Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Yuki; Minemoto, Kojiro*; Nemoto, Makoto*; Matsuura, Yasutaka*; Hayashi, Keisuke*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Decommissioning; Addressing the Past and Ensuring the Future 2023 (Internet), 4 Pages, 2025/00
The development of technology to visualize the distribution of radioactive substances at the decommissioning site of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) is important for reducing worker exposure and developing a detailed work plan. Sato, one of the authors, developed an integrated Radiation Imaging System (iRIS) that combines a Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) device, a Compton camera (a type of gamma-ray imager), and a survey meter, and have successfully produced a 3-D map of the working environment inside the FDNPS that visualizes the location of radioactive hot spots and the distribution of air dose rates. In addition, the authors are developing a system that enables users to experience the radiation environment of the FDNPS in virtual reality (VR) using the 3-D map visualizing such radiation information as input data. This VR system can use a commercially available portable VR head-mounted display, which not only displays the location of the radiation source in a virtual space, but also has the ability to calculate the exposure dose according to the working time. The development status of this VR system, which is expected to be effective in educating inexperienced workers and planning work, will be presented at the conference.
Sano, Yuichi; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, So; Morita, Keisuke; Emori, Tatsuya; Ban, Yasutoshi; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Energy Beyond the Pandemic (GLOBAL 2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/07
We developed a hybrid MA(III) recovery process combining MA(III)+Ln(III) co-recovery flowsheet by solvent extraction with TBP and MA(III)/Ln(III) separation flowsheet by simulated moving bed chromatography using HONTA impregnated adsorbents with large particle size porous silica support.
 Fe
Fe O
O Cl
Cl with tunable direction in three dimensions
with tunable direction in three dimensionsAbe, Nobuyuki*; Shiozawa, Shunsuke*; Matsuura, Keisuke*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Tokunaga, Yusuke*; Arima, Takahisa*
Physical Review B, 101(18), p.180407_1 - 180407_5, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:15.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Goto, Minoru; Okumura, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Nakaya, Hiroyuki*; Katayama, Kazunari*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 136(Part A), p.357 - 361, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)A High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is proposed as a tritium production device, which has the potential to produce a large amount of tritium using  Li(n,
Li(n, )T reaction. In the HTGR design, generally, boron is loaded into the core as a burnable poison to suppress excess reactivity. In this study, lithium is loaded into the HTGR core instead of boron and is used as a burnable poison aiming to produce thermal energy and tritium simultaneously. The nuclear characteristics and the fuel temperature were calculated to confirm the feasibility of the lithium-loaded HTGR. It was shown that the calculation results satisfied the design requirements and hence the feasibility was confirmed for the lithium-loaded HTGR, which produce thermal energy and tritium.
)T reaction. In the HTGR design, generally, boron is loaded into the core as a burnable poison to suppress excess reactivity. In this study, lithium is loaded into the HTGR core instead of boron and is used as a burnable poison aiming to produce thermal energy and tritium simultaneously. The nuclear characteristics and the fuel temperature were calculated to confirm the feasibility of the lithium-loaded HTGR. It was shown that the calculation results satisfied the design requirements and hence the feasibility was confirmed for the lithium-loaded HTGR, which produce thermal energy and tritium.
 O
O
Matsuura, Keisuke*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Uehara, Amane*; Nii, Yoichi*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Ji, S.*; Abe, Nobuyuki*; Arima, Takahisa*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 536, p.372 - 376, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.03(Physics, Condensed Matter) O
O
Matsuura, Keisuke*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Uehara, Amane*; Nii, Yoichi*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Ji, S.*; Abe, Nobuyuki*; Arima, Takahisa*
Physical Review Letters, 119(1), p.017201_1 - 017201_6, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.21(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Numakura, Masahiko*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Bessada, C.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akatsuka, Hiroshi*; Nezu, Atsushi*; Shimohara, Yasuaki*; Tajima, Keisuke*; Kawano, Hirokazu*; Nakahagi, Takeshi*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 53(7), p.994 - 998, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:67.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements on thorium fluoride in molten lithium-calcium fluoride mixtures and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of zirconium and yttrium fluoride in molten lithium-calcium fluoride mixtures have been carried out. In the molten state, coordination number of thorium and inter ionic distances between thorium and fluorine in the first neighbor are nearly constant in all mixtures. However the fluctuation factors (Debye-Waller factor and C cumulant) increase until
cumulant) increase until  CaF
CaF = 0.17 and decrease by addition of excess CaF
= 0.17 and decrease by addition of excess CaF . It means that the local structure around Th
. It means that the local structure around Th is disordered until
is disordered until  CaF
CaF =0.17 and stabilized over
=0.17 and stabilized over  CaF
CaF = 0.17. The variation of fluctuation factors is related to the number density of F
= 0.17. The variation of fluctuation factors is related to the number density of F in ThF
in ThF mixtures and the stability of local structure around Th
mixtures and the stability of local structure around Th increases with decreasing the number density of F
increases with decreasing the number density of F in ThF
in ThF mixtures. This tendency is common to those in the ZrF
mixtures. This tendency is common to those in the ZrF and YF
and YF mixtures.
mixtures.
