Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimer
with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimerMetoki, Naoto; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Hagihara, Masato; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko*; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuda, Masaaki*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104424_1 - 104424_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering experiments were carried out to understand the unusual successive order in NdB with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with
with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with 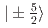 and
and 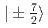 splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction
splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction 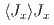 , the coupling of
, the coupling of 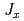 with quadrupole
with quadrupole 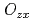 , and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The
, and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The  -electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment
-electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment 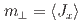 which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced
which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced 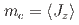 as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Pellemoine, F.*; Liu, Z.*; Lynch, K.*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165543_1 - 165543_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of displacements per atom is widely used as an indicator of irradiation damage to materials in proton accelerator facilities. Experiments have been carried out on protons below 3 GeV to verify the dpa of metallic materials. However, the dpa for high-energy protons above 3 GeV has not been measured. In order to validate the displacement cross sections of metals in the high-energy region, the electrical resistivity changes of aluminium, copper and tungsten wires at a temperature of 8 K were measured using protons with energy of 120 GeV. The results show that the conventional irradiation damage model of PHITS overestimates the experimental data. On the other hand, the calculation results using the athermal recombination correction model were in agreement with the experimental data.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.05001_1 - 05001_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and the spallation neutron source, it is crucial to evaluate the damage of beam-interception materials and accelerator components, such as a magnet coil. The displacement per atom (dpa) is used as a damage index, which is derived by integrating the particle flux and the displacement cross section based on the NRT model. Although the dpa is employed as the standard, the experimental data of displacement cross section are scarce for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV. To obtain the data for superconducting materials for high-intensity accelerators and magnets, the displacement cross section of Nb for proton irradiation with a kinetic energy range between 0.4 and 3 GeV was measured. For sustaining damage in the sample, the Nb sample was cooled at a cryogenic temperature ( 8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:213 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ni and
Ni and  Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV
Zr at 0.4, 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeVTakeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, p.17 - 27, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Instruments & Instrumentation)To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems and so on, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations, JENDL/HE-2007 and so on.
 Al
Al and Nd
and Nd Pd
Pd Ge
Ge
Metoki, Naoto; Shibata, Kaoru; Matsuura, Masato*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Hagihara, Masato; Frontzek, M. D.*; Matsuda, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054710_1 - 054710_6, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hyperfine splitting of Nd nuclei in NdPd Al
Al has been studied by means of high-resolution neutron spectroscopy. We observed inelastic peaks at
has been studied by means of high-resolution neutron spectroscopy. We observed inelastic peaks at 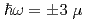 eV coming from the hyperfine splitting in the magnetically ordered phase due to the hyperfine interactions between Nd nuclei (
eV coming from the hyperfine splitting in the magnetically ordered phase due to the hyperfine interactions between Nd nuclei ( =7/2) and the 4
=7/2) and the 4 electrons with
electrons with 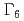 ground state composed of mainly
ground state composed of mainly 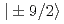 . At very low temperatures, nuclear spin of Nd is polarized with increasing occupation probability of low energy levels and contributes to the enhancement of the antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities: the elastic non-spin-flip channel is dominant. As an application of this phenomenon, we determined the Nd moment and hyperfine splitting from the temperature dependence of an antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities for Nd
. At very low temperatures, nuclear spin of Nd is polarized with increasing occupation probability of low energy levels and contributes to the enhancement of the antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities: the elastic non-spin-flip channel is dominant. As an application of this phenomenon, we determined the Nd moment and hyperfine splitting from the temperature dependence of an antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities for Nd Pd
Pd Ge
Ge .
.
Nakano, Keita; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-014, 25 Pages, 2022/03
For the development of accelerator-driven transmutation system (ADS), measurement of nuclide production cross-sections in proton-induced reactions on  Be, C,
Be, C,  Al,
Al,  Sc, and V have been performed. The measured data are compared with the calculations by the latest nuclear reaction models and with the nuclear data library to investigate the reproducibilities.
Sc, and V have been performed. The measured data are compared with the calculations by the latest nuclear reaction models and with the nuclear data library to investigate the reproducibilities.
 Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protons
Lu target irradiated with 0.4-, 1.3-, 2.2-, and 3.0-GeV protonsTakeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.207 - 212, 2022/03
Prediction of nuclide production of spallation products by high-energy proton injection plays a fundamental and important role in shielding design of high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS). Since the prediction accuracy of the nuclear reaction models used in the production quantity prediction simulation is insufficient, it is necessary to improve the nuclear reaction models. We have measured nuclide production cross sections for various target materials with the aim of acquiring experimental data and improving nuclear reaction models. In this study, 1.3-, 2.2- and 3.0-GeV proton beams were irradiated to  Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Lu target, and nuclide production cross-section data were acquired by the activation method. The measured data were compared with several nuclear reaction models used in Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes to grasp the current prediction accuracy and to study how the nuclear reaction model could be improved.
Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.30 - 41, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:67.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nuclide production cross sections for proton-induced reactions on Mn and Co at incident energies of 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV were measured by the activation method at the J-PARC. In total, 143 production cross sections of reaction products were obtained. Among them, the cross sections of  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) S and
S and  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki
Isotope News, (774), p.27 - 31, 2021/04
no abstracts in English
Takeshita, Hayato; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011045_1 - 011045_6, 2021/03
To improve accuracy of nuclear design of accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems, nuclide production cross sections on Ni and Zr, which were candidate materials to be used in ADS, were measured for GeV energy protons. The measured results were compared with PHITS calculations and JENDL/HE-2007.
 Fe for 0.4-3.0 GeV protons in J-PARC
Fe for 0.4-3.0 GeV protons in J-PARCMatsuda, Hiroki; Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011047_1 - 011047_6, 2021/03
Accurate nuclide production cross-section data are required for the design of Accelerator-Driven nuclear transmutation System (ADS) such as the design of radioactive waste disposal, design of remote-handling procedure of highly activated components, and evaluation of exposure doses of rad-workers. Although much efforts have been devoted to nuclide production cross-section measurements so far, uncertainties of the measured data are sometimes large as several tens percentage, and there is no experimental data in the GeV energy region even for some of important nuclides. In this study, proton induced nuclide production cross-section of iron, which is the most important constituent element of steel, was measured. The present experiment was compared with calculations by the PHITS code with several physics models including Bertini and INCL4.6 and evaluated nuclear data JENDL-HE/2007. The most significant discrepancy found in this study was the production cross sections via the (p,xn) reaction. It was suggested that further improvements, such as the in-medium effect on the nucleon-nucleon scattering and the Pauli blocking, were required in the intra-nuclear cascade models used in this study.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011050_1 - 011050_6, 2021/03
R&D of the beam window is crucial in the ADS, which serves as a partition between the accelerator and the target region. Although the displacement per atom (DPA) is used to evaluate the damage on the window, experimental data on the displacement cross section is scarce in the energy region above 20 MeV. We started to measure the displacement cross section for the protons in the energy region between 0.4 to 3 GeV. The displacement cross section can be derived by resistivity change divided by the proton flux and the resistivity change per Frankel pair on cryo-cooled sample to maintain damage. Experiments were conducted at the 3 GeV proton synchrotron at the J-PARC Center, and aluminum and copper was used as samples. As a result of comparison between the present experiment and the calculation of the NRT model, which is widely used for calculation of the displacement cross section, it was found that the calculation of the NRT model overestimated the experiment by about 3 times.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Shima, Tatsushi*
Materials Science Forum, 1024, p.95 - 101, 2021/03
To predict the lifetime of target materials in high-energy radiation environments at spallation neutron sources, radiation transport codes such as PHITS are used to calculate the displacements per atom (DPA) value. In this work, to validate calculated DPA values of tungsten, we implemented 0.25-mm-diameter wire sample of tungsten in a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler and measured the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the displacement cross section using 389-MeV protons at 10 K. As well as our previous results for aluminum and copper, calculated results with defect production efficiencies provided good agreements with experimental data. Based on measurements of recovery of the defects through annealing, about 85% of the damage remained at 60 K, and the same tendency is observed in other experimental result for reactor neutron irradiation.
