Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
西村 昇一郎*; 鳥居 寛之*; 深尾 祥紀*; 伊藤 孝; 岩崎 雅彦*; 神田 聡太郎*; 川越 清以*; Kawall, D.*; 河村 成肇*; 黒澤 宣之*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:83.13(Optics)As a method to determine the resonance frequency, Rabi-oscillation spectroscopy has been developed. In contrast to conventional spectroscopy which draws the resonance curve, Rabi-oscillation spectroscopy fits the time evolution of the Rabi oscillation. By selecting the optimized frequency, it is shown that the precision is twice as good as conventional spectroscopy with a frequency sweep. Furthermore, the data under different conditions can be treated in a unified manner, allowing more efficient measurements for systems consisting of a limited number of short-lived particles produced by accelerators such as muons. We have developed a fitting function that takes into account the spatial distribution of muonium and the spatial distribution of the microwave intensity to apply this method to ground-state muonium hyperfine structure measurements at zero field. It was applied to the actual measurement data, and the resonance frequencies were determined under various conditions. The result of our analysis gives  = 4 463 301.61
= 4 463 301.61  0.71 kHz.
0.71 kHz.
Strasser, P.*; 阿部 充志*; 青木 正治*; Choi, S.*; 深尾 祥紀*; 東 芳隆*; 樋口 嵩*; 飯沼 裕美*; 池戸 豊*; 石田 勝彦*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:99.06(Quantum Science & Technology)High precision measurements of the ground state hyperfine structure (HFS) of muonium is a stringent tool for testing bound-state quantum electrodynamics (QED) theory, determining fundamental constants of the muon magnetic moment and mass, and searches for new physics. Muonium is the most suitable system to test QED because both theoretical and experimental values can be precisely determined. Previous measurements were performed decades ago at LAMPF with uncertainties mostly dominated by statistical errors. At the J-PARC Muon Science Facility (MUSE), the MuSEUM collaboration is planning complementary measurements of muonium HFS both at zero and high magnetic field. The new high-intensity muon beam that will soon be available at H-Line will provide an opportunity to improve the precision of these measurements by one order of magnitude. An overview of the different aspects of these new muonium HFS measurements, the current status of the preparation for high-field measurements, and the latest results at zero field are presented.
上野 恭裕*; 青木 正治*; 深尾 祥紀*; 東 芳隆*; 樋口 嵩*; 飯沼 裕美*; 池戸 豊*; 石田 勝彦*; 伊藤 孝; 岩崎 雅彦*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:86.59(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)MuSEUM is an international collaboration aiming at a new precise measurement of the muonium hyperfine structure at J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex). Utilizing its intense pulsed muon beam, we expect a ten-fold improvement for both measurements at high magnetic field and zero magnetic field. We have developed a sophisticated monitoring system, including a beam profile monitor to measure the 3D distribution of muonium atoms to suppress the systematic uncertainty.
Strasser, P.*; 青木 正治*; 深尾 祥紀*; 東 芳隆*; 樋口 嵩*; 飯沼 裕美*; 池戸 豊*; 石田 勝彦*; 伊藤 孝; 岩崎 雅彦*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:90.97(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)At the Muon Science Facility (MUSE) of J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), the MuSEUM collaboration is planning new measurements of the ground state hyperfine structure (HFS) of muonium both at zero field and at high magnetic field. The previous measurements were performed both at LAMPF (Los Alamos Meson Physics Facility) with experimental uncertainties mostly dominated by statistical errors. The new high intensity muon beam that will soon be available at MUSE H-Line will provide an opportunity to improve the precision of these measurements by one order of magnitude. An overview of the different aspects of these new muonium HFS measurements, the current status of the preparation, and the results of a first commissioning test experiment at zero field are presented.
