Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
中堂 博之; 横井 直人*; 松尾 衛; 針井 一哉*; 鈴木 淳*; 今井 正樹; 佐藤 正寛*; 前川 禎通*; 齊藤 英治*
Physical Review Letters, 134(13), p.130603_1 - 130603_5, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A spin 1/2 is the simplest system that has been believed to support a single two-level quantum system, represented by a single resonance. We experimentally demonstrate that a spin-1/2 nucleus of  F in C
F in C F
F exhibits an extra resonance corresponding to the emergence of the states, by mechanically rotating a sample and a coil in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements. On the basis of the Floquet formalism, we identify the emergence of the extra two-level state due to the temporal periodicity generated by the mechanical rotation (mechanical spin multiplexing) and derive an operator algebra analogous to the planar rotor algebra in an effective description of the system. The observed multiplexing allows a single spin 1/2 to carry more than two states and potentially enabling the processing of multiple quantum bits on a single spin.
exhibits an extra resonance corresponding to the emergence of the states, by mechanically rotating a sample and a coil in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements. On the basis of the Floquet formalism, we identify the emergence of the extra two-level state due to the temporal periodicity generated by the mechanical rotation (mechanical spin multiplexing) and derive an operator algebra analogous to the planar rotor algebra in an effective description of the system. The observed multiplexing allows a single spin 1/2 to carry more than two states and potentially enabling the processing of multiple quantum bits on a single spin.
Zhang, X.-T.*; Xing, Y.-H.*; Yao, X.-P.*; 大湊 友也*; Zhang, L.*; 松尾 衛
Communications Physics (Internet), 8, p.103_1 - 103_8, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Spin pumping effect is a sensitive and well-established experimental method in two-dimensional (2D) magnetic materials. We propose that spin pumping effect can be a valuable probe for non-Fermi liquid (NFL) behaviors at the 2D interface of magnetic heterostructures. We show that the modulations of ferromagnetic resonance exhibit power-law scalings in frequency and temperature for NFL metals induced near a quantum critical point (QCP). At the Ising nematic QCP, we demonstrate that the enhanced Gilbert damping coefficient 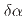 acquires negative power-law exponents in distinct frequency regimes. The exponents convey universal parameters inherited from the QCP and reflect the non- quasiparticle nature of the spin carriers in the NFL metal. At finite temperature, we show that the Gilbert damping mechanism is restored in the quantum critical regime and
acquires negative power-law exponents in distinct frequency regimes. The exponents convey universal parameters inherited from the QCP and reflect the non- quasiparticle nature of the spin carriers in the NFL metal. At finite temperature, we show that the Gilbert damping mechanism is restored in the quantum critical regime and 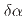 measures the temperature dependence of the correlation length.
measures the temperature dependence of the correlation length.
山本 啓介; 中川 拓哉; 下条 裕人; 木島 惇; 三浦 大矢; 小野瀬 芳彦*; 難波 浩司*; 内田 広明*; 坂本 和彦*; 小野 千佳*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-019, 211 Pages, 2025/02
日本原子力研究開発機構(以下、「JAEA」という。)核燃料サイクル工学研究所旧ウラン濃縮施設は、遠心分離法によるウラン濃縮技術を確立させるための技術開発を本格的に行う目的で建設された施設であり、単機遠心分離機の開発、遠心機材料の開発及び遠心機によるウラン濃縮処理を主に実施したG棟及びG棟に付属するH棟、遠心分離機の小規模カスケード試験を行っていたJ棟、遠心分離機の寿命試験を行っていたL棟、その他ウラン貯蔵施設、廃棄物保管施設、廃水処理施設など複数の施設で構成されていた。これらの施設におけるウラン濃縮技術開発は、開発技術の日本原燃(株)のウラン濃縮工場及びウラン濃縮技術開発センターへの技術移転が完了し、JAEAにおける技術開発の当初の目的が達成されたため、平成13年に終了した。廃水処理室は、昭和51年に建設され、旧ウラン濃縮施設で発生した放射性廃水の処理を行ってきたが、平成20年度に廃水処理室以外の施設に廃水処理設備が整備されて以降は、施設のバックアップ的な位置づけとして維持管理されてきた。さらに、昨今においては、他の施設における廃水処理の実績等からバックアップとしての必要性が無くなり、施設も建設後約48年が経過し、老朽化も進んでいたことから、施設中長期計画に基づき同施設を廃止措置することになり、令和3年11月から令和5年8月に内装設備の解体撤去を行った。本報告は令和5年9月から令和6年3月に行った管理区域解除のための放射線測定に係る実積と関連する知見をまとめたものである。
能崎 幸雄*; 介川 裕章*; 渡邉 紳一*; 柚木 清司*; 洞口 泰輔*; 中山 颯人*; 山野井 一人*; Wen, Z.*; He, C.*; Song, J.*; et al.
