Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(2), p.96 - 110, 2024/12
Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste requires not only selecting sites appropriate for the waste repository, where its isolation ability would not be damaged by natural phenomena for several tens of thousands of years, but also rationally constructing the disposal system depending on site-specific geological environments and their anticipated long-term variability. Recently, elemental/isotopic compositions of underground fluids (deep groundwaters, hot/cold spring waters, brines associated with oil and natural gas reservoirs, and so on) in Japan have been studied for evaluating the long-term stability of the geological environments of this country. Iodine and its radioactive isotope  I (half-life = 15.7 million years) are included in the subjects of the study. The current review paper provides overviews of (i) the iodine content and iodine-129/127 ratio (
I (half-life = 15.7 million years) are included in the subjects of the study. The current review paper provides overviews of (i) the iodine content and iodine-129/127 ratio ( I/
I/ I ratio) of various materials in Earth's surface layers, (ii) relevant sample pretreatments and measurements, and (iii)
I ratio) of various materials in Earth's surface layers, (ii) relevant sample pretreatments and measurements, and (iii)  I/
I/ I data of the underground fluids in Japan, then gives (iv) some interpretations of the fluid
I data of the underground fluids in Japan, then gives (iv) some interpretations of the fluid  I/
I/ I data, along with their problems and uncertainties, and (v) some implications towards evaluating the long-term stability of geological environments.
I data, along with their problems and uncertainties, and (v) some implications towards evaluating the long-term stability of geological environments.
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
 Fe and
Fe and  Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovae
Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovaeWallner, A.*; Froehlich, M. B.*; Hotchkis, M. A. C.*; Kinoshita, N.*; Paul, M.*; Martschini, M.*; Pavetich, S.*; Tims, S. G.*; Kivel, N.*; Schumann, D.*; et al.
Science, 372(6543), p.742 - 745, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:97.04(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Half of the chemical elements heavier than iron are produced by the rapid neutron capture process (r-process). The sites and yields of this process are disputed, with candidates including some types of supernovae (SNe) and mergers of neutron stars. We search for two isotopic signatures in a sample of Pacific Ocean crust-iron-60 ( Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and
Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and  Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of
Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of  Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of
Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of  Pu. The
Pu. The  Pu/
Pu/ Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The
Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The  Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Nagano, Hirohiko*; Sugiharto, U.*; Saengkorakot, C.*; Suzuki, Takashi; Kokubu, Yoko; Fujita, Natsuko; Kinoshita, Naoki; Nagai, Haruyasu; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-012, 53 Pages, 2020/10
There is growing concern that recent rapid changes in climate and environment could have a significant influence on carbon cycling in terrestrial ecosystems (especially forest ecosystems) and could consequently lead to a positive feedback for global warming. The magnitude and timing of this feedback remain highly uncertain largely due to a lack of quantitative understanding of the dynamics of organic carbon stored in soils and its responses to changes in climate and environment. The tracing of radiocarbon (natural and bomb-derived  C) and stable carbon (
C) and stable carbon ( C) isotopes through terrestrial ecosystems can be a powerful tool for studying soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics. The primary aim of this guide is to promote the use of isotope-based approaches to improve our understanding of the carbon cycling in soils, particularly in the Asian region. The guide covers practical methods of soil sampling; treatment and fractionation of soil samples; preparation of soil samples for
C) isotopes through terrestrial ecosystems can be a powerful tool for studying soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics. The primary aim of this guide is to promote the use of isotope-based approaches to improve our understanding of the carbon cycling in soils, particularly in the Asian region. The guide covers practical methods of soil sampling; treatment and fractionation of soil samples; preparation of soil samples for  C (and stable nitrogen isotope,
C (and stable nitrogen isotope,  N) and
N) and  C analyses; and
C analyses; and  C,
C,  N, and
N, and  C measurements by the use of isotope ratio mass spectrometry and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). The guide briefly introduces ways to report
C measurements by the use of isotope ratio mass spectrometry and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). The guide briefly introduces ways to report  C data, which are frequently used for soil carbon cycling studies. The guide also reports results of a case study conducted in a Japanese forest ecosystem, as a practical application of the use of isotope-based approaches. This guide is mainly intended for researchers who are interested but are not experienced in this research field. The guide will hopefully encourage readers to participate in soil carbon cycling studies, including field works, laboratory experiments, isotope analyses, and discussions with great interest.
C data, which are frequently used for soil carbon cycling studies. The guide also reports results of a case study conducted in a Japanese forest ecosystem, as a practical application of the use of isotope-based approaches. This guide is mainly intended for researchers who are interested but are not experienced in this research field. The guide will hopefully encourage readers to participate in soil carbon cycling studies, including field works, laboratory experiments, isotope analyses, and discussions with great interest.