伊藤 孝; 豊田 晃久*; 髭本 亘; 田島 美典*; 松田 恭幸*; 下村 浩一郎*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 754, p.1 - 9, 2014/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:48.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new muon beam profile monitor (MBPM) was developed to diagnose pulsed muon beams in J-PARC MUSE, mainly composed of a scintillation screen, a gated image intensifier (II), and a cooled CCD camera. The MBPM was designed to be compact so that it could be inserted into the bore of the  SR spectrometer in the D1 area and used concurrently. The spatial resolution of the MBPM was evaluated to be in the range from one to two line-pair/mm, depending on II gain. Such high-resolution muon beam profiles were obtained online for a positive muon beam with a kinetic energy of
SR spectrometer in the D1 area and used concurrently. The spatial resolution of the MBPM was evaluated to be in the range from one to two line-pair/mm, depending on II gain. Such high-resolution muon beam profiles were obtained online for a positive muon beam with a kinetic energy of  4 MeV. The contribution from decay positrons was significantly reduced owing to II gating. The linearity of the MBPM was evaluated on the bases of the number of decay positrons monitored by the
4 MeV. The contribution from decay positrons was significantly reduced owing to II gating. The linearity of the MBPM was evaluated on the bases of the number of decay positrons monitored by the  SR spectrometer. A linear response within five percent deviations was confirmed over more than two orders of magnitude. In addition, 3D imaging capability, use in vacuum, and immunity against moderate magnetic fields were demonstrated.
SR spectrometer. A linear response within five percent deviations was confirmed over more than two orders of magnitude. In addition, 3D imaging capability, use in vacuum, and immunity against moderate magnetic fields were demonstrated.
三宅 康博*; 下村 浩一郎*; 河村 成肇*; Strasser, P.*; 牧村 俊助*; 幸田 章宏*; 藤森 寛*; 中原 一隆*; 門野 良典*; 加藤 峯夫*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.957 - 961, 2009/04
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:47.84(Physics, Condensed Matter)ミュオン科学実験施設(MUSE)はJ-PARCの実験施設の一つである、MUSEは中性子とミュオン利用の実験施設である物質生命科学実験施設(MLF)の中にある。MLFの建屋建設は2004年にはじまり、2006年度末に完了した。われわれはそこにビームライン機器の設置を行っており、最初のミュオンビームが2008年の秋に発生する予定である。
三宅 康博*; 西山 樟生*; 河村 成肇*; 牧村 俊助*; Strasser, P.*; 下村 浩一郎*; Beveridge, J. L.*; 門野 良典*; 福地 光一*; 佐藤 伸彦*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.484 - 487, 2006/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:31.27(Physics, Condensed Matter)物質生命科学実験施設の建屋の建設は2004年度の初めに開始された。2008年に加速器とビーム輸送系のコミッショニングが行われた後、2009年にはミュオンのユーザー利用が開始される。この論文ではJ-PARCミュオン科学実験施設建設の現状について述べる。
三宅 康博*; 河村 成肇*; 牧村 俊助*; Strasser, P.*; 下村 浩一郎*; 西山 樟生*; Beveridge, J. L.*; 門野 良典*; 佐藤 伸彦*; 福地 光一*; et al.
Nuclear Physics B; Proceedings Supplements, 149, p.393 - 395, 2005/12
J-PARCミュオン施設は物質生命科学実験施設の中に位置する。中性子標的の手前に置かれたミュオン標的から得られるミュオンを用いた研究が行われる。このJ-PARCミュオン科学施設の概要を報告する。
 -forbidden transitions in
-forbidden transitions in  Os
Os静間 俊行; 松浦 勝之*; 藤 暢輔; 早川 岳人; 大島 真澄; 初川 雄一; 松田 誠; 古野 興平*; 佐々木 康之*; 小松原 哲朗*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 696(3-4), p.337 - 370, 2001/12
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:73.84(Physics, Nuclear) Osの高スピン状態を、170Er(18O,5n)反応を用いて生成した。その結果、5つの回転バンドを新たに観測し、gファクターから準粒子配位を決定した。また、励起状態 5000MeV程度に、2つの核異性体を観測した。その内の1つは、K量子数43/2を有し、基底状態回転帯(K=9/2)へ、K量子数の差17を伴う遷移をしていることが明らかになった。本論文では、量子力学的トンネリグ模型を用いて、この核異性体の崩壊機構を解明する。
Osの高スピン状態を、170Er(18O,5n)反応を用いて生成した。その結果、5つの回転バンドを新たに観測し、gファクターから準粒子配位を決定した。また、励起状態 5000MeV程度に、2つの核異性体を観測した。その内の1つは、K量子数43/2を有し、基底状態回転帯(K=9/2)へ、K量子数の差17を伴う遷移をしていることが明らかになった。本論文では、量子力学的トンネリグ模型を用いて、この核異性体の崩壊機構を解明する。
三井 光; 田中 隆一; 須永 博美; 金沢 孝夫; 田中 進; 春山 保幸; 上松 敬; 松田 純夫*; 野口 敬*; 田村 高志*; et al.