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 26(1), p.2428153_1 - 2428153_39, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a novel method for generating spin currents using the gyromagnetic effect, a phenomenon discovered over a century ago. This effect, crucial for understanding the origins of magnetism, enables the coupling between various macroscopic rotational motions and electron spins. While higher rotational speeds intensify the effect, conventional mechanical rotations, typically, below 10,000 RPM, produce negligible results comparable to geomagnetic fluctuations, limiting applied research. Our studies demonstrate that spin current generation comparable to that of rare metals can be achieved through atomic rotations induced by GHz- range surface acoustic waves and the rotational motion of conduction electrons in metallic thin films with nanoscale gradient modulation of electrical conductivity. These effects, termed the acoustic gyromagnetic effect and the current-vorticity gyromagnetic effect, are significant in different contexts.
古谷 峻介*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 110(16), p.165129_1 - 165129_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate spin pumping into a quantum easy-plane ferromagnetic spin chain system. This quantum spin chain is effectively described by the Tomonaga-Luttinger (TL) liquid despite the ferromagnetic exchange interaction because of the easy-plane magnetic anisotropy. This TL liquid state has an extremely strong interaction that is hardly realized in other quantum antiferromagnetic chain systems or weakly interacting electron systems. We show how the strongly interacting TL liquid affects the ferromagnetic resonance that occurs in the ferromagnetic insulator. In particular, we discuss the dependence of the Gilbert damping on the temperature and the junction length. The Gilbert damping allows us to extract information about the above-mentioned strong interaction within the quantum ferromagnetic spin chain. We also point out that a well-known compound CsCuCl will be suitable for the realization of our setup.
will be suitable for the realization of our setup.
大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physica Status Solidi (B), 261(9), p.2300469_1 - 2300469_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)In this article, the spin transfer between two ferromagnetic insulators is studied. There is a narrow gap between the ferromagnetic insulators so that they are weakly interacting with each other. One of the ferromagnetic insulators is moving at a constant speed while the other is at rest; hence, the system is out of equilibrium. In the presence of the shearing motion, the interaction amplitude is periodically modulated at the Doppler frequency. A unitary transformation allows us to regard the periodic modulation of the interaction amplitude as an effective potential, which drives the spin transfer. The amount of the spin current is controlled by the spectral overlap and the carrier population difference between the two ferromagnetic media. If the spectra of the two ferromagnets are moderately broadened, the overlap in the spectral domain increases, enlarging the spin current.
細川 海慈*; 山 正樹*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 110(3), p.035309_1 - 035309_12, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Our result provides an important foundation for an accurate analysis of the inverse Rashba-Edelstein effect induced by thermal spin injection.
船戸 匠*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review Letters, 132(23), p.236201_1 - 236201_7, 2024/06
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:85.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Our results clearly illustrate the microscopic origin of spin current generation by chiral phonons and may lead to a breakthrough in the development of spintronic devices without heavy elements.
佐野 涼太郎*; 大湊 友也*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review Letters, 132(23), p.236302_1 - 236302_9, 2024/06
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:85.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We propose an ac intrinsic magnon spin Hall current driven by surface acoustic waves as a novel probe for such antiferromagnets. Our results pave the way towards mechanical detection and manipulation of the magnetic order in two-dimensional antiferromagnets.
Yao, D.*; 松尾 衛; 横山 毅人*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(16), p.162603_1 - 162603_5, 2024/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:82.03(Physics, Applied)We propose a mechanism of spin current generation under an external electric field due to chiral phonons in a chiral-structure superconductor based on the Bogoliubov de Gennes and the Boltzmann equations.
大湊 友也*; 山影 相*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 109(12), p.L121405_1 - L121405_5, 2024/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:62.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study a dynamical spin response of surface Majorana modes in a topological superconductor-magnet hybrid under microwave irradiation. We find a method to toggle between dissipative and nondissipative Majorana Ising spin dynamics by adjusting the external magnetic field angle and the microwave frequency. This reflects the topological nature of the Majorana modes, enhancing the Gilbert damping of the magnet, thereby providing a detection method for the Majorana Ising spins. Our findings illuminate a magnetic probe for Majorana modes, paving the path to innovative spin devices.
松島 悠*; Zhang, Z.*; 大橋 由梨*; 畠山 紘*; Xiao, G.*; 船戸 匠*; 松尾 衛; 海住 英生*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(2), p.022404_1 - 022404_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:74.90(Physics, Applied)We report the discovery of a stepwise magnetic field-induced emergent magneto-inductance effect in Permalloy thin films deposited on polycarbonate substrates. This study opens up exciting avenues for advancing our understanding of emergent inductance in fundamental physics and paves the way for practical applications in flexible magnetic devices.
山 正樹*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 108(14), p.144430_1 - 144430_15, 2023/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:50.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The inverse Rashba-Edelstein effect (IREE) in a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) induced by spin pumping from an adjacent ferromagnetic insulator (FI) is investigated theoretically. In particular, spin and current densities in the 2DEG in which both Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit interactions coexist are formulated, and their dependencies on ferromagnetic resonance frequency and orientation of the spin in the FI are clarified. It is shown that spin density diverges when the ratio between the Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit interactions approaches unity, while current density stays finite there. These results can be applied for evaluating spin splitting on the Fermi surface in a 2DEG and designing spintronic devices using IREE.
