Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopyMibu, Ko*; Mitsui, Takaya; Tanaka, Masaaki*; Masuda, Ryo*; Kitao, Shinji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Seto, Makoto*
Journal of Applied Physics, 117(17), p.17E126_1 - 17E126_4, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.37(Physics, Applied) Fe polarization dependent synchrotron M
Fe polarization dependent synchrotron M ssbauer spectroscopy using a diamond phase plate and an iron borate nuclear Bragg monochromator
ssbauer spectroscopy using a diamond phase plate and an iron borate nuclear Bragg monochromatorMitsui, Takaya; Imai, Yasuhiko*; Masuda, Ryo*; Seto, Makoto*; Mibu, Ko*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 22(2), p.427 - 435, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.01(Instruments & Instrumentation) Fe-M
Fe-M ssbauer spectroscopy using nuclear monochromator
ssbauer spectroscopy using nuclear monochromatorMitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo; Hirao, Naohisa*; Mibu, Ko*; Seto, Makoto
Hyperfine Interactions, 204(1-3), p.97 - 100, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:86.30(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical) Fe-M
Fe-M ssbauer spectroscopy using a nuclear Bragg monochromator and its application to the study of magnetic thin films
ssbauer spectroscopy using a nuclear Bragg monochromator and its application to the study of magnetic thin filmsMitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo*; Seto, Makoto; Suharyadi, E.*; Mibu, Ko*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 19(2), p.198 - 204, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:66.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)An energy-domain grazing-incidence  Fe-M
Fe-M ssbauer spectroscopy(E-GIMS) with synchrotron radiation (SR) has been developed to studysurface and interface structures of thin films. A high-brilliant
ssbauer spectroscopy(E-GIMS) with synchrotron radiation (SR) has been developed to studysurface and interface structures of thin films. A high-brilliant  Fe-M
Fe-M ssbauer radiation, filtered from SR by a
ssbauer radiation, filtered from SR by a  FeBO
FeBO single crystal nuclear Bragg monochromator (NBM), allows us to perform the conventional M
single crystal nuclear Bragg monochromator (NBM), allows us to perform the conventional M ssbauer spectroscopy (MS) for the dilute
ssbauer spectroscopy (MS) for the dilute  Fe in a mirror-like film in any bunch-mode operation of SR. Theoretical and experimental study of the specular reflections from isotope-enriched (
Fe in a mirror-like film in any bunch-mode operation of SR. Theoretical and experimental study of the specular reflections from isotope-enriched ( Fe: 95%) and natural-abundance (
Fe: 95%) and natural-abundance ( Fe:
Fe:  2%) iron thin films has been carried out to clarify the basic features of coherent interference between electronic and nuclear resonant scattering of
2%) iron thin films has been carried out to clarify the basic features of coherent interference between electronic and nuclear resonant scattering of  Fe-Mo"ssbauer radiation in thin films. Moreover, a new surface and interface sensitive method has been developed by the combination of SR based E-GIMS and
Fe-Mo"ssbauer radiation in thin films. Moreover, a new surface and interface sensitive method has been developed by the combination of SR based E-GIMS and  Fe-probe layer technique, which enables us to probe interfacial complex magnetic structures in thin film with atomic-scale depth resolution.
Fe-probe layer technique, which enables us to probe interfacial complex magnetic structures in thin film with atomic-scale depth resolution.
Takeda, Masayasu; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Mibu, Ko*; Leli vre-Berna, E.*
vre-Berna, E.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 397(1-2), p.56 - 58, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)In Cr/Sn(001) multilayers in which monatomic Sn nonmagnetic layers are periodically embedded, spin-density-wave(SDW)s are formed below N el temperature like that in bulk Cr. It is, however, quite different to the SDW in bulk Cr. For instance the wavelength of the SDW is defined not by the nesting vector of Cr, but by the artificial periodicity introduced by the Sn layers. We did the spherical polarization analysis of this anomalous SDW structures by using CRYOPAD (CRYOgenics Polarization Analysis Device) as well as the one-dimensional polarization analysis.
el temperature like that in bulk Cr. It is, however, quite different to the SDW in bulk Cr. For instance the wavelength of the SDW is defined not by the nesting vector of Cr, but by the artificial periodicity introduced by the Sn layers. We did the spherical polarization analysis of this anomalous SDW structures by using CRYOPAD (CRYOgenics Polarization Analysis Device) as well as the one-dimensional polarization analysis.