JAERI-M 89-085, 164 Pages, 1989/07
宇宙開発事業団が開発した宇宙用シリコン薄型太陽電池とGaAs太陽電池の耐放射線性について、原研と宇宙開発事業団は共同研究を実施した。この共同研究に関し、本報告では、先ず、人工衛星用太陽電池が遭遇する宇宙の放射線環境について述べる。次いで、共同研究に使用した太陽電池および実験方法について記述する。その後、電子線照射方法の検討結果について報告する。電子線照射方法の検討では、固定照射法(走査ビームによる静止試料の照射法)、移動照射法(走査ビームによる移動試料の照射法)、およびスポット照射法(無走査ビームによる静止試料の照射法)の3方法について検討した。その結果、固定照射法が宇宙用太陽電池の耐放射線性評価試験における最も妥当な電子線の照射方法であると結論した。さらに、この研究において、電子線照射による太陽電池の電気特性の変化に関する若干の知見を得た。
伊藤 孝; 豊田 晃久*; 髭本 亘; 田島 美典*; 松田 恭幸*; 下村 浩一郎*
no journal, ,
パルスミュオンビームを用いる実験では、大量のミュオンがその寿命よりも短い時間内に標的にやってくるため、ミュオン1個毎の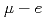 崩壊を識別することは不可能である。このため、標的外に止まったミュオンの崩壊イベントを識別してリジェクトするという、連続状ビームに対してよく用いられる方法は使えない。よって、パルスミュオンビームによる実験では、ビームを標的に対し効率よく照射することが求められる。これを実現するためには、標的周辺の詳細なビームプロファイルをオンラインで測定し、ビームチューニングにフィードバックする必要がある。このためのビームプロファイルモニタには、高空間分解能とリアルタイム性が要求される。我々は、J-PARCミュオン科学実験施設の
崩壊を識別することは不可能である。このため、標的外に止まったミュオンの崩壊イベントを識別してリジェクトするという、連続状ビームに対してよく用いられる方法は使えない。よって、パルスミュオンビームによる実験では、ビームを標的に対し効率よく照射することが求められる。これを実現するためには、標的周辺の詳細なビームプロファイルをオンラインで測定し、ビームチューニングにフィードバックする必要がある。このためのビームプロファイルモニタには、高空間分解能とリアルタイム性が要求される。我々は、J-PARCミュオン科学実験施設の SR分光器との共存を考慮して、新たにコンパクトなミュオンビームプロファイルモニタを開発した。ミュオンビームがシンチレータに入射した際に発生したシンチレーション光を撮像することによりビームプロファイルを得る。イメージインテンシファイアを用いて光学像を増強することにより、明瞭なビームプロファイルが数十秒という短時間で得られた。
SR分光器との共存を考慮して、新たにコンパクトなミュオンビームプロファイルモニタを開発した。ミュオンビームがシンチレータに入射した際に発生したシンチレーション光を撮像することによりビームプロファイルを得る。イメージインテンシファイアを用いて光学像を増強することにより、明瞭なビームプロファイルが数十秒という短時間で得られた。
伊藤 孝; 豊田 晃久*; 髭本 亘; 田島 美典*; 松田 恭幸*; 下村 浩一郎*
no journal, ,
パルスミュオンビームを用いる実験では、大量のミュオンがその寿命よりも短い時間内に標的にやってくるため、ミュオン1個毎の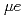 崩壊を識別することは不可能である。このため、標的外に止まったミュオンの崩壊イベントを識別してリジェクトするという、連続状ビームに対してよく用いられる方法は使えない。よって、パルスミュオンビームによる実験では、ビームを標的に対し効率よく照射することが求められる。これを実現するためには、標的周辺の詳細なビームプロファイルをオンラインで測定し、ビームチューニングにフィードバックする必要がある。このためのビームプロファイルモニタには、高空間分解能とリアルタイム性が要求される。我々は、J-PARCミュオン科学実験施設の
