Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Kubota, Tomohiro; Kuroda, Hisao*; Watanabe, Mirai*; Takahashi, Akiko*; Nakazato, Ryoji*; Tarui, Mika*; Matsumoto, Shunichi*; Nakagawa, Keita*; Numata, Yasuko*; Ouchi, Takao*; et al.
Atmospheric Environment, 243, p.117856_1 - 117856_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.84(Environmental Sciences)The dry and wet depositions of atmospheric ammonia (NH ) is one of the important pathways of nitrogen loads to aquatic ecosystems. Crop and livestock agriculture, one of the largest emitters of NH
) is one of the important pathways of nitrogen loads to aquatic ecosystems. Crop and livestock agriculture, one of the largest emitters of NH in Asian countries, are known to cause high spatial and seasonal variation of NH
in Asian countries, are known to cause high spatial and seasonal variation of NH and influence the surrounding lake basin areas via its dry and wet deposition. However, the spatial characteristics of the NH
and influence the surrounding lake basin areas via its dry and wet deposition. However, the spatial characteristics of the NH concentration in basin scale are not completely understood for regulation in NH
concentration in basin scale are not completely understood for regulation in NH emission. Here we aim to clarify dominant factors of spatial and seasonal variations of the NH
emission. Here we aim to clarify dominant factors of spatial and seasonal variations of the NH concentration in a eutrophic lake basin surrounded by agricultural areas in Japan. Passive sampling over various land use categories in the basin was conducted at 36 sites in total from October 2018 to January 2020. Interestingly, the observed NH
concentration in a eutrophic lake basin surrounded by agricultural areas in Japan. Passive sampling over various land use categories in the basin was conducted at 36 sites in total from October 2018 to January 2020. Interestingly, the observed NH concentration near the livestock houses were higher in winter than summer, which was inconsistent with knowledge of seasonal changes of current NH
concentration near the livestock houses were higher in winter than summer, which was inconsistent with knowledge of seasonal changes of current NH emission inventory based on temperature-driven volatilization process. Comparing monthly NH
emission inventory based on temperature-driven volatilization process. Comparing monthly NH concentrations with various meteorological factors, we suggested the importance of seasonal advection of NH
concentrations with various meteorological factors, we suggested the importance of seasonal advection of NH from high emission sources to which has been rarely paid attention by the previous past studies. As for this, should be considered for lake ecosystem management since deposition of NH
from high emission sources to which has been rarely paid attention by the previous past studies. As for this, should be considered for lake ecosystem management since deposition of NH is known to be closely related to the ecological processes such as phytoplankton blooming.
is known to be closely related to the ecological processes such as phytoplankton blooming.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Su, Y. H.; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Harjo, S.; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.436 - 442, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)Cheng, S.; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Gondai, Yoji*; Nakamura, Yuya*; Zhang, B.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 48, p.110 - 121, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.07(Thermodynamics)Cheng, S.; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Gondai, Yoji*; Nakamura, Yuya*; Zhang, B.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*
Proceedings of 8th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2012/12
Cheng, S.*; Kai, Takayuki*; Gondai, Yoji*; Nakamura, Yuya*; Fuke, Fusata*; Zhang, B.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tagami, Hirotaka; et al.
Proceedings of 4th International Symposium on Heat Transfer and Energy Conservation (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2012/01
Cheng, S.*; Tanaka, Yohei*; Gondai, Yoji*; Kai, Takayuki*; Zhang, B.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(10), p.1327 - 1336, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:86.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)To clarify this behavior, a series of experiments have been performed in which nitrogen gas has been percolated uniformly through a particle bed. In these experiments, solid particles and water contained in a rectangular tank simulate respectively fuel debris and coolant. Based on the data obtained, an empirical model was developed to describe the transient variation in the bed inclination angle during the self-leveling process. Good agreement has been obtained between calculated and experimental values. Verification of the model has been confirmed through detailed analysis of the effects of experimental parameters such as particle size, particle density, and gas flow rate. Its applicability to extended conditions was further discussed by performing modeling simulations and comparing results against experimental data obtained from a larger-scale experimental system that employed a conventional boiling method.