 C activities in tree rings near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
C activities in tree rings near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantMatsunaka, Tetsuya*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Takahashi, Tsutomu*; Matsumura, Masumi*; Satou, Yukihiko; Shen, H.*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Radiocarbon, 61(6), p.1633 - 1642, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.19(Geochemistry & Geophysics) Be concentrations in bed-sediments of Ado and Yasu rivers flowing into Lake Biwa
Be concentrations in bed-sediments of Ado and Yasu rivers flowing into Lake BiwaFujisawa, Jumpei*; Minami, Masayo*; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
JAEA-Conf 2018-002, p.91 - 94, 2019/02
Beryllium-10 ( Be) of a cosmogenic nuclide precipitates in forms of BeO and Be(OH)
Be) of a cosmogenic nuclide precipitates in forms of BeO and Be(OH) attaching with aerosol on the Earth surface. It is accumulated on the sea- and lake-bottoms. Recently, the meteoric
attaching with aerosol on the Earth surface. It is accumulated on the sea- and lake-bottoms. Recently, the meteoric  Be is attracting attention as a powerful tool for investigating the past climate change, because it is affected by the earth- and lorcal- cyclical changes of materials such as atmosphere and water circulation. The
Be is attracting attention as a powerful tool for investigating the past climate change, because it is affected by the earth- and lorcal- cyclical changes of materials such as atmosphere and water circulation. The  Be exists mostly as hydroxide at pH
Be exists mostly as hydroxide at pH  5, and is easy to adhere to soil and mineral surface. Therefore,
5, and is easy to adhere to soil and mineral surface. Therefore,  Be concentration in sediment could be influenced by its grain size composition because fine-grained sediment has a big surface area per unit mass. The purpose of this study is to reveal the relationship between
Be concentration in sediment could be influenced by its grain size composition because fine-grained sediment has a big surface area per unit mass. The purpose of this study is to reveal the relationship between  Be concentrations and the grain-size of river sediments. The samples used were bottom-sediments of 18 rivers flowing into Lake Biwa, Japan. The sediments were sieved to 5 fractions and analyzed each for
Be concentrations and the grain-size of river sediments. The samples used were bottom-sediments of 18 rivers flowing into Lake Biwa, Japan. The sediments were sieved to 5 fractions and analyzed each for  Be concentration by JAEA-AMS-TONO.
Be concentration by JAEA-AMS-TONO.
Togo, Yoko*; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Amano, Yuki; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*; Suzuki, Yohei*; Terada, Yasuko*; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Ito, Kazumasa*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 191, p.165 - 186, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:76.66(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Iodine distribution, speciation, and isotope ratio ( I/
I/ I) in both rock and groundwater phases were determined to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shale. It was suggested that I
I) in both rock and groundwater phases were determined to investigate long-term migration of iodine in diatomaceous and siliceous shale. It was suggested that I is released to the ground water during the progress of the maturation of organic matter. Dissociated I
is released to the ground water during the progress of the maturation of organic matter. Dissociated I could move toward the surface because of the upward water flow driven by the compaction during burial diagenetic process. Thus, iodine rich brine is created by integration of iodine released from underlying formations. Because of low affinity of I
could move toward the surface because of the upward water flow driven by the compaction during burial diagenetic process. Thus, iodine rich brine is created by integration of iodine released from underlying formations. Because of low affinity of I to solid phase, released I
to solid phase, released I remains in solution phase, and the concentration of the iodine in the solution has been possibly increasing during sedimentation history.
remains in solution phase, and the concentration of the iodine in the solution has been possibly increasing during sedimentation history.
 O
O thin films on Si (100) by ion beam sputter deposition
thin films on Si (100) by ion beam sputter depositionMao, W.*; Fujita, Masaya*; Chikada, Takumi*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Surface & Coatings Technology, 283, p.241 - 246, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.82(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Single-phase nanocrystalline thin films of Er O
O (440) has been first prepared using Si (100) substrates by ion beam sputter deposition at 973 K at a pressure of
(440) has been first prepared using Si (100) substrates by ion beam sputter deposition at 973 K at a pressure of  10
10 Pa and
Pa and 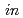 -
-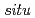 annealing at 1023 K at a pressure of
annealing at 1023 K at a pressure of  10
10 Pa. Er silicides formed during the deposition are eliminated via the annealing, which results in the single phase and the smooth surface of the Er
Pa. Er silicides formed during the deposition are eliminated via the annealing, which results in the single phase and the smooth surface of the Er O
O thin films. The epitaxial relationship between Si (100) and Er
thin films. The epitaxial relationship between Si (100) and Er O
O (110) is clarified by X-ray diffraction and reflection high energy electron diffraction.
