Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikawa, Akihisa; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Hirai, Yuta*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Radiological Physics and Technology, 17(2), p.553 - 560, 2024/06
Wang, Z.; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Duan, G.*; Matsunaga, Takuya*
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 414, p.116168_1 - 116168_49, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:89.36(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Furuta, Takuya; Koba, Yusuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Ishikawa, Akihisa*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(14), p.145002_1 - 145002_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:68.93(Engineering, Biomedical)Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. The Monte Carlo simulation is a good candidate for the tool to assess secondary cancer risk, including the contributions of secondary particles produced by nuclear reactions. We therefore developed a new dose reconstruction system implementing PHITS as the engine. In this system, the PHITS input is automatically created from the DICOM data sets recorded in the treatment planning. The developed system was validated by comparing to experimental dose distribution in water and treatment plan on an anthropomorphic phantom. This system will be used for retrospective studies using the patient data in National Institute for Quantum and Science and Technology.
Chang, W.*; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(5), p.846 - 855, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.45(Biology)With the aim of developing a revaluation tool of treatment plan in carbon-ion radiotherapy using Monte Carlo (MC) simulation, we propose two methods; one is dedicated to identify realistic-tissue materials from a CT image with satisfying the well-calibrated relationship between CT numbers and stopping power ratio (SPR) provided by TPS, and the other is to estimate dose to water considering the particle- and energy-dependent SPR between realistic tissue materials and water. We validated these proposed methods by computing depth dose distribution in homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms composed of human tissue materials and water irradiated by a 400 MeV/u carbon beam with 8 cm SOBP using a MC simulation code PHITS and comparing with results of conventional treatment planning system (TPS). Our result suggested that use of water as a surrogate of real tissue materials, which is adopted in conventional TPS, is inadequate for dose estimation from secondary particles because their production rates cannot be scaled by SPR of the primary particle in water. We therefore concluded that the proposed methods can play important roles in the reevaluation of the treatment plans in carbon-ion radiotherapy.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Omae, Kazuma*; Pham, A.*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harjo, S.; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.207 - 213, 2020/02
Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu
Journal of Supercomputing, 75(12), p.8115 - 8146, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.81(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)A communication-avoiding generalized minimum residual method (CA-GMRES) is implemented on a hybrid CPU-GPU cluster, targeted for the performance acceleration of iterative linear system solver in the gyrokinetic toroidal five-dimensional Eulerian code GT5D. In addition to the CA-GMRES, we implement and evaluate a modified variant of CA-GMRES (M-CA-GMRES) proposed in our previous study to reduce the amount of floating-point calculations. This study demonstrates that beneficial features of the CA-GMRES are in its minimum number of collective communications and its highly efficient calculations based on dense matrix-matrix operations. The performance evaluation is conducted on the Reedbush-L GPU cluster, which contains four NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs per compute node. The evaluation results show that the M-CA-GMRES is 1.09x, 1.22x and 1.50x faster than the CA-GMRES, the generalized conjugate residual method (GCR), and the GMRES, respectively, when 64 GPUs are used.
Nakata, Kotaro*; Hasegawa, Takuma*; Solomon, D. K.*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Tomioka, Yuichi*; Ota, Tomoko*; Matsumoto, Takuya*; Hama, Katsuhiro; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Ono, Masahiko*; et al.
