Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 by tuning nematicity and magnetism in FeSe
by tuning nematicity and magnetism in FeSe S
S superconductors
superconductors松浦 康平*; 水上 雄太*; 新井 佑基*; 杉村 優一*; 前島 尚行*; 町田 晃彦*; 綿貫 徹*; 福田 竜生; 矢島 健*; 廣井 善二*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 8, p.1143_1 - 1143_6, 2017/10
被引用回数:97 パーセンタイル:91.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A fundamental issue concerning iron-based superconductivity is the roles of electronic nematicity and magnetism in realising high transition temperature ( ). To address this issue, FeSe is a key material, as it exhibits a unique pressure phase diagram involving nonmagnetic nematic and pressure-induced antiferromagnetic ordered phases. However, as these two phases in FeSe have considerable overlap, how each order affects superconductivity remains perplexing. Here we construct the three-dimensional electronic phase diagram, temperature (
). To address this issue, FeSe is a key material, as it exhibits a unique pressure phase diagram involving nonmagnetic nematic and pressure-induced antiferromagnetic ordered phases. However, as these two phases in FeSe have considerable overlap, how each order affects superconductivity remains perplexing. Here we construct the three-dimensional electronic phase diagram, temperature ( ) against pressure (
) against pressure ( ) and iso-valent S-substitution (
) and iso-valent S-substitution ( ), for FeSe
), for FeSe S
S . By simultaneously tuning chemical and physical pressures, against which the chalcogen height shows a contrasting variation, we achieve a complete separation of nematic and antiferromagnetic phases. In between, an extended nonmagnetic tetragonal phase emerges, where
. By simultaneously tuning chemical and physical pressures, against which the chalcogen height shows a contrasting variation, we achieve a complete separation of nematic and antiferromagnetic phases. In between, an extended nonmagnetic tetragonal phase emerges, where  shows a striking enhancement. The completed phase diagram uncovers that high-
shows a striking enhancement. The completed phase diagram uncovers that high- superconductivity lies near both ends of the dome-shaped antiferromagnetic phase, whereas
superconductivity lies near both ends of the dome-shaped antiferromagnetic phase, whereas  remainslow near the nematic critical point.
remainslow near the nematic critical point.
中嶋 洋輔*; 武田 寿人*; 市村 和也*; 細井 克洋*; 大木 健輔*; 坂本 瑞樹*; 平田 真史*; 市村 真*; 池添 竜也*; 今井 剛*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.537 - 540, 2015/08
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:84.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A divertor simulation experimental module (D-module) with a V-shaped divertor target is installed in the west end-sell in GAMMA 10 large tandem mirror device, and a hydrogen plasma irradiation experiment to the target have been started to investigate radiation cooling mechanism on the target. A gas injection system is installed in the D-module and Langmuir probe and calorie meter array are mounted on the target plate. During the plasma irradiation, the highest electron density of 2.4  10
10 m
m and a significant reduction of the electron temperature from a few tens of eV to 2 eV are achieved on the target plate by hydrogen and noble gas injection into the D-module.
and a significant reduction of the electron temperature from a few tens of eV to 2 eV are achieved on the target plate by hydrogen and noble gas injection into the D-module.
中嶋 洋輔*; 坂本 瑞樹*; 吉川 正志*; 大木 健輔*; 武田 寿人*; 市村 和也*; 細井 克洋*; 平田 真史*; 市村 真*; 池添 竜也*; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
In the large tandem mirror device GAMMA 10/PDX, a divertor simulation experimental module (D-module) with a V-shaped divertor target have been installed in the end-mirror. A massive gas injection of hydrogen and noble gases (argon and xenon) into the D-module during hydrogen plasma irradiation onto the target was performed, and plasma detachment from the target was investigated. Electron temperature measured by Langmuir probe array on the target was significantly reduced from a few tens of eV to  3 eV, and particle flux was also reduced. A bright H
3 eV, and particle flux was also reduced. A bright H emission in the upstream region of the D-module and strong reduction near the target were observed by a two-dimensional image of H
emission in the upstream region of the D-module and strong reduction near the target were observed by a two-dimensional image of H emission in the target observed with a high-speed camera. Molecular activated recombination (MAR) process is expected to contribute to the reduction of the electron temperature and the particle flux.
