Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
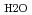 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and 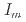 = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters of the hydrated (Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 and SiO
and SiO (OH)
(OH)
 ) and fictive dehydrated (SiO
) and fictive dehydrated (SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 ) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at
) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at  = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
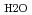 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100
, and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100 C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
Koike, Ayaka*; Takubo, Yusaku*; Mihara, Morihiro
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.81 - 84, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Koike, Ayaka*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Mihara, Morihiro
NUMO-TR-24-01, p.98 - 101, 2024/05
no abstracts in English
Hanamachi, Yuji*; Walker, C.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
NIMS Bisai Kozo Kaiseki Purattofuomu Riyo Hokokusho (Internet), 2 Pages, 2023/12
A High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) has been considered as the use of concrete support of drift in deep disposal of radioactive wastes. JAEA has been carried out experiments and modeling studies to evaluate chemical stability of C-A-S-H gel synthesized which would be believed as the dominant component of the HFSC. For the modeling purpose, it is necessary to evaluate the chemical composition both of C-A-S-H gel synthesized and accompanied minerals in the experiment. In the year of 2020,  Al and
Al and  Si NMR measurement were performed to identify Al and Si distribution in the sample and chemical composition of C-A-S-H gel was derived. However, it was impossible to derive the C-A-S-H gel composition having the expected Al/Si molar ratio since there were several accompanied minerals produced in the experiment due to the short term of immersion. This time similar approach to derive C-A-S-H gel composition is adopted using NMR measurement for the sample of longer time (6 months).
Si NMR measurement were performed to identify Al and Si distribution in the sample and chemical composition of C-A-S-H gel was derived. However, it was impossible to derive the C-A-S-H gel composition having the expected Al/Si molar ratio since there were several accompanied minerals produced in the experiment due to the short term of immersion. This time similar approach to derive C-A-S-H gel composition is adopted using NMR measurement for the sample of longer time (6 months).
Minari, Eriko*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.793 - 803, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)Koike, Ayaka*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Mihara, Morihiro
NUMO-TR-22-02, p.74 - 77, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Oda, Chie; Kawama, Daisuke*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Benbow, S. J.*; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 19(10), p.1075 - 1087, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)Concrete in a transuranic (TRU) waste repository is considered a suitable material to ensure safety, provide structural integrity and retard radionuclide migration after the waste containers fail. In the current study, coupling between chemical, mass-transport and mechanical, so-called non-linear processes that control concrete degradation and crack development were investigated by coupled numerical models. Application of such coupled numerical models allows identification of the dominant non-linear processes that will control long-term concrete degradation and crack development in a TRU waste repository.
Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Oda, Chie; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Crystals (Internet), 10(9), p.767_1 - 767_33, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.76(Crystallography)Details are presented of the development of a coupled modeling simulator for assessing the evolution in the near-field of a geological repository for radioactive waste disposal where concrete is used as a backfill. The simulator uses OpenMI, a standard for exchanging data between simulation software programs at run-time, to form a coupled chemical-mechanical-hydrogeological model of the system. The approach combines a tunnel scale stress analysis finite element model, a discrete element model for accurately modeling the patterns of emerging cracks in the concrete, and a finite element and finite volume model of the chemical processes and alteration in the porous matrix and cracks in the concrete, to produce a fully coupled model of the system. Combining existing detailed simulation software in this way with OpenMI has the benefit of not relying on simplifications that might be necessary to combine all of the modeled processes in a single piece of software.
Abe, Toru*; Hirano, Fumio; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(1), p.3 - 11, 2020/06
Degradation of TRU waste in a geological disposal facility may cause the formation of a nitrate plume. A Nitrate Evolution model due to mineral reactions, microbial activity, and metal corrosiON (NEON) has therefore been developed to evaluate the safety case for geological disposal of TRU waste. Small scale laboratory experiments can be reproduced satisfactorily, however, it is necessary to demonstrate the applicability of the NEON model on scales relevant to the geological disposal of TRU waste. In the current study, an industrial analogue of a nitrate plume from the pollution of groundwater from nitrate fertilizers used on Ikuchi Island, Japan was selected to test the applicability of the NEON model. Concentration profiles of nitrate ions in the groundwater were successfully reproduced over the hundreds of meters scale demonstrating the applicability of the NEON model in evaluating the chemical behavior of a nitrate plume derived from the geological disposal of TRU waste.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Mihara, Morihiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-021, 101 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption of radionuclides in cement and bentonite as engineered barrier materials, and rocks as natural barrier is the one of key processes in the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU and high-level waste. The magnitude of sorption, expressed normally by a distribution coefficient (K ), needs to be measured and determined taking into account the properties of barrier materials and geochemical conditions and associated uncertainty in the performance assessment. The basic concept for TRU waste disposal contains cementitious materials as an engineered barrier materials, in addition to bentonite and rock. It is therefore needed to consider the effects of the cement degradation and co-existing substances such as nitrates on radionuclide sorption. This report focused on data acquisition of distribution coefficient (K
), needs to be measured and determined taking into account the properties of barrier materials and geochemical conditions and associated uncertainty in the performance assessment. The basic concept for TRU waste disposal contains cementitious materials as an engineered barrier materials, in addition to bentonite and rock. It is therefore needed to consider the effects of the cement degradation and co-existing substances such as nitrates on radionuclide sorption. This report focused on data acquisition of distribution coefficient (K ) by batch sorption experiments for the systems coupling barrier material-chemical condition-radionuclides that are needed to consider for the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. The barrier materials considered are ordinary Portland cement (OPC), degraded OPC and tuff rock. The chemical conditions are distilled water and synthetic seawater equilibrated with OPC and those containing nitrates and ammonium salts, etc. The radionuclides considered are organic carbon, inorganic carbon, Cl, I, Cs, Ni, Se, Sr, Sn, Nb, Am and Th. Although K
) by batch sorption experiments for the systems coupling barrier material-chemical condition-radionuclides that are needed to consider for the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. The barrier materials considered are ordinary Portland cement (OPC), degraded OPC and tuff rock. The chemical conditions are distilled water and synthetic seawater equilibrated with OPC and those containing nitrates and ammonium salts, etc. The radionuclides considered are organic carbon, inorganic carbon, Cl, I, Cs, Ni, Se, Sr, Sn, Nb, Am and Th. Although K values have been partly reported previously as RAMDA (Radionuclide Migration Datasets) for the performance assessment in the TRU-2 report, these results and addition K
values have been partly reported previously as RAMDA (Radionuclide Migration Datasets) for the performance assessment in the TRU-2 report, these results and addition K data are reported with the details of experimental methods and conditions.
