Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Seki, Akiyuki; Mayumi, Akie; Wainwright-Murakami, Haruko*; Saito, Kimiaki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.158 - 164, 2020/10
We developed a method to estimate the temporal change of the air dose rate at the location with sparse (in time) measurements by using the continuous measurement data from the nearby monitoring post. This method determines an observation model from the correlation between sparse data at the target location and dense data at the monitoring post based on a hierarchical Bayesian model. The developed method was validated against the air dose rate measured at the monitoring posts in Fukushima prefecture from 2012 to 2017. The results showed that the developed method can predict the air dose rate at almost all target locations with an error rate of less than 10%.
Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu
Journal of Supercomputing, 75(12), p.8115 - 8146, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.73(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)A communication-avoiding generalized minimum residual method (CA-GMRES) is implemented on a hybrid CPU-GPU cluster, targeted for the performance acceleration of iterative linear system solver in the gyrokinetic toroidal five-dimensional Eulerian code GT5D. In addition to the CA-GMRES, we implement and evaluate a modified variant of CA-GMRES (M-CA-GMRES) proposed in our previous study to reduce the amount of floating-point calculations. This study demonstrates that beneficial features of the CA-GMRES are in its minimum number of collective communications and its highly efficient calculations based on dense matrix-matrix operations. The performance evaluation is conducted on the Reedbush-L GPU cluster, which contains four NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs per compute node. The evaluation results show that the M-CA-GMRES is 1.09x, 1.22x and 1.50x faster than the CA-GMRES, the generalized conjugate residual method (GCR), and the GMRES, respectively, when 64 GPUs are used.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.257 - 273, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.36(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)A preconditioned Chebyshev basis communication-avoiding conjugate gradient method (P-CBCG) is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in a multiphase thermal-hydraulic CFD code JUPITER, and its computational performance and convergence properties are compared against a preconditioned conjugate gradient (P-CG) method and a preconditioned communication-avoiding conjugate gradient (P-CACG) method on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8,208 KNLs. The P-CBCG method reduces the number of collective communications with keeping the robustness of convergence properties. Compared with the P-CACG method, an order of magnitude larger communication-avoiding steps are enabled by the improved robustness. It is shown that the P-CBCG method is 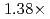 and
and 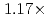 faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Asahi, Yuichi*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 8th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA 2017), p.7_1 - 7_8, 2017/11
A communication-avoiding generalized minimal residual (CA-GMRES) method is applied to the gyrokinetic toroidal five dimensional Eulerian code GT5D, and its performance is compared against the original code with a generalized conjugate residual (GCR) method on the JAEA ICEX (Haswell), the Plasma Simulator (FX100), and the Oakforest-PACS (KNL). The CA-GMRES method has 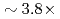 higher arithmetic intensity than the GCR method, and thus, is suitable for future Exa-scale architectures with limited memory and network bandwidths. In the performance evaluation, it is shown that compared with the GCR solver, its computing kernels are accelerated by
higher arithmetic intensity than the GCR method, and thus, is suitable for future Exa-scale architectures with limited memory and network bandwidths. In the performance evaluation, it is shown that compared with the GCR solver, its computing kernels are accelerated by 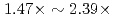 , and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from
, and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from 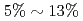 to
to 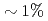 of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 7th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA 2016) (Internet), p.17 - 24, 2016/11
The left-preconditioned communication avoiding conjugate gradient (LP-CA-CG) method is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in the multiphase CFD code JUPITER. The arithmetic intensity of the LP-CA-CG method is analyzed, and is dramatically improved by loop splitting for inner product operations and for three term recurrence operations. Two LP-CA-CG solvers with block Jacobi preconditioning and with underlap preconditioning are developed. It is shown that on the K computer, the LP-CA-CG solvers with block Jacobi preconditioning is faster, because the performance of local point-to-point communications scales well, and the convergence property becomes worse with underlap preconditioning. The LP-CA-CG solver shows good strong scaling up to 30,000 nodes, where the LP-CA-CG solver achieved higher performance than the original CG solver by reducing the cost of global collective communications by 69%.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamada, Susumu; Ina, Takuya; Yamashita, Susumu
no journal, ,
In order to simulate molten core relocation behavior in the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, JAEA has been developed the JUPITER code, which analyzes a multi-phase thermal-hydraulic problem. Although the current simulation can analyze a fraction of a single fuel assembly, Exa-scale machines are needed to simulate whole part of the molten core. The JUPITER code is based on a incompressible fluid model, and thus, the main part of the computational cost comes from an iterative solver for the Poisson equation. Since the communication cost in the Poisson solver is a bottleneck in improving scalability, avoiding the communication is of critical importance. In this work, we apply the Communication-Avoiding GMRES algorithm to the Poisson solver and evaluate its utility by investigating its convergence property in real problems.