Takeda, Masayasu; Mibu, Ko*; Shinjo, Teruya*; Endo, Yasuo*; Suzuki, Junichi
Physical Review B, 70(10), p.104408_1 - 104408_9, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:40.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Detailed magnetic structure of spin-density waves (SDWs) in epitaxial Cr(001)/Sn multilayer was investigated by neutron scattering combined with M ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
ssbauer spectroscopic studies. Monatomic Sn layers were embedded in 240 nm thick Cr(001) films with varying the periodic spacing from 4.2 to 16.2 nm. All samples were revealed to be a commensurate antiferromagnetic (CAF) phase at 300 K. The CAF structures changed to incommensurate SDW states with complex waveforms whose wavelength are controlled by the artificial periodicity at low temperatures although the CAF structure in the sample with the period of 4.2 nm persisted even at 10 K. The phase transition depends on the thickness of the Cr layers intervening between Sn monatomic layers. An appreciable phase slip in the SDW was observed during the phase transition in the sample with the period of 10.2 nm. The SDW structure is discussed by taking account of the competing forces between the nesting of Fermi surface and a pinning of antinodes at the Sn monatomic layers.
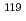 Sn monatomioc layers
Sn monatomioc layersJiko, Norihiro*; Almokhtar, M.*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Shinjo, Teruya*; Mibu, Ko*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 272-276(Part2), p.1233 - 1234, 2004/05
The growth-orientation dependence of magnetism of Cr/Sn and Fe/Cr/Sn/Cr multilayers was studied. For Fe/Cr/Sn/Cr multilayers, reduction of Cr magnetic moments was found in both (011)- and (001)-orientated samples, and the effect is larger in the former than the latter. In Cr/Sn multilayers, the (011)-oriented sample with the Cr layer thickness (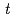
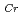
 ) of 80
) of 80
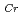
 80AA have a spin-density-wave structure with the wave vector perpendicular to the film plane.
80AA have a spin-density-wave structure with the wave vector perpendicular to the film plane.
Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Mibu, Ko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mibu, Ko*; Jiko, Norihiro*; Otsuka, Yuhei*; Takeda, Masayasu
no journal, ,
Magnetic structures of epitaxial Cr(001)/X multilayers, where monatomic layers of X (X = Sn, Au, Ag, V, or Fe) are periodically embedded in Cr, have been studied by neutron diffraction measurements using a triple-axis spectrometer. The temperature dependence of neutron diffraction patterns around the Cr(100) and Cr(010) reciprocal points, where magnetic peaks due to antiferromagnetic structures appear, was compared for Cr(001)/X multilayers with the same layer thickness, e.g., for [Cr(16.0 nm)/X(0.2 nm)] multilayers. It was clearly shown that the spin structure of Cr is quite different dependent on the monatomic counter metal, even when the Cr layer thickness is the same. The results are interpreted as a consequence of a competition between the interface effect, which enhances or quenches the magnetic moment of Cr at the interface regions, and the nesting effect, which stabilizes the incommensurate SDW structure with the modulation along the [001] axis.
Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Mibu, Ko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ssbauer spectroscopy using ultrahigh-brilliant probe beam
ssbauer spectroscopy using ultrahigh-brilliant probe beamMitsui, Takaya; Seto, Makoto; Masuda, Ryo; Mibu, Ko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ssbauer spectroscopy with diamond phase retarder and nuclear Bragg monochromator
ssbauer spectroscopy with diamond phase retarder and nuclear Bragg monochromatorMitsui, Takaya; Imai, Yasuhiko*; Seto, Makoto*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Matsuoka, Takehiro*; Mibu, Ko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English