Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 symmetry in CeCu
symmetry in CeCu Ge
Ge ; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy荒谷 秀和*; 中谷 泰博*; 藤原 秀紀*; 川田 萌樹*; 金井 惟奈*; 山神 光平*; 藤岡 修平*; 濱本 諭*; 久我 健太郎*; 木須 孝幸*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(12), p.121113_1 - 121113_6, 2018/09
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:25.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed study on the 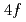 ground state symmetry of the pressure-induced superconductor CeCu
ground state symmetry of the pressure-induced superconductor CeCu Ge
Ge probed by soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. The revised Ce
probed by soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. The revised Ce 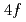 ground states are determined as
ground states are determined as 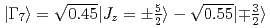 with
with 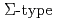 in-plane rotational symmetry. This gives an in-plane magnetic moment consistent with the antiferromagnetic moment as reported in neutron measurements. Since the in-plane symmetry is the same as that for the superconductor CeCu
in-plane rotational symmetry. This gives an in-plane magnetic moment consistent with the antiferromagnetic moment as reported in neutron measurements. Since the in-plane symmetry is the same as that for the superconductor CeCu Si
Si , we propose that the charge distribution along the
, we propose that the charge distribution along the  -axis plays an essential role in driving the system into a superconducting phase.
-axis plays an essential role in driving the system into a superconducting phase.
祐延 悟*; 正木 健太郎*; 大釜 一真*; 荻原 徳男
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 56(4), p.142 - 145, 2013/04
Monte-Carlo method is useful for the transmission probability calculation of a complicated shaped tube under molecular flow conditions. However the shape data should be fed into the computer for each simulation. In the present study, transmission probability was calculated by KPCalc, which is the Monte-Carlo simulation software. KPCalc can calculate the transmission probability from the 3D-CAD data without preparing the source code of the shape data. Therefore, KPCalc is easily applied even for the complicated shape which the conventional Monte-Carlo method was hardly applied because of much labor. Calculation was carried out for cylindrical tubes, conical tubes, and bellows-shaped tubes. Results are in good agreement with previous results within the data scattering. As an example, transmission probabilities of formed bellows tubes with a complicated shape were calculated.
山崎 智*; 寺田 透*; 河野 秀俊; 清水 謙多郎*; 皿井 明倫*
Nucleic Acids Research, 40(17), p.e129_1 - e129_7, 2012/09
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:44.94(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Proteins recognize a specific DNA sequence not only through direct contact (direct readout) with base pairs but also through sequence-dependent conformation and/or flexibility of DNA (indirect readout). However, it is difficult to assess the contribution of indirect readout to the sequence specificity. What is needed is a straightforward method for quantifying its contributions to specificity. Using Bayesian statistics, we derived the probability of a particular sequence for a given DNA structure from the trajectories of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of DNAs containing all possible tetramer sequences. Then, we quantified the specificity of indirect readout based on the information entropy associated with the probability. We tested this method with known structures of protein-DNA complexes. This method enabled us to correctly predict those regions where experiments suggested the involvement of indirect readout. The results also indicated new regions where the indirect readout mechanism makes major contributions to the recognition. The present method can be used to estimate the contribution of indirect readout without approximations to the distributions in the conformational ensembles of DNA, and would serve as a powerful tool to study the mechanism of protein-DNA recognition.
山崎 智*; 寺田 透*; 清水 謙多郎*; 河野 秀俊; 皿井 明倫*
Nucleic Acids Research, 37(20), p.e135_1 - e135_9, 2009/09
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:15.1(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Proteins recognize DNA sequences by two different mechanisms. The first is direct readout, in which recognition is mediated by direct interactions between the protein and the DNA bases. The second is indirect readout, which is caused by the dependence of conformation and the deformability of the DNA structure on the sequence. Various energy functions have been proposed to evaluate the contribution of indirect readout to the free-energy changes in complex formations. We developed a new generalized energy function to estimate the dependence of the deformability of DNA on the sequence. This function was derived from molecular dynamics (MD) simulations previously conducted on B-DNA dodecamers, each of which had one possible tetramer sequence embedded at its center. By taking the logarithm of the probability distribution function (PDF) for the base-step parameters of the central base-pair step of the tetramer, its ability to distinguish the native sequence from random ones was superior to that with the previous method that approximated the energy function in harmonic form. From a comparison of the energy profiles calculated with these two methods, we found that the harmonic approximation caused significant errors in the conformational energies of the tetramers that adopted multiple stable conformations.
