Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
 -gas exposure at high temperatures
-gas exposure at high temperaturesTakeda, Yusuke; Iida, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Shinji*; Matsuo, Tadatoshi*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hirade, Tetsuya
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 25, p.011023_1 - 011023_3, 2019/03
In this study, we prepared samples under two different conditions, (1) 810 C, for 600 min, and (2) 850
C, for 600 min, and (2) 850 C, for 720 min. A depth-profile analysis of the surfaces of the samples is conducted through Doppler broadening (DB) measurements of positron annihilation
C, for 720 min. A depth-profile analysis of the surfaces of the samples is conducted through Doppler broadening (DB) measurements of positron annihilation  rays using a slow positron beam. It was indicated that many of positrons annihilated in defects near the surface. According to the TEM image, there are nano-crystal grains near the surface and then positrons can diffuse in the grains and annihilate in defects at the grain boundaries. Furthermore, DB measurements indicated that there is a depth dependence on the chemical composition where positrons annihilate. EDS spectroscopy measurements also indicated that there is a depth dependence of impurities such as Vanadium. These results indicated change of the chemical composition at the grain boundaries.
rays using a slow positron beam. It was indicated that many of positrons annihilated in defects near the surface. According to the TEM image, there are nano-crystal grains near the surface and then positrons can diffuse in the grains and annihilate in defects at the grain boundaries. Furthermore, DB measurements indicated that there is a depth dependence on the chemical composition where positrons annihilate. EDS spectroscopy measurements also indicated that there is a depth dependence of impurities such as Vanadium. These results indicated change of the chemical composition at the grain boundaries.
 -gas exposure at high temperatures
-gas exposure at high temperaturesTakeda, Yusuke; Iida, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Shinji*; Matsuo, Tadatoshi*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hirade, Tetsuya
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 791(1), p.012022_1 - 012022_4, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Titanium alloy is widely used for applications such as golf club heads and structural materials for aircrafts. The surface can be exceedingly hardened by nitriding treatment that initiates defects, but there are some difficulties on use of titanium nitride because the layer can be exfoliated by stress. Therefore, we prepared samples in two different treatment conditions, (1) 810 C 600 min and (2) 850
C 600 min and (2) 850 C 720 min and performed depth profile analysis of Doppler broadening of positron annihilation
C 720 min and performed depth profile analysis of Doppler broadening of positron annihilation  -rays (DB) for these samples. According to a calculation of nitrogen diffusion depth, the nitride layer should be only about 0.05-0.1
-rays (DB) for these samples. According to a calculation of nitrogen diffusion depth, the nitride layer should be only about 0.05-0.1 m. However, the depth profile analysis of the DB measurement indicated that the defects introduced by nitriding treatment extended to a depth of 0.5
m. However, the depth profile analysis of the DB measurement indicated that the defects introduced by nitriding treatment extended to a depth of 0.5 m.
m.
Li, T.*; Garg, U.*; Liu, Y.*; Marks, R.*; Nayak, B. K.*; Madhusudhana Rao, P. V.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru*; Hashimoto, Hisanobu*; Nakanishi, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 81(3), p.034309_1 - 034309_11, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:97.52(Physics, Nuclear) Mn
Mn O
O (0
(0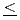 x
x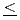 1)
1)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Michiuchi, Takamasa*; Yokota, Yusuke*; Okajima, Yuka; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Matsuo, Yoji*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 182(7), p.1611 - 1618, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.37(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have investigated the magnetic and dielectric properties of YbFe Mn
Mn O
O (0
(0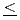 x
x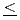 1), which is an Fe-site-substituted system of new multiferroic oxides RFe
1), which is an Fe-site-substituted system of new multiferroic oxides RFe O
O (R=Y, Ho-Lu). X-ray diffraction measurements show that a solid solution is formed between YbFe
(R=Y, Ho-Lu). X-ray diffraction measurements show that a solid solution is formed between YbFe O
O (x=0) and YbFeMnO
(x=0) and YbFeMnO (x=1) for 0
(x=1) for 0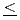 x
x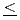 1. The valence of the Mn ion is determined to be
1. The valence of the Mn ion is determined to be  2+, consistently with the suppression of low-temperature magnetization by the Mn substitution. The magnetic transition temperature and the dielectric constant decrease monotonically with increasing x. This result plausibly confirms that the magnetic and dielectric properties in oxides isostructural with RFe
2+, consistently with the suppression of low-temperature magnetization by the Mn substitution. The magnetic transition temperature and the dielectric constant decrease monotonically with increasing x. This result plausibly confirms that the magnetic and dielectric properties in oxides isostructural with RFe O
O are governed by the electron transfer between Fe-site ions, unlike ordinary ferroelectrics and dielectrics, in which the ionic displacement plays a key role. The possibility for application is briefly discussed.
