Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 beam at J-PARC RCS
beam at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.59 - 63, 2023/11
 beam at J-PARC
beam at J-PARCSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Johnson, D. E.*
Proceedings of 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 23) (Internet), p.2335 - 2338, 2023/09
 laser stripping at J-PARC RCS
laser stripping at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.272 - 276, 2023/01
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.656 - 660, 2021/10
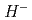 beam at J-PARC RCS
beam at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Liu, Y.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011025_1 - 011025_7, 2021/03
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011026_1 - 011026_6, 2021/03
The charge-exchange multi-turn injection by using a carbon stripper foil is adopted in high-intensity proton ring accelerators worldwide. It is a beneficial method to compress the pulsed proton beam with high intensity but there are serious issues for high intensity. First issue is a short lifetime of the foil by deformation or breaking itself. Another issue is high radiation dose corresponding to the scattered particles on the foil. Therefore, a non-destructive stripping injection method is required for higher intensity proton beam. We newly propose a non-destructive method of H stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
 laser stripping at J-PARC
laser stripping at J-PARCSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.436 - 440, 2020/09
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.441 - 445, 2020/09
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator. In order to realize higher intensity, new injection scheme of non-destructive type is needed instead of the foil. We newly propose laser stripping injection scheme by using laser pulse. We plan proof of principle experiment at J-PARC and are developing the laser system. In my presentation, we introduce the overview of laser stripping injection scheme and report the status of laser development.
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Sato, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.841 - 845, 2019/07
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Inoue, Shunsuke*; Sato, Atsushi*; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Yamane, Isao*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.811 - 815, 2018/08
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses occur by scattering at the foil. Additionally, the beam collision at the foil may cause the break itself. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. We newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme. At the first step, we propose a proof-of-principle (POP) experiment of the scheme in J-PARC and develop a laser system. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe an overview of a POP experiment. We will report a current status of the laser system.
 laser stripping at J-PARC 3-GeV RCS
laser stripping at J-PARC 3-GeV RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Miura, Akihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Okabe, Kota; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Yamane, Isao*; Irie, Yoshiro*; Liu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.806 - 810, 2018/08
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Miura, Akihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Irie, Yoshiro*; Yamane, Isao*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*
Proceedings of 61st ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams (HB 2018) (Internet), p.422 - 427, 2018/07
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Shibata, Takanori*
no journal, ,
In high-intensity proton accelerator, H beams are injected with charge exchange into the ring by using a carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by foil scattering and the foil breaking are a key issue in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. We developed laser system and optical cavity and performed the second trial of the experiment. We were successfully matched laser pulse to ion beam one in time-space dimension. As this experimental result, we realized the charge exchange ratio of 16.8%, which is 30 times higher than first result of 0.57%. We present the experimental results with introducing the scheme.
beams are injected with charge exchange into the ring by using a carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by foil scattering and the foil breaking are a key issue in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. We developed laser system and optical cavity and performed the second trial of the experiment. We were successfully matched laser pulse to ion beam one in time-space dimension. As this experimental result, we realized the charge exchange ratio of 16.8%, which is 30 times higher than first result of 0.57%. We present the experimental results with introducing the scheme.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme by using a laser and develop the laser system for a test. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection and report the status of the development.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection. Additionally, we report the status of the development and the schedule of the experiment.
Fuchi, Aoi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In the J-PARC as high-intensity proton accelerator, beam injection into a synchrotron uses for charge exchange process from hydrogen to proton. For higher intensity beam, we study laser development and POP experiment for charge exchange by using laser. In our method, we consider doppler shift and multi process of electron stripping. Therefore, we are developing high power laser and the 5th harmonics. In order to reduce laser power, we must increase the utilization rate of laser. So, we develop multi-pass cavity and beam shaper. In our presentation, we will report about a status of high-repetition laser and optics devices under developing.
Fuchi, Aoi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In high-intensity proton accelerator, accelerated H beams in linac are injected with charge exchange in the ring by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. We developed laser system and optical cavity and started the first trial of the experiment. As this experimental result, we realized the charge exchange of 0.57% for final goal one of 99%. In our presentation, developed laser system and optics will be explained and we will report first results of the experiment.
beams in linac are injected with charge exchange in the ring by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. We developed laser system and optical cavity and started the first trial of the experiment. As this experimental result, we realized the charge exchange of 0.57% for final goal one of 99%. In our presentation, developed laser system and optics will be explained and we will report first results of the experiment.
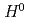 atoms generated by laser
atoms generated by laser 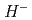 stripping
strippingShibata, Takanori*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In order to further increase the intensity of the proton beam at J-PARC, we are planning a laser charge conversion test to convert the proton beam to protons nondestructively instead of the current carbon film. In the laser charge conversion process, we are considering a scenario in which neutral hydrogen 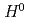 is passed through excited
is passed through excited 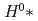 . For this experiment, it is necessary to understand the energy levels of
. For this experiment, it is necessary to understand the energy levels of 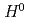 and its excitation efficiency. In this study, we are developing a spectroscopic measurement system to spectroscopically detect the light emitted from the excited
and its excitation efficiency. In this study, we are developing a spectroscopic measurement system to spectroscopically detect the light emitted from the excited 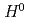 . In this presentation, we will report on the development of the spectroscopic measurement system, which is important for laser charge conversion.
. In this presentation, we will report on the development of the spectroscopic measurement system, which is important for laser charge conversion.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Onoda, Genki*; Yamada, Ippei; Shibata, Takanori*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In high-intensity proton accelerators, two electrons of negative hydrogen ions accelerated in a linac are stripped by a charge-exchange carbon foil installed at the injection point of a ring accelerator, and converted to protons. While this method can produce a high-intensity proton beam, it is a destructive method that are passed through the foil, which leads to a short lifetime of the foil itself, and to high radiation of the equipment due to the foil scattering. Therefore, at J-PARC, a non-destructive laser stripping injection method has been proposed as an alternative to carbon foil and is being developed as a proof-of-principle experiment. In addition, a laser-based non-destructive beam profile monitor is being developed as an alternative to destructive wires. At present, a new long-range laser optical path line of about 70 m has been constructed for laser irradiation of a 400 MeV negative hydrogen ion beam. In this presentation, the status of the experiment preparation is reported together with an overview of the laser stripping injection and non-destructive beam monitoring.
Onoda, Genki*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yamada, Ippei; Shibata, Takanori*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
At the J-PARC, a material-free laser stripping system using only light is being developed. A laser source is installed outside the radiation controlled area, laser pulse needs to translate a long-distance optical path line of about 70 m to the experiment area. In this case, the stable and precise experiment cannot be achieved without reducing vibrations in the light source area. Therefore, in this study, vibration measurements of the floor and the positional stability of the transmitted light were carried out. As a result, a characteristic vibration of 20 Hz caused by the motor was identified. The measured oscillations can be reduced by constructing a new feedback system using two mirrors. In this situation, the pointing stability transmitted through all optical paths was evaluate. The oscillation was less than 0.001 mm, but this was confirmed to be no problem when compared to a laser diameter of 3 mm. These results and future plans are reported in this presentation.