Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oda, Chie; Kawama, Daisuke*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Benbow, S. J.*; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 19(10), p.1075 - 1087, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Construction & Building Technology)Concrete in a transuranic (TRU) waste repository is considered a suitable material to ensure safety, provide structural integrity and retard radionuclide migration after the waste containers fail. In the current study, coupling between chemical, mass-transport and mechanical, so-called non-linear processes that control concrete degradation and crack development were investigated by coupled numerical models. Application of such coupled numerical models allows identification of the dominant non-linear processes that will control long-term concrete degradation and crack development in a TRU waste repository.
Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Oda, Chie; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Crystals (Internet), 10(9), p.767_1 - 767_33, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.57(Crystallography)Details are presented of the development of a coupled modeling simulator for assessing the evolution in the near-field of a geological repository for radioactive waste disposal where concrete is used as a backfill. The simulator uses OpenMI, a standard for exchanging data between simulation software programs at run-time, to form a coupled chemical-mechanical-hydrogeological model of the system. The approach combines a tunnel scale stress analysis finite element model, a discrete element model for accurately modeling the patterns of emerging cracks in the concrete, and a finite element and finite volume model of the chemical processes and alteration in the porous matrix and cracks in the concrete, to produce a fully coupled model of the system. Combining existing detailed simulation software in this way with OpenMI has the benefit of not relying on simplifications that might be necessary to combine all of the modeled processes in a single piece of software.
Abe, Toru*; Hirano, Fumio; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(1), p.3 - 11, 2020/06
Degradation of TRU waste in a geological disposal facility may cause the formation of a nitrate plume. A Nitrate Evolution model due to mineral reactions, microbial activity, and metal corrosiON (NEON) has therefore been developed to evaluate the safety case for geological disposal of TRU waste. Small scale laboratory experiments can be reproduced satisfactorily, however, it is necessary to demonstrate the applicability of the NEON model on scales relevant to the geological disposal of TRU waste. In the current study, an industrial analogue of a nitrate plume from the pollution of groundwater from nitrate fertilizers used on Ikuchi Island, Japan was selected to test the applicability of the NEON model. Concentration profiles of nitrate ions in the groundwater were successfully reproduced over the hundreds of meters scale demonstrating the applicability of the NEON model in evaluating the chemical behavior of a nitrate plume derived from the geological disposal of TRU waste.
Anraku, Sohtaro; Walker, C.*; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
Walker, C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
Hirano, Fumio; Otani, Yoshiteru*; Kyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Mihara, Morihiro; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Akira
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(2), p.97 - 114, 2016/06
A mechanical analysis code MACBECE2014 has been developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to make realistic simulations of the physical integrity of the near-field for performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste in Japan. The MACBECE2014 code can be used to evaluate long-term changes in the mechanical behavior and any subsequent changes in the permeability of engineering barrier components, including crack formation in cementitious materials caused by expansion due to metal corrosion. Simulated results of the TRU waste disposal system with a bentonite buffer using the MACBECE2014 code demonstrated that the low permeability of the engineering barrier system could be maintained for long time periods after disposal because the physical integrity of the bentonite buffer remained intact. Simulated results of the disposal system with a concrete backfill, showed that crack formation leads to a significant increase in permeability of the system.
 C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions
C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutionsWalker, C.; Suto, Shunkichi; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Cement and Concrete Research, 79, p.1 - 30, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:90.65(Construction & Building Technology)Modeling the solubility behavior of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel is important to make quantitative predictions of the degradation of hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC) based materials. Experimental C-S-H gel solubility data have been compiled from the literature, critically evaluated and supplemented with new data from the current study for molar Ca/Si ratios = 0.2-0.83. All these data have been used to derive a discrete solid phase (DSP) type C-S-H gel solubility model based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions in aqueous solution(SSAS). Features of the DSP type C-S-H gel solubility model include satisfactory predictions of pH values and Ca and Si concentrations for all molar Ca/Si ratios = 2.7  0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios
0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios  1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO
1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO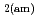 ) for Ca/Si ratios
) for Ca/Si ratios  0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mihara, Morihiro; Cowper, M.*; Kamei, Gento
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 298(1), p.485 - 493, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.2(Chemistry, Analytical)Solubility of thorium and americium in pore water squeezed from a cement paste was investigated by a batch method from oversaturation. The ordinary Portland cement was mixed with deionised water to prepare a cement paste from which the pore water was squeezed following solidification. Another batch of pore water was collected by the same method except that a superplasticiser was added to the deionised water used to prepare the cement paste. The aim was to investigate an effect of superplasticiser on solubility of thorium and americium in the squeezed cement porewaters. The obtained solubility values in the two squeezed pore waters (with and without superplasticiser present) were similar. Thermodynamic calculations were performed with the JAEA-TDB thermodynamic database and compared with the experimental data to verify their applicability. This result showed that superplasticisers after mixing with the cement paste did not have a significant effect on solubility of thorium and americium, and the thermodynamic calculations were applicable in the present system. Size distribution of colloidal species of thorium and americium was also investigated.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Ichige, Satoru; Kurimoto, Yoshitaka; Hoshino, Seiichi; Akagi, Yosuke; Sato, Nobuyuki; Murakami, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-002, 82 Pages, 2011/03
