Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimer
with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimerMetoki, Naoto; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Hagihara, Masato; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko*; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuda, Masaaki*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104424_1 - 104424_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering experiments were carried out to understand the unusual successive order in NdB with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with
with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with 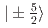 and
and 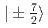 splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction
splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction 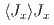 , the coupling of
, the coupling of 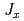 with quadrupole
with quadrupole 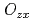 , and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The
, and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The  -electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment
-electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment 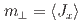 which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced
which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced 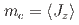 as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
Maeda, Mizuho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kimura, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.024707_1 - 024707_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Lee, S.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Higemoto, Wataru; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 95, p.292 - 299, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.55(Chemistry, Physical)Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were conducted on Al-0.06%Mn, Al-0.06%Cr, Al-0.02%Fe, and Al-0.02%Ni alloys (at.%) across the temperature ranging from 5 to 300 K. The temperature-dependent variations of the dipole field widths ( ) elucidated four distinct peaks for the prepared alloys. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed
) elucidated four distinct peaks for the prepared alloys. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks below 200 K were meticulously characterized utilizing first-principles calculations for the trapping energies of hydrogen in proximity to a solute and solute-vacancy pair. This comprehensive analysis facilitated the establishment of a linear correlation between the muon
peaks below 200 K were meticulously characterized utilizing first-principles calculations for the trapping energies of hydrogen in proximity to a solute and solute-vacancy pair. This comprehensive analysis facilitated the establishment of a linear correlation between the muon  peak temperature and the hydrogen trapping energy. However, significant deviations from this linear relationship were observed for the fourth
peak temperature and the hydrogen trapping energy. However, significant deviations from this linear relationship were observed for the fourth  peaks above 200 K in Al-Mn, Al-Cr, Al-Fe, and Al-Ni alloys. This discrepancy can be interpreted by considering the disparate distribution functions of muon and hydrogen within the tetrahedral site, wherein two of the four Al atoms are substituted by the solute element and vacancy (solute-vacancy pair).
peaks above 200 K in Al-Mn, Al-Cr, Al-Fe, and Al-Ni alloys. This discrepancy can be interpreted by considering the disparate distribution functions of muon and hydrogen within the tetrahedral site, wherein two of the four Al atoms are substituted by the solute element and vacancy (solute-vacancy pair).
 -phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys during aging treatment
-phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys during aging treatmentAhmed, A.*; Uttarasak, K.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 988, p.174234_1 - 174234_9, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:95.29(Chemistry, Physical)This study aims to clarify the growth process of the -phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys from the point of view of morphology evolution. For this research, the
-phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys from the point of view of morphology evolution. For this research, the  -phase orientation relationship, shape, growth process, misfit value, and interfacial condition between the
-phase orientation relationship, shape, growth process, misfit value, and interfacial condition between the  -phase and Al matrix were investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), focus ion beam (FIB), and optical microscope (OM). Results include the identification of {111}
-phase and Al matrix were investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), focus ion beam (FIB), and optical microscope (OM). Results include the identification of {111}  facets at the edges of the
facets at the edges of the  -phase, as well as the proposal of two new three-dimensional shapes for the
-phase, as well as the proposal of two new three-dimensional shapes for the  -phase. We purposed the morphology evolution during the growth process of Mg
-phase. We purposed the morphology evolution during the growth process of Mg Si crystal and calculated the misfit to understand the unstable (111)
Si crystal and calculated the misfit to understand the unstable (111) facet has a higher misfit value as compared to the (001)
facet has a higher misfit value as compared to the (001) and (011)
and (011) facets. Our observations provide how they influence the behavior of Mg
facets. Our observations provide how they influence the behavior of Mg Si crystals.
Si crystals.
 Mn
MnShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 245, p.116051_1 - 116051_6, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.76(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Hydrogen at the mass ppm level causes hydrogen embrittlement in metallic materials, but it is extremely difficult to experimentally elucidate the hydrogen trapping sites. We have taken advantage of the fact that positive muons can act as light isotopes of hydrogen to study the trapping state of hydrogen in matter. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments and the density functional theory (DFT) calculations for hydrogen trapping energy are carried out for Al Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al
Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width (
Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width ( ) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed
) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed  change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Tada, Kenichi; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.14001_1 - 14001_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iyota, Muneyoshi*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Sano, Tomokazu*; Shigeta, Masaya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yumoto, Hirokatsu*; Koyama, Takahisa*; Yamazaki, Hiroshi*; Semba, Yasunori*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; et al.
Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 94, p.424 - 434, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:69.06(Engineering, Manufacturing)Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:213 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Suyama, Kazuya*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Raymond, S.*; Steffens, P.*; Yamada, Akira*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kawasaki, Ikuto; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter
clusters in dilute neutron-rich matterTanaka, Junki*; Yang, Z.*; Typel, S.*; Adachi, Satoshi*; Bai, S.*; van Beek, P.*; Beaumel, D.*; Fujikawa, Yuki*; Han, J.*; Heil, S.*; et al.
Science, 371(6526), p.260 - 264, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.30(Multidisciplinary Sciences)By employing quasi-free  -cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of
-cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of  clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between
clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between  -cluster formation and the neutron skin.
-cluster formation and the neutron skin.