 for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protons
for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protonsMatsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 483, p.33 - 40, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)A thick target neutron yield for a mercury target at an angle of 180 from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(10), p.1141 - 1151, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:81.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)To estimate the structural damages of materials in accelerator facilities, displacement per atom (dpa) is widely employed as a damage index, calculated based on the displacement cross-section obtained using a calculation model. Although dpa is applied as standard, the experimental data of the displacement cross-section for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV are scarce. Among the calculation models, difference of about factor 8 exist, so that the experimental data of the cross-section are crucial to validate the model. To obtain the displacement cross-section, we conducted experiments at J-PARC. The displacement cross-section of copper and iron was successfully obtained for a proton projectile with the kinetic energies, 0.4 - 3 GeV. The results were compared with those obtained using the widely utilized Norgertt-Robinson-Torrens (NRT) model and the athermal-recombination-corrected (arc) model based on molecular dynamics. It was found that the NRT model overestimates the present displacement cross-section by 3.5 times. The calculation results obtained using with the arc model based on the Nordlund parameter show remarkable agreement with the experimental data. It can be concluded that the arc model must be employed for the dpa calculation for the damage estimation of copper and iron.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06004_1 - 06004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:65.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the Accelerator-Driven nuclear transmutation System (ADS), nuclide production yield estimation in the lead-bismuth target is important to manage the target. However, experimental data of nuclide production yield by spallation and high-energy fission reactions are scarce. In order to obtain the experimental data, we experimented in J-PARC using  Pb and
Pb and  Bi samples. The samples were irradiated with protons at various kinematic energy points between 0.4 and 3.0 GeV. After the irradiation, the nuclide production cross section over
Bi samples. The samples were irradiated with protons at various kinematic energy points between 0.4 and 3.0 GeV. After the irradiation, the nuclide production cross section over  Be to
Be to 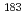 Re was obtained by spectroscopic measurement of decay gamma-rays from the samples with HPGe detectors. The present experimental results were compared with the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007) and the calculation with the PHITS code and the INCL++ code. The present experiment data showed consistency with other experimental data with better accuracy than other ones. In reactions to produce light nuclides, JENDL and calculation with the PHITS and INCL++ for
Re was obtained by spectroscopic measurement of decay gamma-rays from the samples with HPGe detectors. The present experimental results were compared with the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007) and the calculation with the PHITS code and the INCL++ code. The present experiment data showed consistency with other experimental data with better accuracy than other ones. In reactions to produce light nuclides, JENDL and calculation with the PHITS and INCL++ for 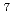 Be production agreed with the data.
Be production agreed with the data.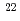 Na production, however, underestimated about 1/10 times. For middle to heavy nuclide productions cases, both calculations agreed with the experiment by a factor of two. JENDL showed lower energy having a maximum value of excitation function maximal value than the experimental data.
Na production, however, underestimated about 1/10 times. For middle to heavy nuclide productions cases, both calculations agreed with the experiment by a factor of two. JENDL showed lower energy having a maximum value of excitation function maximal value than the experimental data.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06006_1 - 06006_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)R&D of the beam window is crucial in the ADS, which serves as a partition between the accelerator and the target region. Although the displacement per atom (DPA) is used to evaluate the damage on the window, experimental data on the displacement cross section is scarce in the energy region above 20 MeV. We started to measure the displacement cross section for the protons in the energy region between 0.4 to 3 GeV. The displacement cross section can be derived by resistivity change divided by the proton flux and the resistivity change per Frankel pair on cryo-cooled sample to maintain damage. Experiments were conducted at the 3 GeV proton synchrotron at the J-PARC Center, and copper was used as samples. As a result of comparison between the present experiment and the calculation of the NRT model, which is widely used for calculation of the displacement cross section, it was found that the calculation of the NRT model overestimated the experiment by about 3 times.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06001_1 - 06001_6, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:65.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 -electron state of the heavy fermion superconductor NpPd
-electron state of the heavy fermion superconductor NpPd Al
Al and the isostructural family
and the isostructural familyMetoki, Naoto; Aczel, A. A.*; Aoki, Dai*; Chi, S.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Griveau, J.-C.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Hong, T.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011123_1 - 011123_6, 2020/03
Rare earths (4 ) and actinides (5
) and actinides (5 ) provide variety of interesting states realized with competing interactions between the increasing number of
) provide variety of interesting states realized with competing interactions between the increasing number of  electrons. Since crystal field splitting of many-body
electrons. Since crystal field splitting of many-body  electron system is smaller than the bandwidth, (1) high resolution experiments are needed, (2) essentially no clear spectrum with well defined peaks is expected in itinerant Ce and U compounds, and (3) Np and Pu is strictly regulated. Therefore, systematic research on magnetic excitations by neutron scattering experiments of localized compounds and rare earth iso-structural reference is useful. We describe the
electron system is smaller than the bandwidth, (1) high resolution experiments are needed, (2) essentially no clear spectrum with well defined peaks is expected in itinerant Ce and U compounds, and (3) Np and Pu is strictly regulated. Therefore, systematic research on magnetic excitations by neutron scattering experiments of localized compounds and rare earth iso-structural reference is useful. We describe the  electron states of heavy electron compounds NpPd
electron states of heavy electron compounds NpPd Al
Al and actinide and rare earth based iso-structural family.
and actinide and rare earth based iso-structural family.