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H20 (2008) Japanese fiscal year, which are (1) evaluation of long-term mechanical stability in the near-field including development of a creep mode of rock and analyses of mechanical behavior of TRU waste repository, (2) performance assessment of the disposal system including data acquisition and preparation on radionuclides migration, cementitious material alteration, bentonite and hostrock alteration with alkaline solution and nitrate effect, and (3) alternative technology development including decomposition of nitrate.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Doi, Reisuke; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Mihara, Morihiro; Terashima, Motoki; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-024, 84 Pages, 2010/03
A thermodynamic database was established to develop a thermodynamic database for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level and TRU wastes. Twenty-four elements (actinides, fission products and their daughters) which are of importance for the performance assessment of geological disposal have been selected. The fundamental plan was in principle based on the guidelines established by the Nuclear Energy Agency in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). Additional unique guidelines were established due to a requirement from the performance assessment to select tentative thermodynamic values obtained from chemical analogues and/or models for elements with insufficient thermodynamic values. Selected thermodynamic data were compiled for geochemical calculation programs.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Murakami, Hiroshi; Masuda, Kenta; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Matsuda, Setsuro; Ichige, Satoru; Takahashi, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-046, 80 Pages, 2010/01
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H20 (2008) Japanese fiscal year.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Murakami, Hiroshi; Masuda, Kenta; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Matsuda, Setsuro; Ichige, Satoru; Takahashi, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-082, 84 Pages, 2008/11
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H19 (2007) fiscal year, which are (1) treatment and packaging of TRU waste including applicability of calcination for unpacking and sorting of wastes, characterization and inspection methodology of TRU waste, (2) mechanical assessment for the near-field structure including model development and preparation, introduction of hostrock creep model and coupling analysis of deformation of hostrock and engineered barrier. (3) performance assessment of the disposal system including data acquisition and preparation on radionuclides migration, cementitious material alteration, bentonite and hostrock alteration with alkaline solution and nitrate effect, and (4) alternative technology development including decomposition of nitrate.
Umeda, Koji; Oi, Takao; Osawa, Hideaki; Oyama, Takuya; Oda, Chie; Kamei, Gento; Kuji, Masayoshi*; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kobayashi, Yasushi; Sasaki, Yasuo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-050, 82 Pages, 2007/12
This report shows the annual report which shows the summarized results and topic outline of each project on geological disposal technology in the fiscal year of 2006.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Murakami, Hiroshi; Masuda, Kenta; Yamaguchi, Kohei; Nakanishi, Hiroshi*; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Ichige, Satoru*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2007-067, 130 Pages, 2007/09
After the publication of the 2nd progress report of geological disposal of TRU waste in Japan, policy and general scheme of future study for the waste disposal in Japan was published by ANRE and JAEA. This annual report summarized aim and progress of individual problem, which was assigned into JAEA in the published policy and general scheme. The problems are as follows; characteristics of TRU waste and its geologic disposal, treatment and waste production, quality control and inspection methodology for waste, mechanical analysis of near-field, data acquisition and preparation on radionuclides migration, cementitious material transition, bentonite and rock alteration in alkaline solution, nitrate effect, performance assessment of the disposal system and decomposition of nitrate as an alternative technology.
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:89.22(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Shiotsuki, Masao; Kuroda, Shigeki*; ; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Ono, Fumihiko*; Kozawa, Takashi*; Tsukamoto, Masaki*
IAEA-CN-135/59, p.229 - 232, 2005/10
None
Shibata, Masahiro; Mihara, Morihiro; Sasaki, Ryoichi; Honda, Akira
JNC TN8400 2005-025, 17 Pages, 2005/09
In the performance assessment for the geological disposal of the TRU waste, effect of organic material (i.e. organic wastes, cement additives, and natural organism) should be considered. The waste solvent (including TBP and its deterioration products) is contained in the asphalt waste generated from the reprocessing facility of JNC. These solvent and deterioration products have the possibility of forming the complexes with actinide elements if a chemical condition is satisfactory. It influences solubility and the sorption behavior of the radionuclide when the complexes are soluble in aqueous solution. In that case, there is a possibility to influence the behavior of the radionuclide migration. In this report, to evaluate the influence of TBP and its deterioration products (DBP and MBP) on the solubility and the sorption behavior of the actinide, (1) literature survey for the experimental research, (2) survey for the thermodynamics data concerning the interaction with the radionuclide and calculation for solubility and speciation in the expected environments, were conducted. As a result, it was thought that the influences of TBP and its degradation products on the solubility and speciation of radionuclides were small (Times of several in solubility at most).
