Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Heussner, F.*; Talmelli, G.*; Geilen, M.*; Heinz, B.*; Br cher, T.*; Meyer, T.*; Ciubotaru, F.*; Adelmann, C.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Serga, A. A.*; et al.
cher, T.*; Meyer, T.*; Ciubotaru, F.*; Adelmann, C.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Serga, A. A.*; et al.
Physica Status Solidi; Rapid Research Letters, 14(4), p.1900695_1 - 1900695_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Gepr gs, S.*; Kehlberger, A.*; Coletta, F.*; Qiu, Z.*; Guo, E.-J.*; Schulz, T.*; Mix, C.*; Meyer, S.*; Kamra, A.*; Althammer, M.*; et al.
gs, S.*; Kehlberger, A.*; Coletta, F.*; Qiu, Z.*; Guo, E.-J.*; Schulz, T.*; Mix, C.*; Meyer, S.*; Kamra, A.*; Althammer, M.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 7, p.10452_1 - 10452_6, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:155 Percentile:97.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -decay half-lives of 110 neutron-rich nuclei across the
-decay half-lives of 110 neutron-rich nuclei across the  =82 shell gap; Implications for the mechanism and universality of the astrophysical
=82 shell gap; Implications for the mechanism and universality of the astrophysical  process
processLorusso, G.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Shimizu, Y.*; Simpson, G. S.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Watanabe, H.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Watanabe, H.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 114(19), p.192501_1 - 192501_7, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:164 Percentile:98.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Althammer, M.*; Meyer, S.*; Nakayama, Hiroyasu*; Schreier, M.*; Altmannshofer, S.*; Weiler, M.*; Huebl, H.*; Gepr gs, S.*; Opel, M.*; Gross, R.*; et al.
gs, S.*; Opel, M.*; Gross, R.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 87(22), p.224401_1 - 224401_15, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:422 Percentile:99.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We experimentally investigate and quantitatively analyze the spin Hall magnetoresistance (SMR) effect in ferromagnetic insulator (FI)/Pt and FI/nonmagnetic metal/Pt hybrid structures. For the FI, we use either YIG, nickel ferrite, or magnetite and for the nonmagnet, Cu or Au. The SMR is theoretically ascribed to the combined action of spin Hall and inverse spin Hall effect in the Pt top layer. It therefore should characteristically depend upon the orientation of the magnetization in the adjacent ferromagnet and prevail even if an additional, nonmagnetic metal layer is inserted between Pt and the ferromagnet. Our experimental data corroborate these theoretical conjectures. Using the SMR theory to analyze our data, we extract the spin Hall angle and the spin diffusion length in Pt. For a spin-mixing conductance of 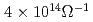 m
m , we obtain a spin Hall angle of 0.11
, we obtain a spin Hall angle of 0.11  0.08 and a spin diffusion length of (1.5
0.08 and a spin diffusion length of (1.5  0.5) nm for Pt in our samples.
0.5) nm for Pt in our samples.
Ostermeyer, M.*; Kong, H.-J.*; Kovalev, V. I.*; Harrison, R. G.*; Fotiadi, A. A.*; M gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
gret, P.*; Kalal, M.*; Slezak, O.*; Yoon, J. W.*; Shin, J. S.*; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 26(3), p.297 - 362, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:55.6(Physics, Applied)Frank, T.*; Pensl, G.*; Tana-Zaera, R.*; Z
 iga-P
iga-P rez, J.*; Mart
rez, J.*; Mart nez-Tom
nez-Tom s, C.*; Mu
s, C.*; Mu oz-Sanjos
oz-Sanjos , V.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; Hofmann, D.*; Pfisterer, D.*; et al.
, V.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; Hofmann, D.*; Pfisterer, D.*; et al.
Applied Physics A, 88(1), p.141 - 145, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:82.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy (DLTS) measurements were carried out to investigate defects in vapor-phase grown ZnO crystals. The generation of defect center labeled E4 subsequent to annealing in different ambients was monitored. By conducting electron irradiations with energies, where either both the Zn- and O-sublattice are damaged or according to only the Zn-lattice, a chemical assignment to the defect centers E4 and E3 could be accomplished. DLTS investigations of ZnO samples under illumination give an evidence that E4 is a negative-U center.