林 孝夫; 落合 謙太郎; 正木 圭; 後藤 純孝*; 沓掛 忠三; 新井 貴; 西谷 健夫; 宮 直之
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 349(1-2), p.6 - 16, 2006/02
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:56.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)核反応分析法(NRA)を用いてJT-60Uダイバータ部のプラズマ対向壁に用いられている炭素タイル中の重水素保持量深さ分布を測定した。最も重水素濃度が高かったのは外側ドームウィングタイルでD/ Cの値は0.053であり、その重水素蓄積過程は炭素-重水素の共堆積によるものと推定された。また外側及び内側のダイバータターゲットタイルにおいてはD/
Cの値は0.053であり、その重水素蓄積過程は炭素-重水素の共堆積によるものと推定された。また外側及び内側のダイバータターゲットタイルにおいてはD/ Cは0.006以下であった。軽水素を含めた水素同位体の濃度については、NRA及びSIMS分析結果からドーム頂部タイルの(H+D)/
Cは0.006以下であった。軽水素を含めた水素同位体の濃度については、NRA及びSIMS分析結果からドーム頂部タイルの(H+D)/ Cを0.023と推定した。一方OFMC計算を用いてNBIで入射した高エネルギー重水素がドーム領域に打ち込まれることを示した。また重水素の打ち込みや炭素との共堆積などによる重水素蓄積は、タイルの表面温度や損耗・堆積などの表面状態の影響を受けることを示した。重水素保持量深さ分布,SEM分析及びOFMC計算により、重水素分布はおもに重水素-炭素の共堆積,重水素イオンの打ち込み及びバルクへの拡散の複合したプロセスにより決まることを明らかにした。
Cを0.023と推定した。一方OFMC計算を用いてNBIで入射した高エネルギー重水素がドーム領域に打ち込まれることを示した。また重水素の打ち込みや炭素との共堆積などによる重水素蓄積は、タイルの表面温度や損耗・堆積などの表面状態の影響を受けることを示した。重水素保持量深さ分布,SEM分析及びOFMC計算により、重水素分布はおもに重水素-炭素の共堆積,重水素イオンの打ち込み及びバルクへの拡散の複合したプロセスにより決まることを明らかにした。
正木 圭; 杉山 一慶*; 林 孝夫; 落合 謙太郎; 後藤 純孝*; 柴原 孝宏*; 廣畑 優子*; 大矢 恭久*; 宮 直之; 田辺 哲朗*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.553 - 559, 2005/03
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:84.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)JT-60Uにおいて、DD反応で生成されたトリチウム及び重水素のプラズマ対向壁への蓄積分布を評価し、真空容器内での水素同位体挙動を調べた。(1)プラズマ対向壁に蓄積されたトリチウムのIP及び燃焼法による測定と、損耗及び再堆積測定から以下の結果を得た。ドーム頂部でトリチウム濃度が最も高く、厚い堆積層が存在する内側ダイバータ部では低かった。(2)この結果とOFMC解析結果から、JT-60Uで得られたトリチウム分布は、DD反応で生成された高エネルギー(1MeV)トリチウムがリップルロスによりプラズマから損失し、エネルギーをあまり失うことなく壁に深く入射されたものであることが明らかとなった。(3)NRAによる重水素蓄積量測定結果では、プラズマ対向壁における重水素分布は、トリチウム分布と異なり、最も高い重水素蓄積量を示したドーム外側ウイングでもD/C 0.05と低い値を示した。厚い堆積層の存在する内側ダイバータではさらに低く、D/C
0.05と低い値を示した。厚い堆積層の存在する内側ダイバータではさらに低く、D/C 0.01以下であった。いずれの結果も、共堆積により多くのトリチウムが残留するJETのトリチウム分布とは大きく異なり、JT-60Uプラズマ対向壁における水素同位体の挙動は、それぞれの粒子のプラズマ対向壁への入射分布及び壁(炉内構造物)温度の影響を受けていることを示すものである。
0.01以下であった。いずれの結果も、共堆積により多くのトリチウムが残留するJETのトリチウム分布とは大きく異なり、JT-60Uプラズマ対向壁における水素同位体の挙動は、それぞれの粒子のプラズマ対向壁への入射分布及び壁(炉内構造物)温度の影響を受けていることを示すものである。
落合 謙太郎; 林 孝夫; 沓掛 忠三; 後藤 純孝*; 正木 圭; 新井 貴; 宮 直之; 西谷 健夫
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.836 - 839, 2004/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:29.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FNSでは重陽子加速器ビームによる核反応分析法を用いて、黒鉛実機ダイバータ表面のDとTの保持量及び深さ分布について測定を行った。測定対象である黒鉛ダイバータは2つである。利用核反応と検出荷電粒子はD分布測定の場合、D(d,p)T核反応によるプロトン粒子を、T分布測定の場合はT(d, )n核反応による
)n核反応による 粒子である。D(d,p)T核反応によるプロトンとトリトン及び
粒子である。D(d,p)T核反応によるプロトンとトリトン及び C(d,p)
C(d,p) Cのプロトンのスペクトルピークが得られており、その検出エネルギーは計算で求まる試料表面からの放出エネルギーとよく一致していることから、重水素が試料表面から
Cのプロトンのスペクトルピークが得られており、その検出エネルギーは計算で求まる試料表面からの放出エネルギーとよく一致していることから、重水素が試料表面から mオーダーで深く堆積していることが明らかとなった。これらの収量から重水素の平均保持量は内側ダイバータで約1
mオーダーで深く堆積していることが明らかとなった。これらの収量から重水素の平均保持量は内側ダイバータで約1 10
10 cm
cm であり、トリチウムベータ線の放射能は18kBq/cm
であり、トリチウムベータ線の放射能は18kBq/cm に相当するという結果を得た。また350keV入射のみアルファスペクトルを得ている結果から、トリチウムの深さ分布については母材2
に相当するという結果を得た。また350keV入射のみアルファスペクトルを得ている結果から、トリチウムの深さ分布については母材2 mより深い位置にあると考えられる。
mより深い位置にあると考えられる。
森岡 篤彦; 佐藤 聡; 金野 正晴*; 逆井 章; 堀 順一*; 落合 謙太郎; 山内 通則*; 西谷 健夫; 神永 敦嗣; 正木 圭; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(2), p.1619 - 1623, 2004/08