emission in the target observed with a high-speed camera. Molecular activated recombination (MAR) process is expected to contribute to the reduction of the electron temperature and the particle flux.
 scale on fuel tube cladding by the melt of control rod assemble
scale on fuel tube cladding by the melt of control rod assemble中島 正太郎*; 松浦 傑*; 南口 誠*; 倉田 正輝; Pham, V. H.
no journal, ,
For a better understanding of the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, a reaction model of core melting process is very important. In this study, oxidized Zry plates were soaked into molten SS-B C mixture and heated into Ar gas at 1200
C mixture and heated into Ar gas at 1200 C. Recession of ZrO
C. Recession of ZrO scale was observed in the both cases. An oxygen solid solution region in the Zry sample was observed below ZrO
scale was observed in the both cases. An oxygen solid solution region in the Zry sample was observed below ZrO scale, although it was not observed in Zry oxidized at 600
scale, although it was not observed in Zry oxidized at 600 C in high temperature steam conditions. When oxygen supply from the surrounding was halted, ZrO
C in high temperature steam conditions. When oxygen supply from the surrounding was halted, ZrO scale can be reduced at high temperature such as 1200
scale can be reduced at high temperature such as 1200 C by oxygen dissolution into Zry inside.
C by oxygen dissolution into Zry inside.
Pham, V. H.; 松浦 傑*; 中島 正太郎*; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
no journal, ,
In this study, soaking experiments of pre-oxidized zry plates in molten mixture of stainless steel and 5 mol% boron carbide were conducted at 1200-1250 C. Thickness of oxide layer, ZrO
C. Thickness of oxide layer, ZrO was measured before and after the soaking test to investigate the ZrO
was measured before and after the soaking test to investigate the ZrO thickness recession in the molten mixture. Results of the study indicated that the thickness recession of ZrO
thickness recession in the molten mixture. Results of the study indicated that the thickness recession of ZrO was mainly caused by the diffusion of oxygen from oxide layer to metallic-Zr region.
was mainly caused by the diffusion of oxygen from oxide layer to metallic-Zr region.
 スケールにおける酸素供給が絶たれた際の減肉挙動
スケールにおける酸素供給が絶たれた際の減肉挙動中島 正太郎*; 松浦 傑*; 南口 誠*; 倉田 正輝; Pham, V. H.
no journal, ,
沸騰型軽水炉(BWR)では、核燃料ペレット(UO )をZr合金(Zry)製被覆管で構成した燃料棒および炭化ホウ素(B
)をZr合金(Zry)製被覆管で構成した燃料棒および炭化ホウ素(B C)製中性子吸収材料をステンレス鋼(SS)製管で構成された制御棒が隣接して格納されている。全電力喪失時においては、冷却水の供給停止によって核燃料が冷却されず、核燃料の温度が上昇し続けると、冷却水が蒸発して反応炉内が高温水蒸気環境となり、Zry中のZrと反応し燃料棒表面にZrO
C)製中性子吸収材料をステンレス鋼(SS)製管で構成された制御棒が隣接して格納されている。全電力喪失時においては、冷却水の供給停止によって核燃料が冷却されず、核燃料の温度が上昇し続けると、冷却水が蒸発して反応炉内が高温水蒸気環境となり、Zry中のZrと反応し燃料棒表面にZrO スケールを形成するとされている。また、制御棒を構成しているSSおよびB
スケールを形成するとされている。また、制御棒を構成しているSSおよびB Cが共晶反応を起こし、液相が形成される。この液相が燃料被覆管と接触することで燃料被覆管が腐食され、核燃料の暴露に繋がったと考えられている。しかしながら、燃料棒表面に形成されたZrO
Cが共晶反応を起こし、液相が形成される。この液相が燃料被覆管と接触することで燃料被覆管が腐食され、核燃料の暴露に繋がったと考えられている。しかしながら、燃料棒表面に形成されたZrO スケールと液相の腐食プロセスの理解は十分にはされていないのが現状である。そこで本研究では、Ar雰囲気気流下においてZrO
スケールと液相の腐食プロセスの理解は十分にはされていないのが現状である。そこで本研究では、Ar雰囲気気流下においてZrO スケールを形成したZry板に熱処理を加えることで、液相化したSS-B
スケールを形成したZry板に熱処理を加えることで、液相化したSS-B Cに接触して水蒸気の供給が遮断された状況を熱力学的に模擬した実験を行い、シビアアクシデント時の腐食プロセスの解明を行った。
Cに接触して水蒸気の供給が遮断された状況を熱力学的に模擬した実験を行い、シビアアクシデント時の腐食プロセスの解明を行った。
大山 研司*; 横尾 哲也*; 伊藤 晋一*; 鈴木 純一*; 岩佐 和晃*; 佐藤 卓*; 吉良 弘*; 坂口 佳史*; 猪野 隆*; 奥 隆之; et al.