Matsuura, Hideharu*; Izawa, Keisuke*; Minohara, Nobumasa*; Oshima, Takeshi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 47(7), p.5355 - 5357, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.57(Physics, Applied)The reduction in hole concentration ( ) in Al-implanted
) in Al-implanted  -type 6H-SiC due to 1 MeV electron irradiation was studied. By analysis of
-type 6H-SiC due to 1 MeV electron irradiation was studied. By analysis of  , the acceptor density (
, the acceptor density (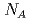 ), its ionizing energy (
), its ionizing energy (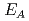 ) and nature of the acceptor are determined. As a result, the acceptor observed in this study is assigned to an Al acceptor.
) and nature of the acceptor are determined. As a result, the acceptor observed in this study is assigned to an Al acceptor. 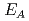 is independent of irradiation fluence (
is independent of irradiation fluence ( ), in spite that
), in spite that 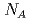 is strongly dependent on
is strongly dependent on  . We derived an analytical expression for the fluence dependence of
. We derived an analytical expression for the fluence dependence of 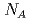 and we estimated the removal coefficient (i.e., removal cross-section) of
and we estimated the removal coefficient (i.e., removal cross-section) of 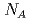 to be 6.4
to be 6.4 10
10 cm
cm for 1 MeV electron irradiation. The reduction in p due to electron irradiation is found to be mainly due to the decrease in
for 1 MeV electron irradiation. The reduction in p due to electron irradiation is found to be mainly due to the decrease in 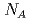 , not to the increase in the density of defects with deep-level, because the decrease in
, not to the increase in the density of defects with deep-level, because the decrease in 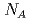 is much larger than the increment in the density of deep-level defects.
is much larger than the increment in the density of deep-level defects.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akie, Hiroshi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Araya, Fumimasa; Okajima, Shigeaki; et al.
JAERI-Research 2004-008, 383 Pages, 2004/06
The present report contains the achievement of "Research and Development on Reduced-Moderation Light Water Reactor with Passive Safety Features", which was performed by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), Hitachi Ltd., Japan Atomic Power Company and Tokyo Institute of Technology in FY2000-2002 as the innovative and viable nuclear energy technology (IVNET) development project operated by the Institute of Applied Energy (IAE). In the present project, the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) has been developed to ensure sustainable energy supply and to solve the recent problems of nuclear power and nuclear fuel cycle, such as economical competitiveness, effective use of plutonium and reduction of spent fuel storage. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as high burnup, long operation cycle, multiple recycling of plutonium (Pu) and effective utilization of uranium resources based on accumulated LWR technologies.
Oyama, Kenji*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Ito, Shinichi*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Sato, Taku*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Ino, Takashi*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
no journal, ,
Goto, Minoru; Okumura, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Nakaya, Hiroyuki*; Katayama, Kazunari*
no journal, ,
A feasibility study of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) for tritium production using  Li(n,
Li(n, )T reaction for fusion reactors has been conducted. In this study, the burn-up chain was modified to treat
)T reaction for fusion reactors has been conducted. In this study, the burn-up chain was modified to treat  Li(n,a)T reaction directory in neutronics calculations, and then the feasibility study was performed from the view point of nuclear characteristics using SRAC code system, which has experience in neutronics analysis of HTGRs.
Li(n,a)T reaction directory in neutronics calculations, and then the feasibility study was performed from the view point of nuclear characteristics using SRAC code system, which has experience in neutronics analysis of HTGRs.
Goto, Minoru; Okumura, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Nakaya, Hiroyuki*; Katayama, Kazunari*
no journal, ,
A feasibility study of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) for tritium production using  Li(n,
Li(n, )T reaction for fusion reactors has been conducted. In this study, the burn-up chain was modified to treat
)T reaction for fusion reactors has been conducted. In this study, the burn-up chain was modified to treat  Li(n,
Li(n, )T reaction directory in neutronics calculations, and then the feasibility study was performed from the view point of nuclear and thermal characteristics using SRAC code system, which has experience in neutronics analysis of HTGRs.
)T reaction directory in neutronics calculations, and then the feasibility study was performed from the view point of nuclear and thermal characteristics using SRAC code system, which has experience in neutronics analysis of HTGRs.
Yanagisawa, Hideki*; Izawa, Keisuke*; Matsuura, Hideharu*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English