Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Torii, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; Kanda, Sotaro*; Kawagoe, Kiyotomo*; Kawall, D.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kurosawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:82.75(Optics)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology)Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:87.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.49(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Ito, Takashi; Toyoda, Akihisa*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tajima, Minori*; Matsuda, Yasuyuki*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 754, p.1 - 9, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Kato, Mineo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.957 - 961, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:46.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)The muon science facility (MUSE) is one of the experimental areas of the J-PARC. The MUSE facility is located in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF), which is a building integrated to include both neutron and muon science programs. Construction of the MLF building was started at the beginning of 2004, and was recently completed at the end of the 2006 fiscal year. We have been working on the installation of the beamline components, expecting the first muon beam in the autumn of 2008.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Beveridge, J. L.*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Fukuchi, Koichi*; Sato, Nobuhiko*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.484 - 487, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.27(Physics, Condensed Matter)The construction of the Materials and Life Science building was started in the beginning of the fiscal year of 2004. After commissioning of the accelerator and beam transport sections in 2008, muon beams will be available for users in 2009. In this letter, the latest construction status of the J-PARC Muon Science Facility is reported.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Beveridge, J. L.*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Sato, Nobuhiko*; Fukuchi, Koichi*; et al.
Nuclear Physics B; Proceedings Supplements, 149, p.393 - 395, 2005/12
The J-PARC muon science experimental area is planned to be located in the integrated building of the facility for materials and life science study. One muon target will be installed upstream of the neutron target. The main feature of the facility is introduced.
 -forbidden transitions in
-forbidden transitions in 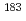 Os
OsShizuma, Toshiyuki; Matsuura, Katsuyuki*; Toh, Yosuke; Hayakawa, Takehito; Oshima, Masumi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Furuno, Kohei*; Sasaki, Yasuyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 696(3-4), p.337 - 370, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:73.35(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states in 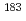 Os have been studied using the 170Er(18O,5n) reaction at a beam energy of 85 MeV. Nine rotational bands based on 1-, 3-, 5- and 7-quasiparticle excitations have been observed. Nilsson configurations are assigned for the newly observed bands using g-factors deduced from M1/E2 branching ratios within the bands. In addition, two isomers with K=(43/2+) and (43/2-) have been identified. The K=(43/2+) isomer decays directly to the K=9/2+ ground state band with a large difference in the
Os have been studied using the 170Er(18O,5n) reaction at a beam energy of 85 MeV. Nine rotational bands based on 1-, 3-, 5- and 7-quasiparticle excitations have been observed. Nilsson configurations are assigned for the newly observed bands using g-factors deduced from M1/E2 branching ratios within the bands. In addition, two isomers with K=(43/2+) and (43/2-) have been identified. The K=(43/2+) isomer decays directly to the K=9/2+ ground state band with a large difference in the  quantum number,
quantum number, 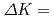 17. The decay rates are disccused in terms of a tunneling model where high-
17. The decay rates are disccused in terms of a tunneling model where high- (isomeric) and low-
(isomeric) and low- states interact via fluctuations towards triaxial nuclear shapes.
states interact via fluctuations towards triaxial nuclear shapes.
; Tanaka, Ryuichi; Sunaga, Hiromi; ; Tanaka, Susumu; Haruyama, Yasuyuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Matsuda, Sumio*; ; ; et al.
JAERI-M 89-085, 164 Pages, 1989/07
no abstracts in English
Ito, Takashi; Toyoda, Akihisa*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tajima, Minori*; Matsuda, Yasuyuki*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Okuyama, Katsushi*; Komatsu, Hisanori*; Oki, Saiko*; Hashimoto, Naoki*; Sano, Hidehiko*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Iwami, Yukiteru*; Hayashi, Mikako*; Nomachi, Masaharu*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Takashi; Toyoda, Akihisa*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tajima, Minori*; Matsuda, Yasuyuki*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
no journal, ,
A high-resolution beam imaging system was newly developed for pulsed muon beams in J-PARC MUSE using a plastic scintillator, a gated image intensifier, and a cooled CCD camera. The system was optimized for observation of 4 MeV muon beams and designed so as to be used with an existing muSR spectrometer in the D1 area, J-PARC MUSE. High-resolution beam profiles were obtained for a surface muon beam after exposure to the beam for several tens of seconds. A contribution from decay positrons was significantly suppressed by gating of the image ntensifier. Details of test experiments (negative muon beam profiles in the D2 area, 3D beam imaging, noise reduction, etc.) were presented.