Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Joffrin, E.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:87.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)
Haga, Yoshinori; Bauer, E. D.*; Tobash, P. H.*; Mitchell, J. N.*; Ayala-Valenzuela, O.*; McDonald, R. D.*; Mielke, C. H.*; Fisk, Z.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 63(3), p.380 - 382, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary) H and H
H and H L transitions
L transitionsMiki, Kazuhiro; Diamond, P. H.*; Fedorczak, N.*; G rcan,
rcan,  . D.*; Malkov, M.*; Lee, C.*; Kosuga, Yusuke*; Tynan, G. R.*; Xu, G. S.*; Estrada, T.*; et al.
. D.*; Malkov, M.*; Lee, C.*; Kosuga, Yusuke*; Tynan, G. R.*; Xu, G. S.*; Estrada, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 53(7), p.073044_1 - 073044_10, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:71.99(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Understanding the L H and H
H and H L transitions is crucial to successful ITER operation. In this paper we present novel theoretical and modelling study results on the spatio-temporal dynamics of the transition. We place a special emphasis on the role of zonal flows and the micro
L transitions is crucial to successful ITER operation. In this paper we present novel theoretical and modelling study results on the spatio-temporal dynamics of the transition. We place a special emphasis on the role of zonal flows and the micro macro connection between dynamics and the power threshold dependences. The model studied evolves five coupled fields in time and one space dimension, in simplified geometry. The content of this paper is (a) the model fundamentals and the space-time evolution during the L
macro connection between dynamics and the power threshold dependences. The model studied evolves five coupled fields in time and one space dimension, in simplified geometry. The content of this paper is (a) the model fundamentals and the space-time evolution during the L I
I H transition, (b) the physics origin of the well-known
H transition, (b) the physics origin of the well-known 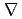 B-drift asymmetry in power threshold, (c) the role of heat avalanches in the intrinsic variability of the L
B-drift asymmetry in power threshold, (c) the role of heat avalanches in the intrinsic variability of the L H transition, (d) the dynamics of the H
H transition, (d) the dynamics of the H L back transition and the physics of hysteresis.
L back transition and the physics of hysteresis.
 L back transition
L back transitionMiki, Kazuhiro; Diamond, P. H.*; Schmitz, L.*; McDonald, D. C.*; Estrada, T.*; G rcan,
rcan,  . D.*; Tynan, G. R.*
. D.*; Tynan, G. R.*
Physics of Plasmas, 20(6), p.062304_1 - 062304_9, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:63.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Since ITER will operate close to threshold and with limited control, the H L back transition is a topic important for machine operations as well as physics. Using a reduced mesoscale model, we investigate ELM-free H
L back transition is a topic important for machine operations as well as physics. Using a reduced mesoscale model, we investigate ELM-free H L back transition dynamics in order to isolate transport physics effects. Model studies indicate that turbulence spreading is the key process which triggers the back transition. The transition involves a feedback loop linking turbulence and profiles. The I-phase appears during the back transition following a slow power ramp down, while fast ramp-downs reveal a single burst of zonal flow during the back transition. The I-phase nucleates at the pedestal shoulder, as this is the site of the residual turbulence in H-mode. Hysteresis in the profile gradient scale length is characterized by the Nusselt number. Relative hysteresis of temperature gradient vs density gradient is sensitive to the pedestal Prandtl number.
L back transition dynamics in order to isolate transport physics effects. Model studies indicate that turbulence spreading is the key process which triggers the back transition. The transition involves a feedback loop linking turbulence and profiles. The I-phase appears during the back transition following a slow power ramp down, while fast ramp-downs reveal a single burst of zonal flow during the back transition. The I-phase nucleates at the pedestal shoulder, as this is the site of the residual turbulence in H-mode. Hysteresis in the profile gradient scale length is characterized by the Nusselt number. Relative hysteresis of temperature gradient vs density gradient is sensitive to the pedestal Prandtl number.
