Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Oketani, Kazuki*; Fujii, Hirokazu*; Zhao, Y.*; Kato, Masaji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya; Kono, Masanori*
Zairyo, 73(3), p.220 - 225, 2024/03
The fractures in the rock are the main pass of groundwater flow and solute transport. The filling of fine-grained particle, such as clay minerals, was confirmed to decrease the permeability of rock by laboratory experiment. This research aimed to verify the occurrence of the phenomena in the field. The water containing the clay minerals was injected into the rock at the 200m stage of the Mizunami Underground research laboratory. The hydraulic conductivity decreased two order before and after the injection. This result suggested that the decrease of hydraulic conductivity by the filling of fine-grained particle in the fractures occurred in the real field.
 and SrLaCuNbO
and SrLaCuNbO ; Spin-
; Spin- quasi-square-lattice
quasi-square-lattice 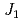 -
-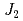 Heisenberg antiferromagnets
Heisenberg antiferromagnetsWatanabe, Masari*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Ueno, Wataru*; Matsui, Kazuki*; Goto, Takayuki*; Hagihara, Masato
Physical Review B, 105(5), p.054414_1 - 054414_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Co
CoLokotko, T.*; Leblond, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Poves, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Authelet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.01(Physics, Nuclear)The structures of the neutron-rich  Co isotopes were investigated via (
Co isotopes were investigated via ( ) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the
) knockout reactions at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory, RIKEN. Level schemes were reconstructed using the 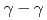 coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the
coincidence technique, with tentative spin-parity assignments based on the measured inclusive and exclusive cross sections. Comparison with shell-model calculations suggests coexistence of spherical and deformed shapes at low excitation energies in the  Co isotopes.
Co isotopes.
 Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,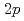 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
, 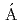 *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:71.31(Physics, Nuclear)The nuclear structure of the  Ni nucleus was investigated by (
Ni nucleus was investigated by ( ,
,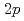 ) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt
) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt  rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by
rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by 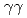 and
and 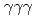 coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
 -Al(OH)
-Al(OH) ; Neutron diffraction measurements and ab initio calculations
; Neutron diffraction measurements and ab initio calculationsMatsui, Masanori*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ikeda, Emi*; Sano, Asami; Goto, Hirotada*; Yagi, Takehiko*
American Mineralogist, 96(5-6), p.854 - 859, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:41.81(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Neutron powder diffraction analyses of  -Al(OD)
-Al(OD) revealed that the crystals are orthorhombic with space group
revealed that the crystals are orthorhombic with space group  2
2 2
2 2
2 , but not
, but not  as reported previously by X-ray diffraction data. The initial lattice parameters and the atomic positions of both Al and O were taken from previous X-ray structural analyses for the
as reported previously by X-ray diffraction data. The initial lattice parameters and the atomic positions of both Al and O were taken from previous X-ray structural analyses for the  structure, while the H atom positions were determined using ab initio calculations. The
structure, while the H atom positions were determined using ab initio calculations. The  -Al(OH)
-Al(OH) structure possesses one relatively long and two short O-H...O hydrogen bonds. Ab initio calculations are also used to find that
structure possesses one relatively long and two short O-H...O hydrogen bonds. Ab initio calculations are also used to find that  -Al(OH)
-Al(OH) with space group
with space group  2
2 2
2 2
2 transforms to another high pressure polymorph with space group
transforms to another high pressure polymorph with space group  at around 67 GPa, and that the two short hydrogen bonds in
at around 67 GPa, and that the two short hydrogen bonds in  -Al(OH)
-Al(OH) become both symmetric through the transformation, in which the protons are located at the midpoints of the O...O hydrogen bonds.
become both symmetric through the transformation, in which the protons are located at the midpoints of the O...O hydrogen bonds.
Oketani, Kazuki*; Nara, Yoshitaka*; Matsui, Hiroya; Fujii, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
For the geological disposal of radioactive wastes, it is important to understand the long-term migration of radionuclides. The network of fractures and pores in a rock mass, which have a role as the pathway of the fluid flow of materials, may change due to sealing of a material in the long term. We measured changes in hydraulic conductivity of crystalline rock mass using water mixed with clays sampled from a fault in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This result indicates that permeability of in-situ rock mass is possible to decrease by fracture filling with a clay material in a fault.
 investigated by time-of-flight neutron diffraction in long-pulse magnetic fields
investigated by time-of-flight neutron diffraction in long-pulse magnetic fieldsWatanabe, Masao; Nakajima, Taro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Matsui, Kazuki*; Kanda, Tomoki*; Nomoto, Tetsuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Saito, Hiraku*; Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, due to advances in precision measurement technology in pulsed magnetic fields, a novel magnetic state was discovered in a strong magnetic field. We constructed a measurement environment that can comprehensively explore the reciprocal lattice space under magnetic fields up to 14 Tesla by combining the long-pulse magnetic field generated by the supercapacitor and pulsed neutrons at J-PARC. This equipment can generate a magnetic field that is sufficiently longer than the time width (about 10 milliseconds) of the multi-wavelength neutron pulse passing through the sample. This method was used to investigate the magnetic phase transition in the frustrated magnet CuFeO .
.