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:55.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)2.45MeVと14MeV中性子源を使用して、ボロン入り低放射化コンクリートの遮蔽性能実験と放射化特性試験を行った。熱中性子遮蔽性能は、2wt%ボロン入りコンクリートが1wt%ボロン入りコンクリートより優れているが、高速中性子遮蔽性能は両者の違いはなかった。14MeV中性子照射から30日以上経過した時点で誘導放射能を比較するとボロン入りコンクリートは、標準コンクリートに比べ約100分の1であった。一方、ボロン添加量の違いによる誘導放射能は差はなかった。以上より、ボロンを添加することにより、熱中性子遮蔽性能と放射化性能を改善できることが確認され、今後の核融合試験装置の遮蔽材料としての有用性が示された。
森岡 篤彦; 佐藤 聡; 落合 謙太郎; 逆井 章; 堀 順一; 山内 通則*; 西谷 健夫; 神永 敦嗣; 正木 圭; 櫻井 真治; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.109 - 112, 2004/03
定常炉心試験装置(JT-60SC)のポート部分の中性子遮へいは、ポリエチレンよりも温度特性に優れたレジン(商標名: KRAFTON)を使用した設計となっている。超伝導コイルの核発熱量低減のための遮へい性能を保ちつつ、ポート重量を軽減させるため、筆者らはレジンに天然ボロンを添加した、ボロン入りレジンを開発した。ボロン添加量を変えた数種類の試料に、DD反応で発生する2.45MeV中性子を照射し、透過中性子を測定し、ボロン入りレジンの遮へい性能を比較した。高速中性子の遮へい性能はボロン添加量に依存せず同じであった。一方、低エネルギー中性子の遮へい性能はボロン2重量%の試験体がボロン1重量%の試験体より約25%良く、ボロン添加の効果が観測された。
 Eu M
Eu M ssbauer spectroscopic study on the Eu
ssbauer spectroscopic study on the Eu M
M O
O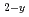 (0
(0 y
y 1.0)(M=Th, U)
1.0)(M=Th, U)正木 信行; 音部 治幹; 中村 彰夫; 原田 大実*; 伊藤 健太郎*; 佐々木 吉慶*; 日夏 幸雄*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.217 - 220, 2002/11
Eu M
M O
O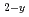 (0
(0 y
y 1.0)(M=Th, U)系について、
1.0)(M=Th, U)系について、 Euメスバウア分光法を用いて局所構造を調べた。粉末X線回折によると、M=Th系では、y
Euメスバウア分光法を用いて局所構造を調べた。粉末X線回折によると、M=Th系では、y 0.5で酸素空格子点(V
0.5で酸素空格子点(V )が無秩序配置をとる欠陥蛍石型相を、0.5
)が無秩序配置をとる欠陥蛍石型相を、0.5 y
y 0.8でV
0.8でV が秩序化したC型相と欠陥蛍石型相を、y
が秩序化したC型相と欠陥蛍石型相を、y 0.85の領域でC型相と単斜晶のFu
0.85の領域でC型相と単斜晶のFu O
O 相となることが示された。この系で、Eu
相となることが示された。この系で、Eu の異性体シフトは、Eu固溶率yに従って増加した。Eu
の異性体シフトは、Eu固溶率yに従って増加した。Eu に対するO
に対するO の配位数(CN)はCN=8-2yに従って減少するので、O
の配位数(CN)はCN=8-2yに従って減少するので、O イオン間の反発力の減少によって、平均Eu-O間距離も減少する。この相関は、酸化物系におけるEu
イオン間の反発力の減少によって、平均Eu-O間距離も減少する。この相関は、酸化物系におけるEu の異性体シフトとEu-O結合距離の経験的相関に従っている。U系において相図はTh系と同様であったが、異性体シフトは変化せずTh系に比べて小さな値をとった。
の異性体シフトとEu-O結合距離の経験的相関に従っている。U系において相図はTh系と同様であったが、異性体シフトは変化せずTh系に比べて小さな値をとった。
山崎 智*; 福井 一彦*; 河野 秀俊; 清水 謙多郎*; 皿井 明倫*; 寺田 透*
no journal, ,
Sequence-specific recognition of DNA by proteins plays a critical role in regulating gene expression. Accurate recognition is achieved by a combination of two different mechanisms. The first is direct readout, in which recognition is mediated by direct interactions between the protein and the DNA bases. The second is indirect readout, which is caused by the sequence-dependence of the conformation and deformability of the DNA structure. In our previous study, the contributions of indirect readout to binding affinity were evaluated for every tetrameric step in given protein-DNA complex structures. Using sequence-structure threading, potential energy differences between native and non-native tetrameric sequences for given tetrameric step conformation were compared. These potential energy functions were derived from the probability distribution function of its tetrameric step conformations calculated from trajectories of MD simulations of free DNAs which include all 136 types of tetramers. This gave good agreement with some experimental results, but shortage of structural sampling made the accurate estimation of distribution function difficult. In this work, we estimate the probability of occurrence of each tetrameric step sequence on given tetrameric step conformation using a Bayesian approach using the same structural dataset. We apply this approach to known protein-DNA complex structures, and assess the performance of predicting the sequence region where indirect readout makes important contribution to the binding affinity.