Yoshida, Maiko; Kaye, S.*; Rice, J.*; Solomon, W.*; Tala, T.*; Bell, R. E.*; Burrell, K. H.*; Ferreira, J.*; Kamada, Yutaka; McDonald, D. C.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 52(12), p.123005_1 - 123005_11, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:61.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The purpose of this study is to find a common feature on momentum transport coefficients including diffusive and non-diffusive terms in all machines. The momentum database enables us to assess a parametric dependency of momentum transport in a wider range of dimensionless parameters related to transport. Such observation will contribute to make a scaling/modeling on momentum transport for future devices like ITER and DEMO. On the other hand, the investigation of a difference in observation by comparing the experimental conditions will give a useful information to realize what plasma parameter is the key for the momentum transport coefficients.
Saibene, G.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; L nnroth, J.*; Andrew, Y.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Andrew, Y.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.969 - 983, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:74.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper summarizes results of dimensionless identity experiments in JT-60U and JET, aimed at the comparison of the H-mode pedestal and ELM behaviour in the two devices. In general, pedestal pressure in JT-60U is lower than in JET. These results motivated a closer investigation of experimental conditions in the two devices, to identify possible "hidden" physics that prevents obtaining a good match of pedestal values over a large range of plasmas parameters. Ripple-induced ion losses of the medium bore plasma used in JT-60U for the similarity experiments are identified as the main difference with JET. The magnitude of the JT-60U ripple losses is sufficient to induce counter-toroidal rotation in co-injected plasma. The influence of ripple losses was demonstrated at high q plasma: reducing ripple losses by  2 by replacing positive with negative neutral beam injection resulted in an increased pedestal pressure in JT-60U, providing a good match to full power JET H-modes.
2 by replacing positive with negative neutral beam injection resulted in an increased pedestal pressure in JT-60U, providing a good match to full power JET H-modes.
McDonald, D. C.*; Cordey, J. G.*; Thomsen, K.*; Kardaun, O. J. W. F.*; Snipes, J. A.*; Greenwald, M.*; Sugiyama, L.*; Ryter, F.*; Kus, A.*; Stober, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(3), p.147 - 174, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:28.07(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper describes the updates to and analysis of the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) Global H-node Confinement Database version 3 (DB3) over the period 1994-2004. Global data, for the energy confinement time and its controlling parameters, have now been collected from 18 machines of different sizes and shapes: ASDEX, ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod CoMPASS-D, DIII-D, JET, JFT-2M, JT-60U, MAST, NSTX, PBX-M, PDX, START, T-10, TCV, TdeV, TFTR and TUMAN-3M. A wide range of physics studies has been performed on DB3 with particular progress made in the separation of core and edge behavior, dimensionless parameter analyses and the comparison of the database with one-dimensional transport code. A key aim of the database has always been to provide a basis for estimating the energy confinement properties of next step machines such as ITER, and so the impact of the database and its analysis on such machines is also discussed.
Kaye, S. M.*; Valovic, M.*; Chudnovskiy, A.*; Cordey, J. G.*; McDonald, D.*; Meakins, A.*; Thomsen, K.*; Akers, R.*; Bracco, G.*; Brickley, C.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A429 - A438, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:51.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effects of aspect ratio and beta on confinement scaling are studied with the use of the H-mode database extended by the low aspect ratio data from NSTX and MAST. Various statistical methods are applied. Development of scalings using engineering parameters as predictor variables results in the inverse-aspect-ratio scaling with the range from 0.38 to 1.29. The transformation of these scalings to physics variables results in an unfavorouble dependence of the normalized energy confinement time on beta. There is a strong correlation between the inverse aspect ratio and beta, and this makes scalings based on physics variables imprecise.
Stober, J.*; Lomas, P. J.*; Saibene, G.*; Andrew, Y.*; Belo, P.*; Conway, G. D.*; Herrmann, A.*; Horton, L. D.*; Kempenaars, M.*; Koslowski, H.-R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1213 - 1223, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:79.30(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 and collisionality approaching ITER conditions
and collisionality approaching ITER conditionsCordey, J. G.*; Thomsen, K.*; Chudnovskiy, A.*; Kardaun, O. J. W. F.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Snipes, J. A.*; Greenwald, M.*; Sugiyama, L.*; Ryter, F.*; Kus, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(9), p.1078 - 1084, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:82.04(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The condition of the latest version of the ELMy H-mode database has been re-examined. It is shown that there is bias in the ordinary least squares regression for some of the variables. To address these shortcomings three different techniques are employed: (a)principal component regression, (b)an error in variables technique and (c)the selection of a better conditioned dataset with fewer variables. Scalings in terms of the dimensionless physics valiables, as well as the standard set of engineering variables, are derived. The new scalings give a very similar performance for existing scalings for ITER at the standard beta, but a much improvement performance at higher beta.