Cheng, S.*; Hirahara, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Yohei*; Gondai, Yoji*; Zhang, B.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; et al.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 35(2), p.405 - 415, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:75.41(Thermodynamics)The current experiments were conducted under two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) conditions separately, in which water was used as liquid phase, and bubbles were generated by injecting nitrogen gas from the bottom of the viewing tank. Various particle-bed parameters were varied, including particle-bed height (from 30 mm to 200 mm), particle diameter (from 0.4 mm to 6 mm) and particle type (beads made of acrylic, glass, alumina and zirconia). Under these experimental conditions, three kinds of bubbling behavior were observed for the first time using digital image analysis methods that were further verified by quantitative detailed analysis of bubbling properties including surface bubbling frequency and surface bubble size under both 2D and 3D conditions.
Cheng, S.*; Tanaka, Yohei*; Gondai, Yoji*; Kai, Takayuki*; Zhang, B.*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-7) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2010/11
Ota, Yukihiro; Nakai, Noriyuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Inotani, Daisuke*; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review B, 81(21), p.214511_1 - 214511_6, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:74.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An extension of the Ambegaokar-Baratoff relation to a superconductor-insulator-superconductor (SIS) Josephson junction with multiple tunneling channels is derived. Applying the resultant relation to a SIS Josephson junction formed by an iron-based (five-band) and a single-band Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) type superconductors, a theoretical bound of the Josephson critical current (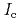 ) multiplied by the resistance of the junction (
) multiplied by the resistance of the junction (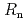 ) is given. We reveal that such a bound is useful for identifying the pairing symmetry of iron-pnictide superconductors. One finds that if a measured value of
) is given. We reveal that such a bound is useful for identifying the pairing symmetry of iron-pnictide superconductors. One finds that if a measured value of 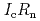 is smaller than the bound then the symmetry is
is smaller than the bound then the symmetry is  -wave, and otherwise
-wave, and otherwise  -wave without any sign changes. In addition, we stress that temperature dependence of
-wave without any sign changes. In addition, we stress that temperature dependence of 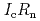 is sensitive to the difference of the gap functions from the BCS type gap formula in the above heterojunction.
is sensitive to the difference of the gap functions from the BCS type gap formula in the above heterojunction.
Cheng, S.*; Hirahara, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Yohei*; Gondai, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/05
A series of experiments on bubble behavior in a particle bed was performed to clarify three-phase flow dynamics in debris bed, which is essential in heat-removal capability, under coolant boiling conditions. The current experiment was conducted in a 2D tank. Water was used as liquid phase, while bubbles were generated by injecting nitrogen gas from the bottom of the tank. Various experimental parameters were taken, including different particle bed height, various particle diameter, different particle type, and different nitrogen gas flow rate. By using digital image analysis method, three kinds of bubble rise behavior were observed under current experimental conditions and confirmed by the quantitative detailed analysis of bubble rise properties including bubble departure frequency and bubble departure size.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
 -leg repulsive Hubbard ladders
-leg repulsive Hubbard laddersMachida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 22(3), p.275 - 279, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.62(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physica C, 468(15-20), p.1237 - 1240, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.68(Physics, Applied)In order to study the vortex core electronic structure in high-T superconductors, we examine 1-D Hubbard model with trap potential by using the density matrix renormalization group method. Instead of directly treating the vortex, the approach mimics the carrier density depression inside the vortex core via the trap potential and exactly calculate strong correlation effects on the depressed region. Consequently, we find that the Mott state emerges in the central region and the metallic edge surrounds the Mott region. Furthermore, when adding spin imbalance, the calculations reveal that a local antiferromagnetic order covers the Mott state region, and moreover, the antiferromagnetic order modulates with a long periodicity. We expect that these results closely relate to the vortex core electronic structure while their calculation results can be directly compared with atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice.
