Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Yamauchi, Hiroki; Metoki, Naoto; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Hong, T.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Hagihara, Masato; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(5), p.054705_1 - 054705_8, 2025/04
Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kobayashi, Naoki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Furukawa, Hazuki*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (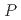
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 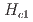 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 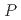 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
 O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Furukawa, Hazuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(9), p.094707_1 - 094707_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Do, S.-H.*; Kaneko, Koji; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Stone, M. B.*; Lin, J. Y. Y.*; Ito, Shinichi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Samolyuk, G. D.*; Dagotto, E.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(18), p.L180403_1 - L180403_6, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:86.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ta
Ta O
O
Kimura, Kenta*; Yagi, Naoki*; Hasegawa, Shunsuke*; Hagihara, Masato; Miyake, Atsushi*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Cao, H.*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(20), p.15078 - 15084, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:21.56(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Chen, Y.*; Sato, Masahiro*; Tang, Y.*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Fujita, Masaki*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.5199_1 - 5199_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Okuma, Ryutaro*; Kofu, Maiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Avdeev, M.*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.4382_1 - 4382_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:92.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) RuO
RuO proved by spin resonance
proved by spin resonanceIida, Kazuki*; Kofu, Maiko; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Murai, Naoki; Kawamura, Seiko; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Hasegawa, Shunsuke*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(5), p.053702_1 - 053702_5, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:78.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary) ladder
ladderUeda, Hiroshi*; Onoda, Shigeki*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Yoshizawa, Daichi*; Morioka, Toshiaki*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Hagihara, Masato*; Soda, Minoru*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(14), p.140408_1 - 140408_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:24.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -electron state of the heavy fermion superconductor NpPd
-electron state of the heavy fermion superconductor NpPd Al
Al and the isostructural family
and the isostructural familyMetoki, Naoto; Aczel, A. A.*; Aoki, Dai*; Chi, S.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Griveau, J.-C.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Hong, T.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011123_1 - 011123_6, 2020/03
Rare earths (4 ) and actinides (5
) and actinides (5 ) provide variety of interesting states realized with competing interactions between the increasing number of
) provide variety of interesting states realized with competing interactions between the increasing number of  electrons. Since crystal field splitting of many-body
electrons. Since crystal field splitting of many-body  electron system is smaller than the bandwidth, (1) high resolution experiments are needed, (2) essentially no clear spectrum with well defined peaks is expected in itinerant Ce and U compounds, and (3) Np and Pu is strictly regulated. Therefore, systematic research on magnetic excitations by neutron scattering experiments of localized compounds and rare earth iso-structural reference is useful. We describe the
electron system is smaller than the bandwidth, (1) high resolution experiments are needed, (2) essentially no clear spectrum with well defined peaks is expected in itinerant Ce and U compounds, and (3) Np and Pu is strictly regulated. Therefore, systematic research on magnetic excitations by neutron scattering experiments of localized compounds and rare earth iso-structural reference is useful. We describe the  electron states of heavy electron compounds NpPd
electron states of heavy electron compounds NpPd Al
Al and actinide and rare earth based iso-structural family.
and actinide and rare earth based iso-structural family.
Hirobe, Daichi*; Sato, Masahiro*; Hagihara, Masato*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review Letters, 123(11), p.117202_1 - 117202_7, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:70.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Watanabe, Masao; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kihara, Takumi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Sahara, Takuro*; Soda, Minoru*; Takahashi, Ryuta
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 25, p.011024_1 - 011024_5, 2019/03
Recently, neutron scattering experiments have been rapidly progressed under high magnetic field. In the J-PARC, proto-type compact pulse magnet system with the power supply, the coil and the sample stick has been developed. Basic specifications of the power supply are as follows; maximum charged voltage with capacitor is 2 kV, maximum current is 8 kA, repetition rate is a pulse per several minutes and pulse duration is several msec. Maximum magnetic field in the coil is more than 30 Tesla. The sample stick is designed for Orange-Cryostat. In this presentation, We report the details of the pulsed magnet system and the performance of it on neutron scattering experiments at MLF beam line (HRC).