Fukuzawa, K.*; 加藤 岳生*; 松尾 衛; Jonckheere, T.*; Rech, J.*; Martin, T.*
Physical Review B, 108(13), p.134429_1 - 134429_9, 2023/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study spin pumping from a ferromagnetic insulator (FI) into a carbon nanotube (CNT). By employing the bosonization method, we formulate the Gilbert damping induced by the FI/CNT junction, which can be measured by ferromagnetic resonance. We show that the increase in the Gilbert damping has a temperature dependence characteristic of a Luttinger liquid and is highly sensitive to the Luttinger parameter of the spin sector for a clean interface. We also discuss the experimental relevance of our findings based on numerical estimates, using realistic parameters.
Zhang, T.*; 大上 能悟*; 田島 裕之*; 松尾 衛; Liang, H.*
Physical Review B, 108(15), p.155303_1 - 155303_9, 2023/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:39.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study the spin current between two polarized Fermi gases with repulsive interactions near the itinerant ferromagnetic phase transition. We consider a two terminal model where the left reservoir is fixed to be fully polarized while the polarization of the right reservoir is tuned through a fictitious magnetic field defined by the chemical potential difference between different atomic hyperfine states. We calculate the spectra of the spin flip susceptibility function, which displays a magnon dispersion emerging from the Stoner continuum at low momentum in the ferromagnetic phase. Based on the spin flip susceptibility and using Keldysh Green's function formalism, we investigate the spin current induced by quasiparticle and spin flip tunneling processes, respectively, and show their dependence on the polarization bias between two reservoirs. The one body (quasiparticle) tunneling demonstrates a linear dependence with respect to the polarization bias.
佐藤 哲也*; 大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 108(9), p.094428_1 - 094428_10, 2023/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We consider a ferromagnetic particle levitated in air under microwave irradiation and theoretically study the noise in its rigid-body rotation induced by the gyromagnetic effect. This rotational noise includes useful information on angular momentum transfer from the magnetization to the rigid-body rotation, such as the unit of angular momentum per one spin relaxation process. We formulate the rotational noise in terms of the Lindblad equation, which describes the quantum stochastic process, and estimate it in the case of realistic experimental parameters. We show that a bifurcation phenomenon observed in our setup amplifies the noise and, therefore, can be exploited, making an accurate measurement of the rotational noise.
山野井 一人*; 榊原 有理*; 藤本 純治*; 松尾 衛; 能崎 幸雄*
Applied Physics Express, 16(6), p.063004_1 - 063004_6, 2023/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)We report a large modulation of spin pumping using temperature-induced magnetic phase transitions in c-axis oriented single crystalline dysprosium (Dy). From the temperature variation of the magnetic susceptibility, transitions from paramagnetic (PM) to ferromagnetic (FM) phases via antiferromagnetic (AFM) phase are clearly observed in the Dy. Unlike polycrystalline Dy, the spin pumping of both PM- and AFM-Dy are strongly suppressed owing to the increased non-dissipative backflow of spin current by the long-range spin transport, although two orders of magnitude difference exist between FM- and AFM-phases.
佐藤 哲也*; 加藤 岳生*; 大上 能悟*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.L180406_1 - L180406_6, 2023/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:27.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We examine the mechanical rotation of a levitated magnetic particle that is induced by ferromagnetic resonance under microwave irradiation. We show that two stable solutions appear in a certain range of parameters by bifurcation when the rotation frequency is comparable to the microwave frequency. This phenomenon originates from the coexistence of the Barnett and the Einstein-de Haas effects. We also reveal that this measurement is sensitive to the strength of the spin-rotation coupling. Our work provides a platform for accessing a microscopic relaxation process from spin to macroscopic rotation.
舟木 博志*; 山影 相*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184437_1 - 184437_10, 2023/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:27.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a microscopic theory of tunneling spin transport at the magnetic interface between a ferromagnetic insulator (FI) and a ferromagnetic superconductor (FSC) driven by ferromagnetic resonance. We show that the spin susceptibilities of the FSC can be extracted from the spin currents by tuning the easy axis of the FI, and thus the spin currents can be a probe for the symmetries of the spin-triplet Cooper pairing. Our results will offer a route to exploiting the synergy of magnetism and superconductivities for spin devices.
山 正樹*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 107(17), p.174414_1 - 174414_15, 2023/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:50.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically consider the effect of vertex correction on spin pumping from a ferromagnetic insulator (FI) into a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) in which the Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit interactions coexist. The Gilbert damping in the FI is enhanced by elastic spin-flipping or magnon absorption. We show that the Gilbert damping due to elastic spin-flipping is strongly enhanced by the vertex correction when the ratio of the two spin-orbit interactions is near a special value at which the spin relaxation time diverges while that due to magnon absorption shows only small modification. We also show that the shift in the resonant frequency due to elastic spin-flipping is strongly enhanced in a similar way as the Gilbert damping.