Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H.; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Instruments & Instrumentation) muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
 H
H perovskite lattice associated with hydrogen exchange and transport
perovskite lattice associated with hydrogen exchange and transportIto, Takashi; Koda, Akihiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Kobayashi, Yoji*; Kageyama, Hiroshi*
Physical Review B, 95(2), p.020301_1 - 020301_5, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:52.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Nakahara, Kazutaka*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Kato, Mineo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.957 - 961, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:46.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)The muon science facility (MUSE) is one of the experimental areas of the J-PARC. The MUSE facility is located in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF), which is a building integrated to include both neutron and muon science programs. Construction of the MLF building was started at the beginning of 2004, and was recently completed at the end of the 2006 fiscal year. We have been working on the installation of the beamline components, expecting the first muon beam in the autumn of 2008.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Beveridge, J. L.*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Fukuchi, Koichi*; Sato, Nobuhiko*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.484 - 487, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.27(Physics, Condensed Matter)The construction of the Materials and Life Science building was started in the beginning of the fiscal year of 2004. After commissioning of the accelerator and beam transport sections in 2008, muon beams will be available for users in 2009. In this letter, the latest construction status of the J-PARC Muon Science Facility is reported.
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Strasser, P.*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Beveridge, J. L.*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Sato, Nobuhiko*; Fukuchi, Koichi*; et al.
Nuclear Physics B; Proceedings Supplements, 149, p.393 - 395, 2005/12
The J-PARC muon science experimental area is planned to be located in the integrated building of the facility for materials and life science study. One muon target will be installed upstream of the neutron target. The main feature of the facility is introduced.
Kato, Mineo; Ito, Takeshi*; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka; Tanase, Masakazu; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
Fusion Science and Technology, 41(3), p.859 - 862, 2002/05
JAERI has a plane to develop a compact tritium gas recycling system for fusion research. This system is also very attractive for the muon-catalyzed fusion ( CF) research at RIKEN-RAL Muon Facility in UK. For the research, JAERI has produced high purity tritium gas of 1,500 Ci and transported it to the Facility. In the
CF) research at RIKEN-RAL Muon Facility in UK. For the research, JAERI has produced high purity tritium gas of 1,500 Ci and transported it to the Facility. In the  CF experiments, the tritium gas was diluted by the deuterium in an optional concentration and the used tritium gas was carried back by the tritium transport container developed to JAERI. If it is possible to recycle the diluted tritium gas, i.e., the used tritium gas is enriched in the experimental site, the
CF experiments, the tritium gas was diluted by the deuterium in an optional concentration and the used tritium gas was carried back by the tritium transport container developed to JAERI. If it is possible to recycle the diluted tritium gas, i.e., the used tritium gas is enriched in the experimental site, the  CF experiments should be conducted efficiently. rom the above point of view, in this paper, we propose the compact tritium gas recycling system based on the gas chromatography that has already developed in JAERI and a proton conductor.
CF experiments should be conducted efficiently. rom the above point of view, in this paper, we propose the compact tritium gas recycling system based on the gas chromatography that has already developed in JAERI and a proton conductor.
; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; Sakamoto, Shinichi*; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.213 - 215, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 He transfer in solid T
He transfer in solid T studied by X-ray and neutron detection
studied by X-ray and neutron detectionMatsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Hashimoto, Masashi; Sugai, Hiroyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.229 - 234, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; ; G.H.Eaton*
Hyperfine Interactions, 119(1-4), p.361 - 363, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 sticking and fusion neutrons in solid/liquid D-T mixtures of high tritium concentration
sticking and fusion neutrons in solid/liquid D-T mixtures of high tritium concentrationIshida, Katsuhiko*; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; ; ; Sakamoto, Shinichi*; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.203 - 208, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Tanase, Masakazu; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
KEK Proceedings 99-11, p.113 - 127, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
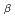 /K
/K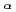 ratio of muon to
ratio of muon to  sticking X-rays in muon catalyzed d-t fusion at RIKEN-RAL muon facility
sticking X-rays in muon catalyzed d-t fusion at RIKEN-RAL muon facility; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; Sakamoto, Shinichi*; ; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 118(1-4), p.209 - 212, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
 /T
/T target of muon-catalyzed fusion experiments
target of muon-catalyzed fusion experimentsKudo, Hiroshi; Fujie, Makoto; Tanase, Masakazu; Kato, Mineo; Kurosawa, Kiyoyuki; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Umezawa, Hirokazu; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Nagamine, Kanetada*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 43(5), p.577 - 583, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 -sticking phenomena in muon catalyzed fusion for a high density D-T mixture with 30% tritium concentration
-sticking phenomena in muon catalyzed fusion for a high density D-T mixture with 30% tritium concentrationNagamine, Kanetada*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; ; ; ; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; ; ; ; et al.
Muon Catal. Fusion, 5-6, p.289 - 295, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
 SR study of BaTiO
SR study of BaTiO hydride
hydrideIto, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Tomono, Dai*; Kobayashi, Yoji*; Sakaguchi, Tatsunori*; Kageyama, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 hydrides probed by
hydrides probed by  SR
SRIto, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Tomono, Dai*; Kobayashi, Yoji*; Sakaguchi, Tatsunori*; Kageyama, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Nakagaki, Reiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Miura, Taichi*; Higemoto, Wataru; Shinohara, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English