 -electron states in PrPd
-electron states in PrPd Al
Al
Metoki, Naoto; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Hagihara, Masato*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Aczel, A. A.*; Chi, S.*; Hong, T.*; Matsuda, Masaaki*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(9), p.094704_1 - 094704_8, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The  -electron states of PrPd
-electron states of PrPd Al
Al were revealed by neutron inelastic scattering. The flat
were revealed by neutron inelastic scattering. The flat  -orbitals with large
-orbitals with large 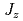 become stable under the two-dimensional CEF potential of unique crystal structure, which is the origin of the Ising anisotropy. A systematic understanding is possible in RPd
become stable under the two-dimensional CEF potential of unique crystal structure, which is the origin of the Ising anisotropy. A systematic understanding is possible in RPd Al
Al based on this CEF potential. Especially the
based on this CEF potential. Especially the 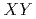 -type anisotropy in NpPd
-type anisotropy in NpPd Al
Al can be qualitatively understood with the positive Stevens factors. It mean that the local property is important for the physical properties of RPd
can be qualitatively understood with the positive Stevens factors. It mean that the local property is important for the physical properties of RPd Al
Al including the heavy fermion superconductivity in NpPd
including the heavy fermion superconductivity in NpPd Al
Al .
.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
 -based magnet in a nanoporous metal complex
-based magnet in a nanoporous metal complexSoda, Minoru*; Homma, Yuki*; Takamizawa, Satoshi*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 85(3), p.034717_1 - 034717_9, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.54(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering experiments are performed on the nanoporous metal complex Cu-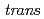 -1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid (Cu-CHD) adsorbing O
-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid (Cu-CHD) adsorbing O molecules to identify the spin model of the O
molecules to identify the spin model of the O -based magnet realized in the host complex. It is found that the magnetic excitations of Cu-CHDs adsorbing low- and high-concentration O
-based magnet realized in the host complex. It is found that the magnetic excitations of Cu-CHDs adsorbing low- and high-concentration O molecules are explained by different spin models, the former by spin dimers and the latter by spin trimers. By using the obtained parameters and by assuming that the levels of the group of the highest energy states are reduced because of the nonnegligible spin dependence of the molecular potential of oxygen, the magnetization curves are explained quantitatively.
molecules are explained by different spin models, the former by spin dimers and the latter by spin trimers. By using the obtained parameters and by assuming that the levels of the group of the highest energy states are reduced because of the nonnegligible spin dependence of the molecular potential of oxygen, the magnetization curves are explained quantitatively.
Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Soda, Minoru*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Kawana, Daichi*; Sato, Taku*; Nambu, Yusuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034001_1 - 034001_6, 2015/09
 CoGe
CoGe O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Matsumoto, Masashige*; M nsson, M.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Shiina, Ryosuke*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
nsson, M.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Shiina, Ryosuke*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Physical Review Letters, 112(12), p.127205_1 - 127205_5, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:85.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We demonstrate the existence of the spin-nematic interactions in an easy-plane type antiferromagnet Ba CoGe
CoGe O
O by exploring the magnetic anisotropy and spin dynamics. The combination of neutron scattering and magnetic susceptibility measurements reveals that the origin of the in-plane anisotropy is an antiferro-type interaction of the spin-nematic operator. The relation between the nematic operator and the electric polarization in the ligand symmetry of this compound is presented. The introduction of the spinnematic interaction is useful to understand the physics of spin and electric dipole in multiferroic compounds.
by exploring the magnetic anisotropy and spin dynamics. The combination of neutron scattering and magnetic susceptibility measurements reveals that the origin of the in-plane anisotropy is an antiferro-type interaction of the spin-nematic operator. The relation between the nematic operator and the electric polarization in the ligand symmetry of this compound is presented. The introduction of the spinnematic interaction is useful to understand the physics of spin and electric dipole in multiferroic compounds.

Masuda, Takatsugu*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(11), p.113705_1 - 113705_4, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:81.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We study a field-induced quantum phase in the weakly-coupled ferromagnetic frustrated chain LiCuVO by a neutron diffraction technique. A new incommensurate magnetic peak is observed at H
by a neutron diffraction technique. A new incommensurate magnetic peak is observed at H  8.5 T. The field-dependent propagation vector is identified with the spin density wave correlation in the theoretically predicted magnetic quadrupole order. Quantum fluctuation, geometrical frustration, and interchain interaction induce an exotic spin density wave long-range order in the insulating magnet.
8.5 T. The field-dependent propagation vector is identified with the spin density wave correlation in the theoretically predicted magnetic quadrupole order. Quantum fluctuation, geometrical frustration, and interchain interaction induce an exotic spin density wave long-range order in the insulating magnet.