Saegusa, Jun; Kawasaki, Katsuya; Mihara, Akira; Ito, Mitsuo; Yoshida, Makoto
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 61(6), p.1383 - 1390, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.49(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Kato, Hiroshige*
JNC TN8400 2004-020, 69 Pages, 2004/11
Cementitious materials will be used expensively in the TRU waste repository. The cementitious materials will keep the high pH condition (pH 12) in the pore water of repository and the surrounding environment for long period. Thus it is necessary to obtain the data measured under the high pH conditions for the performance assessment of the TRU waste repository. However the uumber of the available data are limited. On the other hand, iodine-129 is an important nuclide because of its long half-time and poorly-sorbing nature. Therefore the effective diffusion coefficients De and distribution coefficients Kd of iodine in both crystalline rock and sedimentary rock were estimated in this study. Granodiorite and sandstone were selected as an example of crystalline rock and that of sedimentary rock respectively. Through diffusion experiment were carried out in an argon atmosphere.The diffusivity of iodine in both type rocks saturated by synthetic cement pore water was reduced with increasing experimental period. The analysis of experimental results suggested that this phenomenon was caused by decrease of De values. For granodiorite, the De values obtained in this study using synthetic cement pore water were 2 orders of magnitude smaller than literature values which obtained at neutral pH. For sandstone, the De values using synthetic cement pore water were 1 - 2 orders smaller than literature values, however those using synthetic groundwater were consistent with literature values. SEM observation of sandstone after the diffusion experiment showed that the secondary mineral coated the surface of sandstone. These observation results suggested that decrease of De value in case of synthetic cement pore water was ascribed to the precipitation of secondary mineral.In this study, Kd values of iodine on sandstone were 1.7x10
12) in the pore water of repository and the surrounding environment for long period. Thus it is necessary to obtain the data measured under the high pH conditions for the performance assessment of the TRU waste repository. However the uumber of the available data are limited. On the other hand, iodine-129 is an important nuclide because of its long half-time and poorly-sorbing nature. Therefore the effective diffusion coefficients De and distribution coefficients Kd of iodine in both crystalline rock and sedimentary rock were estimated in this study. Granodiorite and sandstone were selected as an example of crystalline rock and that of sedimentary rock respectively. Through diffusion experiment were carried out in an argon atmosphere.The diffusivity of iodine in both type rocks saturated by synthetic cement pore water was reduced with increasing experimental period. The analysis of experimental results suggested that this phenomenon was caused by decrease of De values. For granodiorite, the De values obtained in this study using synthetic cement pore water were 2 orders of magnitude smaller than literature values which obtained at neutral pH. For sandstone, the De values using synthetic cement pore water were 1 - 2 orders smaller than literature values, however those using synthetic groundwater were consistent with literature values. SEM observation of sandstone after the diffusion experiment showed that the secondary mineral coated the surface of sandstone. These observation results suggested that decrease of De value in case of synthetic cement pore water was ascribed to the precipitation of secondary mineral.In this study, Kd values of iodine on sandstone were 1.7x10 - 3.0x10
- 3.0x10 m
m /kg in synthetic groundwater. However Kd values of other cases could not be estimated.
/kg in synthetic groundwater. However Kd values of other cases could not be estimated.
Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro
JNC TN8400 2004-011, 17 Pages, 2004/07
Hull and end piece wastes are classified in TRU wastes. The hull and end piece wastes are thought to be adequate to the geological disposal. The hull end-piece wastes generated from Tokai Reprocessing Plant of JNC include organic materials such as cotton waste. The organic materials can decompose in the repository due to the alkaline condition brought by cementitious material. The soluble organic species can be produced through the alkaline decomposition of the organic wastes. The soluble organic species potentially complex radioactive metal ions. The complexation can affect the solubility and sorption of radioactive nuclides. The all of organic materials included in hull and end piece wastes assumed to be cellulose which was also assumed to decompose to iso-saccharinic acid (ISA) which can significantly affects the solubility and sorption of radioactive nuclides. Under the assumptions, the effects of organic materials included in hull and end piece wastes on the solubility and sorption of radioactive nuclides were estimated in a conservative manner.If the release of ISA from the repository was taken into account, the maximum concentration of ISA in the repository was estimated as 1.3 x 10-6 mol dm-3. which almost corresponded to be negligible concentration of ISA (~1.0 x 10-6 mol dm-3). The maximum doses in performance assessment were unchanged over the range of 0 to 10-5mol dm-3 in the ISA concentration for 109 years. The maximum concentration of ISA in the pore water of repository without release was estimated as 1.5 x 10-5 mol dm-3. The maximum concentration is similar level to the concentration in which the maximum doses were unchanged.