Applied Geochemistry, 104, p.60 - 70, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Asahi, Yuichi*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 8th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA 2017), p.7_1 - 7_8, 2017/11
A communication-avoiding generalized minimal residual (CA-GMRES) method is applied to the gyrokinetic toroidal five dimensional Eulerian code GT5D, and its performance is compared against the original code with a generalized conjugate residual (GCR) method on the JAEA ICEX (Haswell), the Plasma Simulator (FX100), and the Oakforest-PACS (KNL). The CA-GMRES method has 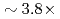 higher arithmetic intensity than the GCR method, and thus, is suitable for future Exa-scale architectures with limited memory and network bandwidths. In the performance evaluation, it is shown that compared with the GCR solver, its computing kernels are accelerated by
higher arithmetic intensity than the GCR method, and thus, is suitable for future Exa-scale architectures with limited memory and network bandwidths. In the performance evaluation, it is shown that compared with the GCR solver, its computing kernels are accelerated by 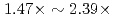 , and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from
, and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from 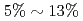 to
to 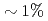 of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
 Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Goh, S. K.*; Kaneko, Koji; Tsutsui, Satoshi; Logg, P. W.*; Grosche, F. M.*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Imai, Masaki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 807(3), p.032002_1 - 032002_4, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:80.71(Physics, Condensed Matter)Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Sazaki, Gen*; Kikko, Tatsuhiko*; Fujiwara, Satoru; Ishikawa, Takuya*; Matsumoto, Osamu*; Morimoto, Yukio*
Crystal Growth & Design, 10(3), p.1090 - 1095, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:47.60(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We propose a technique for DNA crystallization using the thermal reversible process of DNA: a conversion between a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and two single-stranded DNAs (ssDNAs) with temperatures. We investigated the solubility of the crystals of a DNA hexamer d(CGCGCG) and their melting temperature, at which the thermal conversion occurs. The results obtained suggest that the conversion from a dsDNA to ssDNAs results in an increase in solubility. It was shown that using this temperature-controlled technique, high-grade single crystals of the DNA hexamer could be obtained from a small amount of DNA samples. This easy-to-apply technique would be superior to the conventional vapor diffusion technique in that it allows the solubility of DNA crystals to be controlled with no need for expensive setups.
 Si
Si
Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeda, Shugo; Galatanu, A.; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Yamada, Mineko*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hedo, Masato*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(5), p.1552 - 1556, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:72.98(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have succeeded in growing a high-quality single crystal of UCu Si
Si with the tetragonal structure by the Sn-flux method and measured the electrical resistivity, magnetic susceptibility, magnetization and specific heat. UCu
with the tetragonal structure by the Sn-flux method and measured the electrical resistivity, magnetic susceptibility, magnetization and specific heat. UCu Si
Si is found to order antiferromagnetically below
is found to order antiferromagnetically below  = 106 K, and follows a successive ferromagnetic ordering at
= 106 K, and follows a successive ferromagnetic ordering at  = 100 K. The magnetic properties are highly anisotropic, reflecting the crystal structure. An easy-axis of magnetization is found to be the [001] direction (
= 100 K. The magnetic properties are highly anisotropic, reflecting the crystal structure. An easy-axis of magnetization is found to be the [001] direction ( -axis) both in the antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic phases, while the [100] direction (
-axis) both in the antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic phases, while the [100] direction ( -axis) corresponds to the hard-axis in magnetization. The magnetization curve in the antiferromagnetic phase indicates a clear metamagnetic transition at a low field of about 1 kOe and changes smoothly into a ferromagnetic magnetization curve below
-axis) corresponds to the hard-axis in magnetization. The magnetization curve in the antiferromagnetic phase indicates a clear metamagnetic transition at a low field of about 1 kOe and changes smoothly into a ferromagnetic magnetization curve below  = 100 K. The saturation moment is determined as 1.75
= 100 K. The saturation moment is determined as 1.75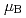 /U at 2 K. The electronic specific heat coefficient is also determined as 20 mJ/K
/U at 2 K. The electronic specific heat coefficient is also determined as 20 mJ/K
 mol.
mol.