are governed by the electron transfer between Fe-site ions, unlike ordinary ferroelectrics and dielectrics, in which the ionic displacement plays a key role. The possibility for application is briefly discussed.
 O
O
Michiuchi, Takamasa*; Yokota, Yusuke*; Komatsu, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Hironori*; Kuroda, Tomoko*; Maeda, Daisuke*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Mori, Shigeo*; Yoshii, Kenji; Hanasaki, Noriaki*; et al.
Ferroelectrics, 378(1), p.175 - 180, 2009/00
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:59.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have synthesized the samples of LuFe O
O , which shows the ferroelectricity due to charge ordering of Fe ions, under several different reducing conditions using a CO
, which shows the ferroelectricity due to charge ordering of Fe ions, under several different reducing conditions using a CO -CO flow. The reducing condition was changed by changing a flow ratio of CO
-CO flow. The reducing condition was changed by changing a flow ratio of CO and CO. It was found that the flow ratio of CO
and CO. It was found that the flow ratio of CO /CO of about 5 provided the sample with the highest magnetic transition temperature of 240-250 K. This sample showed the dielectric constant of 10000 at room temperature. The imaginary part of the dielectric response offered the activation energy of 0.4-0.5 eV, which is slightly larger than that reported previously (about 0.3 eV). We will perform further investigation of the physical properties of this sample to clarify full details and their origin of LuFe
/CO of about 5 provided the sample with the highest magnetic transition temperature of 240-250 K. This sample showed the dielectric constant of 10000 at room temperature. The imaginary part of the dielectric response offered the activation energy of 0.4-0.5 eV, which is slightly larger than that reported previously (about 0.3 eV). We will perform further investigation of the physical properties of this sample to clarify full details and their origin of LuFe O
O .
.
 O
O and R
and R R'
R' Fe
Fe O
O (R, R': rare earths)
(R, R': rare earths)Yoshii, Kenji; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Maeda, Daisuke*; Yokota, Yusuke*; Michiuchi, Takamasa*; Komatsu, Takuma*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Mori, Shigeo*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 47(9), p.7599 - 7602, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.23(Physics, Applied)We have investigated the physical properties of HoFe O
O and R
and R R'
R' Fe
Fe O
O (R, R': rare earths). Dielectric measurements showed their dielectric constants of 1000 at around room temperature, which is characteristic of the RFe
(R, R': rare earths). Dielectric measurements showed their dielectric constants of 1000 at around room temperature, which is characteristic of the RFe O
O series (R: rare earths). However, the magnetic transition temperatures and the coherency in dielectric response were found to be different from those of RFe
series (R: rare earths). However, the magnetic transition temperatures and the coherency in dielectric response were found to be different from those of RFe O
O reported so far. Interestingly, these materials suggested higher ferroelectric temperatures than those reported so far, suggesting a possibility of application of these materials.
reported so far. Interestingly, these materials suggested higher ferroelectric temperatures than those reported so far, suggesting a possibility of application of these materials.
 solutions
solutionsToyoshima, Atsushi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Akiyama, Kazuhiko*; Goto, Shinichi*; Ishii, Yasuo; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 96(3), p.125 - 134, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:84.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Formation of an anionic fluoride-complex of element 104, rutherfordium (Rf) produced in the  Cm(
Cm( O,5n)
O,5n) Rf reaction was studied by an anion-exchange method based on an atom-at-a-time scale. It was found that the hexafluoro complex of Rf, [RfF
Rf reaction was studied by an anion-exchange method based on an atom-at-a-time scale. It was found that the hexafluoro complex of Rf, [RfF ]
] , was formed in the studied fluoride ion concentrations of 0.0005 - 0.013 M. Formation of [RfF
, was formed in the studied fluoride ion concentrations of 0.0005 - 0.013 M. Formation of [RfF ]
] was significantly different from that of the homologues Zr and Hf, [ZrF
was significantly different from that of the homologues Zr and Hf, [ZrF ]
] and [HfF
and [HfF ]
] ; the evaluated formation constant of [RfF
; the evaluated formation constant of [RfF ]
] is at least one-order of magnitude smaller than those of [ZrF
is at least one-order of magnitude smaller than those of [ZrF ]
] and [HfF
and [HfF ]
] .