no journal, ,
We aim at constructing a polarisation analysis neutron spectrometer at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) based on a collaboration of KEK and Tohoku Univ. The proposed instrument, named POLANO, is designed as a compact chopper spectrometer with a rotary detector bank (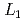 = 17.5 m,
= 17.5 m, 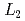 = 2.5 m). At the first phase of the project, we will concentrate the
= 2.5 m). At the first phase of the project, we will concentrate the 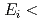 30 meV region using a fan type bender supermirror spin analyser because rich scientific targets in basic and application materials science exist in this region. In the second phase, we will try to install a
30 meV region using a fan type bender supermirror spin analyser because rich scientific targets in basic and application materials science exist in this region. In the second phase, we will try to install a  He spin filter analyser for the
He spin filter analyser for the 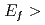 100 meV region. This project passed in the final board of J-PARC on SEP-2011, and the construction has been authorized already.
100 meV region. This project passed in the final board of J-PARC on SEP-2011, and the construction has been authorized already.
 C at elevated temperatures
C at elevated temperaturesPham, V. H.; 松浦 傑*; 南口 誠*; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
no journal, ,
In this study, soaking experiments of Zry plates in molten SS-B C were conducted to investigate the recession rate of Zry plates in molten SS-B
C were conducted to investigate the recession rate of Zry plates in molten SS-B C at 1175-1225
C at 1175-1225 C. The molten SS-B
C. The molten SS-B C mixture was prepared by heat-treatment at 1400
C mixture was prepared by heat-treatment at 1400 C for 12 h of a powder mixture containing 5 mol% B
C for 12 h of a powder mixture containing 5 mol% B C and stainless steel. After decreasing temperature to the testing temperatures, Zry plates were soaked in the molten mixture for 0-60 min. After soaking tests, the Zry plates were pulled out of the molten mixture. The remaining thickness of Zry plates after the tests were measured by using optical microscope. To understand the influences of alloying elements in Zry and SS, three other sets of experiments (Zr plates in Fe-B
C and stainless steel. After decreasing temperature to the testing temperatures, Zry plates were soaked in the molten mixture for 0-60 min. After soaking tests, the Zry plates were pulled out of the molten mixture. The remaining thickness of Zry plates after the tests were measured by using optical microscope. To understand the influences of alloying elements in Zry and SS, three other sets of experiments (Zr plates in Fe-B C, Zr plates in SS-B
C, Zr plates in SS-B C and Zry plates in Fe-B
C and Zry plates in Fe-B C) were also conducted. Results of the study indicated that the thickness of Zry plates decreased linearly with increase of soaking duration. The recession rate of Zry plates was increase with increase of testing temperatures. The value of apparent activation energy on the thickness recession rate of Zry plates was determined to be 333 kJ/mol. The alloying elements in SS showed a positive effect on suppression of Zry corrosion. In contrast, the alloying elements in Zry showed a negative effect on the process.
C) were also conducted. Results of the study indicated that the thickness of Zry plates decreased linearly with increase of soaking duration. The recession rate of Zry plates was increase with increase of testing temperatures. The value of apparent activation energy on the thickness recession rate of Zry plates was determined to be 333 kJ/mol. The alloying elements in SS showed a positive effect on suppression of Zry corrosion. In contrast, the alloying elements in Zry showed a negative effect on the process.