(110) is clarified by X-ray diffraction and reflection high energy electron diffraction.
Katayama, Atsushi; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Dai-10-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.234 - 237, 2008/00
The determination of  I by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) has generally been used measurement targets from AgI precipitation. For more sensitive determination of
I by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) has generally been used measurement targets from AgI precipitation. For more sensitive determination of  I, it is necessary to reduce the quantity of iodine carrier for precipitation. But, more than 1mg is the amount of carrier stable iodine needed at present to make a reliable sample treatment and AMS determination. In this study, we examined the basics of procedures of the direct measurement target that used adsorption reaction of the molecular iodine to the metal silver surface in substitution for precipitation. Using this procedure, we have prepared measurement targets with a carrier from 1 to 0.2 mg iodine.
I, it is necessary to reduce the quantity of iodine carrier for precipitation. But, more than 1mg is the amount of carrier stable iodine needed at present to make a reliable sample treatment and AMS determination. In this study, we examined the basics of procedures of the direct measurement target that used adsorption reaction of the molecular iodine to the metal silver surface in substitution for precipitation. Using this procedure, we have prepared measurement targets with a carrier from 1 to 0.2 mg iodine.
Kato, Mineo; Ito, Takeshi*; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka; Tanase, Masakazu; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
Fusion Science and Technology, 41(3), p.859 - 862, 2002/05
JAERI has a plane to develop a compact tritium gas recycling system for fusion research. This system is also very attractive for the muon-catalyzed fusion ( CF) research at RIKEN-RAL Muon Facility in UK. For the research, JAERI has produced high purity tritium gas of 1,500 Ci and transported it to the Facility. In the
CF) research at RIKEN-RAL Muon Facility in UK. For the research, JAERI has produced high purity tritium gas of 1,500 Ci and transported it to the Facility. In the  CF experiments, the tritium gas was diluted by the deuterium in an optional concentration and the used tritium gas was carried back by the tritium transport container developed to JAERI. If it is possible to recycle the diluted tritium gas, i.e., the used tritium gas is enriched in the experimental site, the
CF experiments, the tritium gas was diluted by the deuterium in an optional concentration and the used tritium gas was carried back by the tritium transport container developed to JAERI. If it is possible to recycle the diluted tritium gas, i.e., the used tritium gas is enriched in the experimental site, the  CF experiments should be conducted efficiently. rom the above point of view, in this paper, we propose the compact tritium gas recycling system based on the gas chromatography that has already developed in JAERI and a proton conductor.
CF experiments should be conducted efficiently. rom the above point of view, in this paper, we propose the compact tritium gas recycling system based on the gas chromatography that has already developed in JAERI and a proton conductor.
 He transfer in solid T
He transfer in solid T studied by X-ray and neutron detection
studied by X-ray and neutron detectionMatsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Hashimoto, Masashi; Sugai, Hiroyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.229 - 234, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; Sakamoto, Shinichi*; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.213 - 215, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 sticking and fusion neutrons in solid/liquid D-T mixtures of high tritium concentration
sticking and fusion neutrons in solid/liquid D-T mixtures of high tritium concentrationIshida, Katsuhiko*; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; ; ; Sakamoto, Shinichi*; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.203 - 208, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Tanase, Masakazu; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
KEK Proceedings 99-11, p.113 - 127, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
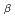 /K
/K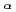 ratio of muon to
ratio of muon to  sticking X-rays in muon catalyzed d-t fusion at RIKEN-RAL muon facility
sticking X-rays in muon catalyzed d-t fusion at RIKEN-RAL muon facility; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; Sakamoto, Shinichi*; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.209 - 212, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
 /T
/T target of muon-catalyzed fusion experiments
target of muon-catalyzed fusion experimentsKudo, Hiroshi; Fujie, Makoto; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Umezawa, Hirokazu; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 43(5), p.577 - 583, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 -sticking phenomena in muon catalyzed fusion for a high density D-T mixture with 30% tritium concentration
-sticking phenomena in muon catalyzed fusion for a high density D-T mixture with 30% tritium concentrationNagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; ; ; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; ; ; ; et al.
Muon Catal. Fusion, 5-6, p.289 - 295, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
Mitsuguchi, Takehiro; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Katayama, Atsushi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Suzuki, Takashi; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*; Kimura, Kenichi*; Kinno, Masaharu*; Amano, Hikaru; Nakashima, Mikio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English