.
Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato; Sato, Tetsuya; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Takatoshi; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 95(1), p.1 - 6, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:70.17(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Nagame, Yuichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Ishii, Yasuo; Sato, Tetsuya; Hirata, Masaru; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 93(9-10), p.519 - 526, 2005/00
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Akiyama, Kazuhiko*; Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Takatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Akiyama, Kazuhiko*; Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Takatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 OH mixed solution
OH mixed solutionTsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Akiyama, Kazuhiko*; Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Yusuke; Iida, Kiyoshi*; Sato, Shinji*; Matsuo, Tadatoshi*; Nagashima, Yasuyuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
The impact stress exfoliates a Nitride surface layer on Titanium alloy prepared in some conditions. So we prepared specimens in two different conditions, (1) 810 C, 600min and (2) 850
C, 600min and (2) 850 C, 720min, and performed depth profile analysis of their surfaces with Doppler broadening measurements of positron annihilation
C, 720min, and performed depth profile analysis of their surfaces with Doppler broadening measurements of positron annihilation  -rays (DB) that is sensitive for defects by Slow Positron beams. Although the specimens (2) is harder than (1) according to the Vickers Hardness test, DB results indicated that defect layer of specimen (1) is thicker than (2). It means that the defect layer thickness was not the cause of surface hardening. Furthermore, chemical elements at the positron annihilation sites could be analyzed qualitatively by DB and the change of the composition appeared in deeper region than the defect layer. The defect layer depth does not match the depth where chemical composition changes by DB appeared. TEM and EDS observation showed different tendency from the results by DB. It is because positrons probe specific sites, and the combination of these methods will be a strong tool to investigate surface structures.
-rays (DB) that is sensitive for defects by Slow Positron beams. Although the specimens (2) is harder than (1) according to the Vickers Hardness test, DB results indicated that defect layer of specimen (1) is thicker than (2). It means that the defect layer thickness was not the cause of surface hardening. Furthermore, chemical elements at the positron annihilation sites could be analyzed qualitatively by DB and the change of the composition appeared in deeper region than the defect layer. The defect layer depth does not match the depth where chemical composition changes by DB appeared. TEM and EDS observation showed different tendency from the results by DB. It is because positrons probe specific sites, and the combination of these methods will be a strong tool to investigate surface structures.
Sasada, Yuto*; Miyazaki, Yuji*; Nakano, Motohiro*; Matsuo, Yusuke*; Walker, C.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
Cementitous materials are to be used in large quantities in the geological disposal of highly radioactive TRU waste. Thermodynamic data on cement hydrate minerals are important to model the long-term dissolution behavior of cement materials during the reaction of these materials with groundwater. Portlandite (Ca(OH) ) is a major component (20 to 25 wt%) of hydrated Portland cement. Low temperature heat capacity measurements of three types of portlandite (low purity, high purity, and large crystal) showed purity dependence. The large crystal sample followed Debye's T
) is a major component (20 to 25 wt%) of hydrated Portland cement. Low temperature heat capacity measurements of three types of portlandite (low purity, high purity, and large crystal) showed purity dependence. The large crystal sample followed Debye's T rule at low temperatures, while the high and low purity samples showed upturn of heat capacity, possibly due to difference in absorbed water vapor and/or calcite (CaCO
rule at low temperatures, while the high and low purity samples showed upturn of heat capacity, possibly due to difference in absorbed water vapor and/or calcite (CaCO ) contamination. Heat capacities of the cement hydrates (ettringite:Ca
) contamination. Heat capacities of the cement hydrates (ettringite:Ca (Al(OH)
(Al(OH) )
) (SO
(SO )
) (H
(H O)
O) and monosulfate:Ca
and monosulfate:Ca Al
Al (OH)
(OH) (SO
(SO )(H
)(H O)
O) ) exhibited phase transitions associated with the hydration water.
) exhibited phase transitions associated with the hydration water.