 Ni
Ni Al
Al
Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Ikeda, Shugo; Galatanu, A.; Matsumoto, Takuya*; Sugimoto, Toyonari*; Tada, Toshiji*; Noguchi, Satoru*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 359-361, p.1006 - 1008, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.30(Physics, Condensed Matter)A new ternary uranium-based intermetallic compound U Ni
Ni Al
Al has been symthesized. It crystallizes in the unique flat orthorhombic structure. Uranium atoms occupy two crystallographic 4
has been symthesized. It crystallizes in the unique flat orthorhombic structure. Uranium atoms occupy two crystallographic 4 and 8
and 8 sites where local chemical environments are quite similar. The temperature dependence of the magnetic susceptibility
sites where local chemical environments are quite similar. The temperature dependence of the magnetic susceptibility 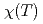 demonstrates peculiar magnetic anisotropy;
demonstrates peculiar magnetic anisotropy; 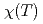 along
along  - and
- and  -axes obeys the Curie-Weiss law above 23 K, while
-axes obeys the Curie-Weiss law above 23 K, while 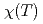 along
along  -axis is small and temperature independent. At 23 K, only
-axis is small and temperature independent. At 23 K, only 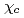 shows a sharp cusp corresponding to the antiferromagnetic ordering, while
shows a sharp cusp corresponding to the antiferromagnetic ordering, while 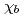 remains paramagnetic behavior down to 2 K. These results and crystallographical considerations lead to a conclusion that only uranium atoms at the 8
remains paramagnetic behavior down to 2 K. These results and crystallographical considerations lead to a conclusion that only uranium atoms at the 8 site order antiferromagnetically at
site order antiferromagnetically at  = 23 K, while uranium atoms at the
= 23 K, while uranium atoms at the 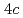 site do not order down to 50 mK.
site do not order down to 50 mK.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Matsumoto, Nobuko*; Yamagishi, Nobuhiro*; Arakawa, Takuya*; Kuraishi, Hideaki*
JAERI-Data/Code 2004-013, 163 Pages, 2005/02
The Center for Promotion of Computational Science and Engineering of the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute has carried out the ITBL (Information-Technology Based Laboratory) project which is one of e-Japan priority policy programs. AVS/ITBL is the visualization tool which has been developed aiming at realizing the efficient visualization in the ITBL environment. This visualization tool is one of the tools of ITBL infrastructure software and operates in cooperation with AVS/Express. In this paper, utilization of AVS/ITBL to the numerical environmental system, which is one of the applications in ITBL project, is presented. And the outline of the operation in this utilization is indicated.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Matsumoto, Nobuko*; Yamagishi, Nobuhiro*; Higuchi, Kenji; Otani, Takayuki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Furuno, Akiko; Chino, Masamichi; Kobayashi, Takuya
Computational Science - ICCS 2003, International Conference Saint Petersburg Russian Federation, Melbourne Australia, June 2-4, 2003 Proceedings, p.120 - 129, 2003/00
Information-Technology Based Laboratory (ITBL) project has been propelled as one of e-Japan priority policy programs. The purposes of the project are to share intellectual resources such as remote computers, programs and data in universities and institutes and to support cooperative studies among researchers, building a virtual research environment, ITBL. Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has been working on installation and management of hardware and development of infrastructure software and applications. As application software, researches on quantum bioinformatics and environmental sciences are carried out. This paper presents utilization of ITBL system infra-structure software for 'Numerical Environment System' which is developed for environmental studies. More effective job executions and visualization are ex-pected by using Task Mapping Editor (TME) and AVS/ITBL, which are tools developed as infrastructure software.
Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu
no journal, ,
Communication avoiding (CA) Krylov methods are promising solutions for communication bottlenecks on supercomputers based on many core processors or accelerators. In this work, we implemented the CA-GMRES method on a GPU cluster, the HA-PACS, and evaluated its performance on a non-symmetric matrix solver from a nuclear CFD code. The result shows that the CA-GMRES method is significantly faster than the conventional Krylov methods such as the GMRES method and the GCR method.