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
 C for 10,000h
C for 10,000hSchroer, C.*; Voss, Z.*; Wedemeyer, O.*; Novotny, J.*; Konys, J.*; Heinzel, A.*; Weisenburger, A.*; M ller, G.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Aoto, Kazumi
ller, G.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Aoto, Kazumi
JNC TY9400 2005-020, 45 Pages, 2005/08
This report summarises the results of exposure experiments on the behaviour of 12Cr-2W steel P122 and an 9Cr-2W ODS-steel in oxygen-containing flowing lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) at 550 C, which were performed in the CORRIDA loop at the Karlsruhe Lead Laboratory (KALLA) as part of the collaboration between the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute and the Karlsruhe Research Centre. The duration of these experiments was nominally 800, 2000, 5000 and 10,000 h. Both steels were tested after surface-finishing by turning and after surface alloying with aluminium in the GESA-facility. Owing to initial problems with the enrichment of oxygen in the flowing LBE, the oxygen content considerably varied during most of these experiments, so that the influence of temporary changes in the oxygen content of the LBE could also be investigated. The behaviour of P122 and ODS at permanently high oxygen content was deduced from an experiment for 4990 h at 550
C, which were performed in the CORRIDA loop at the Karlsruhe Lead Laboratory (KALLA) as part of the collaboration between the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute and the Karlsruhe Research Centre. The duration of these experiments was nominally 800, 2000, 5000 and 10,000 h. Both steels were tested after surface-finishing by turning and after surface alloying with aluminium in the GESA-facility. Owing to initial problems with the enrichment of oxygen in the flowing LBE, the oxygen content considerably varied during most of these experiments, so that the influence of temporary changes in the oxygen content of the LBE could also be investigated. The behaviour of P122 and ODS at permanently high oxygen content was deduced from an experiment for 4990 h at 550 C and (c
C and (c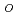
 5
5 10
10 mass-% or a
mass-% or a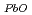
 10
10 ). The results are compared with the findings of exposures to stagnant LBE at 550
). The results are compared with the findings of exposures to stagnant LBE at 550 C and c
C and c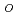 =10
=10 mass-% (COSTA-experiments).
mass-% (COSTA-experiments).
 C for 5,000h
C for 5,000hSchroer, C.*; Voss, Z.*; Wedemeyer, O.*; Novotny, J.*; Konys, J.*; Heinzel, A.*; Weisenburger, A.*; M ller, G.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Aoto, Kazumi
ller, G.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Aoto, Kazumi
JNC TY9400 2005-019, 26 Pages, 2005/08
This report summarises the results of exposure experiments on the behaviour of 12Cr-2W steel P122 joined by multi-run TIG welding in oxygen-containing flowing lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) at 550 C for nominally 800, 2000 and 5000 h. The flow velocity of the LBE and the mean oxygen content were 2 m/s and 5
C for nominally 800, 2000 and 5000 h. The flow velocity of the LBE and the mean oxygen content were 2 m/s and 5 10-7 mass-% (aPbO = 10-3), respectively. The influence of surface-alloying with aluminium (GESA-treatment) was also investigated in an exposure experiment for nominally 5000 h. The behaviour of the welded joint is generally comparable to that of P122 (after the standard heat-treatment), both qualitatively and quantitatively. Only few exceptions were observed which probably result from local peculiarities of the specific sample material. After surface alloying with aluminium, no significant oxidation and no liquid metal corrosion occurred in the centre of the specimens (including the weld seam), where the desired high quality of the aluminised layer was achieved.
10-7 mass-% (aPbO = 10-3), respectively. The influence of surface-alloying with aluminium (GESA-treatment) was also investigated in an exposure experiment for nominally 5000 h. The behaviour of the welded joint is generally comparable to that of P122 (after the standard heat-treatment), both qualitatively and quantitatively. Only few exceptions were observed which probably result from local peculiarities of the specific sample material. After surface alloying with aluminium, no significant oxidation and no liquid metal corrosion occurred in the centre of the specimens (including the weld seam), where the desired high quality of the aluminised layer was achieved.