superconductors, we examine 1-D Hubbard model with trap potential by using the density matrix renormalization group method. Instead of directly treating the vortex, the approach mimics the carrier density depression inside the vortex core via the trap potential and exactly calculate strong correlation effects on the depressed region. Consequently, we find that the Mott state emerges in the central region and the metallic edge surrounds the Mott region. Furthermore, when adding spin imbalance, the calculations reveal that a local antiferromagnetic order covers the Mott state region, and moreover, the antiferromagnetic order modulates with a long periodicity. We expect that these results closely relate to the vortex core electronic structure while their calculation results can be directly compared with atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Ago, Tomonori*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; Harada, Kentaro*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Honda, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.205 - 207, 2008/06
Future synchrotron light sources based on the energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) are expected to be capable of producing super-brilliant and/or ultra-short pulses of synchrotron radiation. Our Japanese collaboration team is making efforts for realizing an ERL-based hard X-ray source. We report recent progress in our R&D efforts.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review A, 77(5), p.053614_1 - 053614_8, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:55.49(Optics)We investigate effects of optical lattice potential in one- and two-dimensional two-component trapped Fermi gases with population imbalances. Using the exact diagonalization and the density matrix renormalization group methods complementarily, we calculate the atom density profile from the groundstate many-body wavefunction as a function of attractive interaction strength for various population imbalances. The numerical results reveal that although a phase separation between the superfluid core and the shell cloud of excess atoms occurs as observed in experiments without the optical lattice, the population imbalance generally remains in the core region in contrast to the non-lattice cases. The essence of the numerical results in a strong attractive regime can be explained by an effective model composed of Cooper pairs and excess major fermions.
Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physica C, 463-465, p.103 - 106, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)In order to study an interplay between electronic inhomogeneity and superconductivity as seen in High-Tc cuprates as well as to predict effects of optical lattice in atomic Fermi gases, we numerically examine attractive Hubbard model in the absence of the translation symmetry. For the purpose, we systematically calculate the particle density profile for both 1-D and 2-D attractive Hubbard models with harmonic potential wells using the exact diagonalization and the density-matrix renormalization group methods. The numerical results reveal that fine inhomogeneous zigzag patterns universally emerge in the 1-D model case and the zig-zag structure becomes checkerboard type in the 2-D one. Moreover, it is numerically and theoretically found that such inhomogeneities are caused by double occupation component, i.e., pairs tightly bound on a site. These calculation results are universal for many-body Fermi-particle systems on lattice. We predict that the behavior described above is widely observable from atomic Fermi gas to strong coupled superconductors including High-Tc superconductors.
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Kano, Takuma; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Earth Simulator, 7, p.23 - 35, 2007/06
In order to explore a possibility of superfluidity in confined strongly-correlated fermion systems, e.g., nano-scale cuprate High-Tc superconductors and atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice, we implement an exact diagonalization code for their mathematical model, i.e., a trapped Hubbard model on the Earth Simulator. We compare two diagonalization algorithms, the traditional Lanczos method and a new algorithm, the preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) method, and find that when using the PCG the total CPU time can be reduced to 1/3  1/5 compared to the former one since the convergence can be dramatically improved by choosing a good preconditioner and the communication overhead is much more efficiently concealed in the PCG method. Consequently, such a performance improvement enables us to do systematic studies for several parameters. Numerical simulation results reveal that an unconventional type of pairing specific to the confined system, which can cause superfluidity, develops under a strong repulsive interaction.
1/5 compared to the former one since the convergence can be dramatically improved by choosing a good preconditioner and the communication overhead is much more efficiently concealed in the PCG method. Consequently, such a performance improvement enables us to do systematic studies for several parameters. Numerical simulation results reveal that an unconventional type of pairing specific to the confined system, which can cause superfluidity, develops under a strong repulsive interaction.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review A, 74(5), p.053621_1 - 053621_6, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:67.56(Optics)In order to explore a universal feature of atomic Fermi gases loaded on optical lattices, we make a systematic study of the particle density profile for 1-D and 2-D attractive Hubbard models with harmonic potential wells. Using the exact diagonalization scheme and the density-matrix renormalization group technique, we show that fine inhomogeneous zigzag patterns universally emerge in the above models. Theoretical and numerical analyses suggest that these structures originate from an effective repulsive interaction between tightly-bound pairs and a breakdown of translational invariance. Furthermore, it is emphasized that the pattern obtained numerically in the 2-D model is the checkerboard type, which is very similar to results recently observed in a vortex core of High-T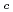 cuprate superconductor.
cuprate superconductor.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physica C, 445-448, p.90 - 93, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.86(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English