 Ir
Ir Sn
Sn
Kaneko, Koji; Matsuda, Masaaki*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Goh, S. K.*; Matsumoto, Takuya*; Imai, Masaki*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oikawa, Kenichi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Pham, A.*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harjo, S.; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
no journal, ,
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Sagisaka, Akito*; et al.
no journal, ,
We present the extension of the maximum energy of protons from the interaction between the short-pulse compact laser system and solid thin-foil target. The laser pulses with parameters of 800 nm in wavelength, 40 fs of pulse width, 7 J of energy, 10 contrast are focused onto the target with the peak intensity of more than 10
contrast are focused onto the target with the peak intensity of more than 10 Wcm
Wcm , which is also well confirmed by the measured electron temperature of 16 MeV. We report about the acceleration mechanism as well as future prospect on the proton acceleration experiment at JAEA.
, which is also well confirmed by the measured electron temperature of 16 MeV. We report about the acceleration mechanism as well as future prospect on the proton acceleration experiment at JAEA.
 oxidation of H-terminated Si(110) surface
oxidation of H-terminated Si(110) surfaceNakano, Takuya*; Togashi, Hideaki*; Matsumoto, Mitsutaka*; Yamamoto, Yoshihisa*; Suzuki, Yasushi*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suemitsu, Maki*
no journal, ,
Time evolution of oxide layers in the H-terminated Si(110) surface by the UV/O treatment at room temperature was observed by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Special oxidation mechanisms for the H-terminated Si(110) surface were found. Si(110) surfaces were hydrogenated by HF treatments. The surface was irradiated and oxidized by UV light (253.7, 184.9 nm) of a low pressure Hg lamp in the air. The UV/O
treatment at room temperature was observed by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. Special oxidation mechanisms for the H-terminated Si(110) surface were found. Si(110) surfaces were hydrogenated by HF treatments. The surface was irradiated and oxidized by UV light (253.7, 184.9 nm) of a low pressure Hg lamp in the air. The UV/O irradiation time dependence of oxide thickness showed a step-wise profile. The step width was about 0.2 nm. The value is close to one oxide layer thickness (0.19 nm) for the Si(110) surface. Si atoms at the Si(110) surface are categolized to A bonds which are chain-like dense bonds, and B bonds which connect up and down A bond chains. The step-wise oxidation behaviour is reasonable if oxidation at the B bonds, in which oxidation strain is smaller than that of A bonds, has larger reaction rate than at the A bonds.
irradiation time dependence of oxide thickness showed a step-wise profile. The step width was about 0.2 nm. The value is close to one oxide layer thickness (0.19 nm) for the Si(110) surface. Si atoms at the Si(110) surface are categolized to A bonds which are chain-like dense bonds, and B bonds which connect up and down A bond chains. The step-wise oxidation behaviour is reasonable if oxidation at the B bonds, in which oxidation strain is smaller than that of A bonds, has larger reaction rate than at the A bonds.
 Mn
Mn O
O , 2
, 2Matsumoto, Keisuke*; Hoshiyama, Takuya*; Oishi, Daisuke*; Akahama, Hiroshi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Kano, Jun*; Hanasaki, Noriaki*; Kambe, Takashi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Mori, Shigeo*
no journal, ,
We have investigated the physical properties of YbFe Mn
Mn O
O , a derivative system of the electronic ferroelectric RFe
, a derivative system of the electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O (R: rare earths). Electron diffraction measurements showed taht long-range charge ordering of the Fe-3d charges was observed at room temperature for x=0; this ordering is the origin of ferroelectricity. The x=0.1 oxide showed diffuse scattering patterns at room temperature, instead of the charge-ordered pattern. Thus, 5% Mn substitution can collapse the long-range charge ordering. We will also present the correlation between the magnetic/dielectric properties and the crystal structure.
(R: rare earths). Electron diffraction measurements showed taht long-range charge ordering of the Fe-3d charges was observed at room temperature for x=0; this ordering is the origin of ferroelectricity. The x=0.1 oxide showed diffuse scattering patterns at room temperature, instead of the charge-ordered pattern. Thus, 5% Mn substitution can collapse the long-range charge ordering. We will also present the correlation between the magnetic/dielectric properties and the crystal structure.