Ina, Takuya; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamada, Susumu; Mayumi, Akie; Yamashita, Susumu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamada, Susumu; Ina, Takuya; Yamashita, Susumu
no journal, ,
In this work, we implemented the Communication-Avoiding CG (CA-CG) method to the Poisson solver in the JUPITER code, which analyzes a multi-phase thermal-hydraulic problem, and evaluated its convergence property and computational performance. We analyzed the degradation of the convergence property due to accumulation of numerical errors associated with CA procedures, and applied quad-precision computation to a part of the CA-CG method to improve the convergence property.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
The left-preconditioned communication avoiding conjugate gradient (LP-CA-CG) method is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in the multiphase CFD code JUPITER. The arithmetic intensity of the LP-CA-CG method is analyzed, and is dramatically improved by loop splitting for inner product operations and for three term recurrence operations. The LP-CA-CG solver shows good strong scaling up to 30,000 nodes on the K computer.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
The left-preconditioned communication avoiding conjugate gradient (LP-CA-CG) method is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in the multiphase CFD code JUPITER. Two LP-CA-CG solvers with block Jacobi preconditioning and with underlap preconditioning are developed. The former is developed based on a hybrid CA approach, in which CA is applied only to global collective communications for inner product operations. The latter is a full CA approach, in which CA is applied also to local point-to-point communications in sparse matrix-vector (SpMV) operations and preconditioning. CA-SpMV requires additional computation for overlapping regions. It is shown that on the K computer, the LP-CA-CG solvers with block Jacobi preconditioning is faster, because the performance of local point-to-point communications scales well, and the convergence property becomes worse with underlap preconditioning. The LP-CA-CG solver shows good strong scaling up to 30,000 nodes.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
Improvement of convergence property is an issue in applying the Communication-Avoiding CG (CA-CG) method to the Poisson solver in the JUPITER code, which analyzes a multi-phase thermal-hydraulic problem. In this work, we implemented the Chebyshev basis CG (CBCG) method and evaluated its convergence property in real problems. As a result, the CBCG method greatly improved robustness of the convergence property and succeeded in reducing collective communication to 2/3 compared with the CA-CG method.
Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu
no journal, ,
Communication avoiding (CA) Krylov methods are promising solutions for communication bottlenecks on supercomputers based on many core processors or accelerators. In this work, we implemented the CA-GMRES method on a GPU cluster, the HA-PACS, and evaluated its performance on a non-symmetric matrix solver from a nuclear CFD code. The result shows that the CA-GMRES method is significantly faster than the conventional Krylov methods such as the GMRES method and the GCR method.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Asahi, Yuichi*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
We propose a modified communication-avoiding generalized minimal residual (CA-GMRES) method, which reduces both computation and memory access by 30% with keeping the same CA property as the original CA-GMRES method. These numerical properties, less communication and computation with higher arithmetic intensity, are promising features for future exascale machines with limited memory and network bandwidths. The modified CA-GMRES method is applied to a large scale non-symmetric matrix in an implicit solver of the gyrokinetic toroidal five dimensional Eulerian code GT5D, and its performance is estimated on the Oakforest-PACS (KNL). The numerical experiment shows that compared with the generalized conjugate residual method, computing kernels are accelerated by 1.5x, and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from 12.5% to 1% of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
To improve the convergence property of the communication avoiding conjugate gradient (CA-CG) method is needed for applying it to ill conditioned problems such as the pressure Poisson equation in the multiphase CFD code JUPITER. In the CA-CG method, one can avoid more communication by increasing the number of CA steps. However, this makes the CA-CG method less robust against numerical errors. To resolve this problem, we apply the Chebyshev basis CG (CBCG) method to JUPITER.
Seki, Akiyuki; Mayumi, Akie; Murakami, Haruko*; Saito, Kimiaki; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Estimation of temporally continuous air dose rate for few measurement results was performed by hierarchical Bayesian estimation using the result of monitoring post (MP) that can measure frequently. In order to improve the accuracy of this estimation, a screening program was used to automatically eliminate the measurement results of MP containing outliers. Then, the validity of this estimation method was verified by comparison with estimation by other methods such as two-component model.