Joffrin, E.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Becoulet, A.*; Bertalot, L.*; Budny, R.*; Buratti, P.*; Belo, P.*; Challis, C. D.*; Crisanti, F.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(7), p.626 - 634, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:101 Percentile:93.07(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Joffrin, E.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Becoulet, A.*; Budny, R.*; Buratti, P.*; Belo, P.*; Challis, C. D.*; Crisanti, F.*; de Baar, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Saibene, G.*; Hatae, Takaki; Campbell, D. J.*; Cordey, J. G.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Guenther, K.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A195 - A205, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:33.90(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Towards establishment of the control scheme and evaluation of the H-mode pedestal structure and behavior of the Edge Localized Mode (ELM) in ITER, we carried out an comparison experiment among the two large tokamaks (JT-60 and JET) for the first time. This paper report the initial results. In both devices, the same plasma shape was adopted and the three non-dimensional parameters (beta, normalized gyro radius and the normalized collisionality) were set identical. The pedestal width was almost similar in the two devices, however the pressure gradient was higher in JET by a factor of 1.5. The possible reason is a small aspect ration in JET.
Saibene, G.*; McDonald, D. C.*; Beurskens, M.*; Salmi, A.*; Lonnroth, J. S.*; Parail, V.*; de Vries, P.*; Andrew, Y.*; Budny, R.*; Boboc, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
This paper describes the results of dedicated experiments carried out in JET, where H-mode plasmas properties were studied for varying levels of toroidal field ripple, in the range from 0.08% (natural 
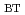 for JET) up to
for JET) up to 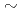 1%. The experiments were carried out in the ELMy H-mode regime with q
1%. The experiments were carried out in the ELMy H-mode regime with q =3 to 3.6, to investigate the effect of
=3 to 3.6, to investigate the effect of 
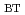 on pedestal and core properties of the plasma. These experiments show that toroidal field ripple has a clear effect on H-mode properties, although the physics mechanisms at the root of the reduced energy confinement with
on pedestal and core properties of the plasma. These experiments show that toroidal field ripple has a clear effect on H-mode properties, although the physics mechanisms at the root of the reduced energy confinement with 
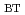 have not been identified unambiguously. Plasma density pump out and reduction of the global energy confinement is found for
have not been identified unambiguously. Plasma density pump out and reduction of the global energy confinement is found for 
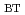
 0.5%, but the magnitude of this effect depends on plasma parameters. Ripple may also affect pedestal pressure, as well as size and frequency of ELMs. Plasma toroidal rotation was also strongly affected by ripple.
0.5%, but the magnitude of this effect depends on plasma parameters. Ripple may also affect pedestal pressure, as well as size and frequency of ELMs. Plasma toroidal rotation was also strongly affected by ripple.

Haga, Yoshinori; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Yasuoka, Hiroshi; Fisk, Z.; Bauer, E. D.*; Mitchell, J. N.*; Tobash, P. H.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ayala-Valenzuela, O.*; McDonald, R.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miki, Kazuhiro; Diamond, P. H.*; Schmitz, L.*; McDonald, D. C.*; Gurcan, O.*; Tynan, G. R.*
no journal, ,
Since ITER will operate close to threshold and with limited control, the H-L back transition is a topic important for machine operations as well as physics. Using a reduced mesoscale model, we investigate ELM-free H-L back transition dynamics. Model studies indicate that turbulence spreading is the key process which triggers the back transition. The transition involves a feedback loop linking turbulence and profiles. The I-phase appears during the back transition following a slow power ramp down, while fast ramp-down reveal a single burst of zonal flow during the back transition. The I-phase nucleates at the pedestal shoulder, as this is the site of the residual turbulence in H-mode. Hysteresis in profile gradient is characterized by the Nusselt number. Relative hysteresis of temperature gradient vs density gradient is sensitive to the pedestal Prandtl number. We expect the H-mode to be somewhat more resilient in density than in temperature.