山崎 智*; 河野 秀俊; 清水 謙多郎*; 皿井 明倫*; 寺田 透*
no journal, ,
Sequence-specific recognition of DNA by proteins plays a critical role in regulating gene expression. Accurate recognition is achieved by a combination of two different mechanisms. The first is direct readout, in which recognition is mediated by direct interactions between amino acids and DNA bases. The second is indirect readout, which is caused by the sequence-dependence of the conformation and deformability of the Drain the present study, we developed a new method for evaluating the contribution of indirect readout. This method uses the information entropy as a measure of the contribution. The entropy was calculated from the probability of DNA sequence given conformation, which was obtained by converting the probability of conformation given sequence using Bays'theorem. We used trajectories of MD simulations for free DNAs that had different tetramer sequences at the center of the sequences to calculate the probability distributions of the conformation. We found that the regions which are shown to be indirectly readout by experiment tend to have smaller information entropies. We therefore concluded that the information entropy is a good measure of the contribution of indirect readout in protein-DNA recognition.
山崎 智*; 寺田 透*; 河野 秀俊; 清水 謙多郎*; 皿井 明倫*
no journal, ,
Sequence-specific recognition of DNA by proteins plays a critical role in regulating gene expression. The accurate recognition of target sequences in the genome can be achieved by a combination of two different mechanisms: the direct readout through the direct interactions between protein and DNA bases; and the indirect readout through the sequence-dependent conformation and/or deformability of DNA structure. While the specificity of direct readout has been well characterized, it is rather difficult to assess the contribution of indirect readout to the specificity. In order to quantify the specificity of indirect readout, we have developed a new method. First, we used Bayesian statistics to derive the probability of a particular sequence for a given DNA structure using ensembles obtained by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of DNAs containing all 136 unique tetramer sequences. Secondly, we used the information entropy to quantify the specificity of indirect readout. We applied this method to protein-DNA complexes of known structures to examine its validity. We could correctly predict those regions where experiments suggested the involvement of indirect readout, and could indicate new regions where the indirect readout mechanism can make major contributions to the recognition. The present probability/entropy-based approach has advantage over the previous energy-based approach in that the trajectories of MD simulation can be directly converted into the probability of sequence and the specificity of indirect readout without any approximation to the distributions in the conformational ensembles of DNA, and would serve as a powerful tool to study the mechanism of protein-DNA recognition.