Roth, J.*; Kirschner, A.*; Bohmeyer, W.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Cambe, A.*; Casarotto, E.*; Doerner, R.*; Gauthier, E.*; Federici, G.*; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.970 - 974, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:98.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In the frame work of the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity an attempt was made to establish a possible dependence of the chemical erosion yield of carbon on the ion flux,  , involving ion beam experiments, plasma simulators, and fusion devices. After data normalization a fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with
, involving ion beam experiments, plasma simulators, and fusion devices. After data normalization a fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with 
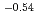 at high ion fluxes. With this dependence on ion flux a comprehensive description is available for chemical erosion as function of energy, temperature and ion flux. Using this dependence the erosion and redeposition of carbon in the ITER divertor can be calculated using the ERO code and the steady-state plasma scenario given by the ITER team. The resulting gross and net erosion rates are compared to previous estimates using a constant erosion yield of 1.5%. The use of the complete parameter dependence results in an order of magnitude lower erosion, most strongly determined by the temperature dependence and the reduction at the highest fluxes.
at high ion fluxes. With this dependence on ion flux a comprehensive description is available for chemical erosion as function of energy, temperature and ion flux. Using this dependence the erosion and redeposition of carbon in the ITER divertor can be calculated using the ERO code and the steady-state plasma scenario given by the ITER team. The resulting gross and net erosion rates are compared to previous estimates using a constant erosion yield of 1.5%. The use of the complete parameter dependence results in an order of magnitude lower erosion, most strongly determined by the temperature dependence and the reduction at the highest fluxes.
Roth, J.*; Preuss, R.*; Bohmeyer, W.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Cambe, A.*; Casarotto, E.*; Doerner, R.*; Gauthier, E.*; Federici, G.*; Higashijima, Satoru; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(11), p.L21 - L25, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:94 Percentile:91.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Chemical erosion of carbon has been studied in ion beam experiments, and the yield values are available as a function of ion energy and surface temperature. ITER divertor condition, however, cannot be simulated by ion beam. For extrapolating to ITER, the erosion must be investigated in plasma simulators and in SOL or divertors of present fusion devices. In the past, erosion values were reported, but the values showed a wide scatter as a function of ion flux,  . Therefore, a joint attempt was made through the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) to clarify the flux dependence. For each data point the local plasma conditions were normalized to impact energy of 30 eV, the data were selected for a surface temperature close to the maximum yield or to room temperature, and the diagnostic was calibrated in-situ. Through this procedure, the previous large scatter could be drastically reduced. A fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with
. Therefore, a joint attempt was made through the EU Task Force on Plasma-Wall Interaction and the International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA) to clarify the flux dependence. For each data point the local plasma conditions were normalized to impact energy of 30 eV, the data were selected for a surface temperature close to the maximum yield or to room temperature, and the diagnostic was calibrated in-situ. Through this procedure, the previous large scatter could be drastically reduced. A fit using Bayesian probability analysis was performed yielding a decrease of the erosion yield with 
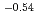 at high ion fluxes.
at high ion fluxes.
 C for 800 and 2000h
C for 800 and 2000hSchroer, G.*; Voss, V.*; Wedemeyer, O.*; Novotny, J.*; Konys, J.*; Heinzel, A.*; Weisenburger, A.*; M ller, G.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Aoto, Kazumi
ller, G.*; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Aoto, Kazumi
JNC TY9400 2004-023, 37 Pages, 2004/05
Johnsen, T.*; Meyer, G.*; Edvardsen, S. T.*; Rindahl, G.*; Sebok, A. L.*; Sivertsen, E. R.*
JNC TJ3440 2004-014, 169 Pages, 2004/03
In the VRdose R5 version the connection with the dynamic radiation evaluation system (DRES) was the main task. DRES can calculate the dose rate field of the Fugen plant in detail. By inserting special markers into the scenario, VRdose tells DRES what changes have been made to the model. The changes are about objects that are inserted, removed, cut or moved. DRES will then calculate new dose rate fields reflecting these changes. VRdose uses the new dose rate fields in the dose calculation of the workers in the scenario. The dose rate fields are switched automatically as VRdose plays the scenario and in the dose calculation. To minimize the calculation needed for DRES, VRdose can provide a volume enclosing only the area of interest for a given scenario and give the resolution of the calculation in all axes. In addition to the DRES connection, version R5 retrieves information about the objects in the model from the Fugen object database. Among the large amount of information available, are size, weight and surface contamination of Co-60 used. The wizard uses the size and weight information in the calculation of the man-work required. The surface contamination is used in a new feature that colorizes the objects after the contamination value. This makes it easier for workers to become aware of the contamination of pipes and pumps etc. R5 has been internationalized on all menus, buttons, messages and other text. VRdose can therefore be translated into any desired language. A feasibility study has been made into using Japanese characters in names and properties in the scenario. The manikins wear different protection masks and in version R5 the efficiency of the protection can be changed for each nuclide. Several other minor changes have been made, such as the ability to switch between extern dose and nuclide intake in the dose graph panels.