Toda, Hiroyuki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*
Kagaku, 75(10), p.48 - 53, 2020/10
Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminum alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
 Si and Al
Si and Al FeCu
FeCu intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculations
intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculationsYamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Materials Transactions, 61(10), p.1907 - 1911, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:72.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Materials Science and Technology, 36(15), p.1621 - 1627, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:53.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable phases in aluminum alloys are the primary nano-scale precipitates which have the biggest contribution to the increase in the tangible mechanical properties. The continuous increase in hardness in the 7xxx aluminum alloys is associated with the phase transformation from clusters or GP-zones to the metastable  phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of
phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of  phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
Nakashima, Nobuaki*; Yatsuhashi, Tomoyuki*; Sakota, Kenji*; Iwakura, Izumi*; Hashimoto, Sena*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Matsuda, Shohei
Chemical Physics Letters, 752, p.137570_1 - 137570_5, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.04(Chemistry, Physical)Photo-redox reactions between Eu and Eu
and Eu ions are induced by laser irradiation in alcoholic solution. Efficiency, wavelength dependence, and laser-power dependence are investigated with three different lasers. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 308 nm is found to cause one-photon redox reactions with a quantum yield around 0.5. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 394 nm induces two-photon reduction of Eu
ions are induced by laser irradiation in alcoholic solution. Efficiency, wavelength dependence, and laser-power dependence are investigated with three different lasers. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 308 nm is found to cause one-photon redox reactions with a quantum yield around 0.5. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 394 nm induces two-photon reduction of Eu to form Eu
to form Eu . When the pulse energy is 5 mJ, the quantum yield is measured to be 0.015. Although the quantum yield is one order of magnitude lower than that of the one photon reduction, reduction phenomena can be easily observed under the moderate laser field strength. Because of the two-photon nature, there should be a room to improve the efficiency by increasing the laser field strength.
. When the pulse energy is 5 mJ, the quantum yield is measured to be 0.015. Although the quantum yield is one order of magnitude lower than that of the one photon reduction, reduction phenomena can be easily observed under the moderate laser field strength. Because of the two-photon nature, there should be a room to improve the efficiency by increasing the laser field strength.
 =0 long-range magnetic order in centennialite CaCu
=0 long-range magnetic order in centennialite CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O; A Spin-
O; A Spin- perfect kagome antiferromagnet with
perfect kagome antiferromagnet with 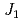 -
-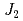 -
-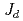
Iida, Kazuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Jeschke, H. O.*; Iqbal, Y.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Munakata, Koji*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Murai, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(22), p.220408_1 - 220408_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:79.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crystal and magnetic structures of the mineral centennialite CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O are investigated by means of synchrotron X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction measurements complemented by density functional theory (DFT) and pseudofermion functional renormalization group (PFFRG) calculations. In CaCu
O are investigated by means of synchrotron X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction measurements complemented by density functional theory (DFT) and pseudofermion functional renormalization group (PFFRG) calculations. In CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O, Cu
O, Cu ions form a geometrically perfect kagome network with antiferromagnetic
ions form a geometrically perfect kagome network with antiferromagnetic 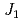 . No intersite disorder between Cu
. No intersite disorder between Cu and Ca
and Ca ions is detected. CaCu
ions is detected. CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O enters a magnetic long-range ordered state below
O enters a magnetic long-range ordered state below  = 7.2 K, and the
= 7.2 K, and the  =0 magnetic structure with negative vector spin chirality is obtained. The ordered moment at 0.3 K is suppressed to 0.58(2)
=0 magnetic structure with negative vector spin chirality is obtained. The ordered moment at 0.3 K is suppressed to 0.58(2) B. Our DFT calculations indicate the presence of antiferromagnetic
B. Our DFT calculations indicate the presence of antiferromagnetic 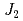 and ferromagnetic
and ferromagnetic 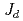 superexchange couplings of a strength which places the system at the crossroads of three magnetic orders (at the classical level) and a spin-
superexchange couplings of a strength which places the system at the crossroads of three magnetic orders (at the classical level) and a spin- PFFRG analysis shows a dominance of
PFFRG analysis shows a dominance of  =0 type magnetic correlations, consistent with and indicating proximity to the observed
=0 type magnetic correlations, consistent with and indicating proximity to the observed  =0 spin structure. The results suggest that this material is located close to a quantum critical point and is a good realization of a
=0 spin structure. The results suggest that this material is located close to a quantum critical point and is a good realization of a 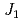 -
-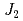 -
-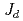 kagome antiferromagnet.
kagome antiferromagnet.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Ebihara, Kenichi; Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.1998_1 - 1998_8, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:88.90(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Age-hardening has been one and only process to achieve high strength aluminum alloys since unlike iron and titanium, pure aluminum does not have other solid phases during heat treatment. Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminium alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Materials Characterization, 158, p.109958_1 - 109958_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:88.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of precipitates in Al-Zn-Mg alloys, using a combination of electron diffraction, bright field transmission electron microscopy and atomic scale scanning transmission electron microscopy imaging revealed the presence of an unreported 
 orientation relationship between the
orientation relationship between the  -MgZn
-MgZn phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
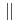 (120)
(120)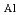 and (
and (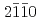 )
)
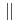 (001)
(001)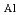 , plate on (120)
, plate on (120)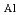 . The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90
. The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90 to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
Kokabu, Hiroki*; Yoon, S.*; Lee, H.*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Toulemonde, M.*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 460, p.34 - 37, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Matsuda, Kenji*; Yasumoto, Toru*; Bendo, A.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Marioara, C. D.*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 60(8), p.1688 - 1696, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:66.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English