崩壊を識別することは不可能である。このため、標的外に止まったミュオンの崩壊イベントを識別してリジェクトするという、連続状ビームに対してよく用いられる方法は使えない。よって、パルスミュオンビームによる実験では、ビームを標的に対し効率よく照射することが求められる。これを実現するためには、標的周辺の詳細なビームプロファイルをオンラインで測定し、ビームチューニングにフィードバックする必要がある。このためのビームプロファイルモニタには、高空間分解能とリアルタイム性が要求される。我々は、J-PARCミュオン科学実験施設の SR分光器との共存を考慮して、新たにコンパクトなミュオンビームプロファイルモニタを開発した。このプロファイルモニタは、プラスチックシンチレータ、ゲートイメージインテンシファイア(ゲートII)、および冷却CCDカメラを主要コンポーネントとし、ミュオンビームがシンチレータに入射した際に発生したシンチレーション光を撮像することによりビームプロファイルを得る。ゲートIIによって光学像を増強することにより、明瞭なビームプロファイルが約20秒という短時間で得られた。
SR分光器との共存を考慮して、新たにコンパクトなミュオンビームプロファイルモニタを開発した。このプロファイルモニタは、プラスチックシンチレータ、ゲートイメージインテンシファイア(ゲートII)、および冷却CCDカメラを主要コンポーネントとし、ミュオンビームがシンチレータに入射した際に発生したシンチレーション光を撮像することによりビームプロファイルを得る。ゲートIIによって光学像を増強することにより、明瞭なビームプロファイルが約20秒という短時間で得られた。
松田 康裕*; 奥山 克史*; 小松 久憲*; 大木 彩子*; 橋本 直樹*; 佐野 英彦*; 山本 洋子*; 岩見 行晃*; 林 美加子*; 能町 正治*; et al.
no journal, ,
本研究では、フッ素による歯の脱灰抑制効果を調べるため、脱灰処理した歯質に充填したフッ化物含有材料からのフッ素の拡散を、マイクロPIGE/PIXEを用いて評価・検討した。試料は以下の3段階の手順で製作した。(1)う蝕のないヒト抜去歯のエナメル質最表層を除去し、頬側の歯冠部エナメル質に窩洞を形成した。(2)これを脱灰溶液中で72時間、37 Cで保管して、歯質表面を脱灰処理し、3種類のフッ素含有材料("フジIXエクストラ(GC)" (EX), "フジIX(GC)" (FN), "フジVII(GC)" (VII))をそれぞれに充填し、更に緩衝液中(pH7.5)で24時間、37
Cで保管して、歯質表面を脱灰処理し、3種類のフッ素含有材料("フジIXエクストラ(GC)" (EX), "フジIX(GC)" (FN), "フジVII(GC)" (VII))をそれぞれに充填し、更に緩衝液中(pH7.5)で24時間、37 Cで保管した。(3)この後、歯軸と平行にカットして厚さ約200
Cで保管した。(3)この後、歯軸と平行にカットして厚さ約200 mの試料を作製した。最表層および窩壁からのフッ素の分布を測定した結果、EX群では他と比較して歯質表層の最も深い領域までフッ素の分布が認められたが、窩洞壁では他と比較してフッ素の拡散が認められなかった。FN群では逆に窩洞壁においてフッ素の拡散が強く認められた。VII群では窩洞壁にのみフッ素の拡散が認められた。これらの結果は、フッ素の拡散に歯質へ直接拡散する経路と溶液に溶出してから歯質へ拡散する経路の2つあることを示しており、フッ素含有材料を使い分けることによって効果的なう蝕予防が可能になると考えられる。
mの試料を作製した。最表層および窩壁からのフッ素の分布を測定した結果、EX群では他と比較して歯質表層の最も深い領域までフッ素の分布が認められたが、窩洞壁では他と比較してフッ素の拡散が認められなかった。FN群では逆に窩洞壁においてフッ素の拡散が強く認められた。VII群では窩洞壁にのみフッ素の拡散が認められた。これらの結果は、フッ素の拡散に歯質へ直接拡散する経路と溶液に溶出してから歯質へ拡散する経路の2つあることを示しており、フッ素含有材料を使い分けることによって効果的なう蝕予防が可能になると考えられる。