and 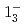 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 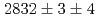 , keV and
, keV and 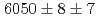 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.