data are reported with the details of experimental methods and conditions.
Anraku, Sohtaro; Walker, C.*; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
Walker, C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
Mihara, Morihiro; Harasawa, Shuichi*; Torii, Kazuyuki*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 26(1), p.15 - 23, 2019/06
Hardened cement pastes (HCPs) of water/cement ratio (W/C) 50% and 30% using fly ash (FA), blast furnace slag (BFS) and silica fume (SF) for 28 days were prepared. Apparent diffusion coefficients (D ) of Cs and I in HCPs were obtained using electron probe microanalysis. For Cs, BFS and SF contributed to a reduction of D
) of Cs and I in HCPs were obtained using electron probe microanalysis. For Cs, BFS and SF contributed to a reduction of D for W/C=50% and 30%, respectively. For I, BFS reduced D
for W/C=50% and 30%, respectively. For I, BFS reduced D for W/C=50%, however a significant reduction in D
for W/C=50%, however a significant reduction in D for W/C=30% was not observed. Using SF enhanced sorption of Cs on HCP, and using BFS slightly improved sorption of Cs on HCP. It was also confirmed that the pore structures of HCP using SF and BFS were connected by fine pores. It was therefore considered that using SF and BFS contributes to the reduction of D
for W/C=30% was not observed. Using SF enhanced sorption of Cs on HCP, and using BFS slightly improved sorption of Cs on HCP. It was also confirmed that the pore structures of HCP using SF and BFS were connected by fine pores. It was therefore considered that using SF and BFS contributes to the reduction of D in HCP.
in HCP.
Mihara, Morihiro; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Kyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Shintaro*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 24(1), p.15 - 25, 2017/06
A computer program MACBECE has been developed to provide rigorous calculations of the long-term mechanical behavior of a TRU waste geological repository. Consideration is given to the expected chemical alteration of repository components, including cementitious materials and bentonite, and the mechanical interactions between repository and host rock. The long-term mechanical behavior of a TRU waste repository was evaluated in a deep soft rock site, where creep deformation is likely to occur from the initial construction phase to 10 years after repository closure. It was found that the stress didn't fall into a singularity of yield surface of the EC model applied to the mechanical behavior model of bentonite. The calculated displacement of the inner diameter of the repository, considering mechanical interaction between repository and host rock, was about half that of a result in 2nd progress report on R&D for TRU waste disposal in Japan.
years after repository closure. It was found that the stress didn't fall into a singularity of yield surface of the EC model applied to the mechanical behavior model of bentonite. The calculated displacement of the inner diameter of the repository, considering mechanical interaction between repository and host rock, was about half that of a result in 2nd progress report on R&D for TRU waste disposal in Japan.
Hirano, Fumio; Otani, Yoshiteru*; Kyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Mihara, Morihiro; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Akira
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(2), p.97 - 114, 2016/06
A mechanical analysis code MACBECE2014 has been developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to make realistic simulations of the physical integrity of the near-field for performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste in Japan. The MACBECE2014 code can be used to evaluate long-term changes in the mechanical behavior and any subsequent changes in the permeability of engineering barrier components, including crack formation in cementitious materials caused by expansion due to metal corrosion. Simulated results of the TRU waste disposal system with a bentonite buffer using the MACBECE2014 code demonstrated that the low permeability of the engineering barrier system could be maintained for long time periods after disposal because the physical integrity of the bentonite buffer remained intact. Simulated results of the disposal system with a concrete backfill, showed that crack formation leads to a significant increase in permeability of the system.
 C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions
C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutionsWalker, C.; Suto, Shunkichi; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Cement and Concrete Research, 79, p.1 - 30, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:90.60(Construction & Building Technology)Modeling the solubility behavior of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel is important to make quantitative predictions of the degradation of hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC) based materials. Experimental C-S-H gel solubility data have been compiled from the literature, critically evaluated and supplemented with new data from the current study for molar Ca/Si ratios = 0.2-0.83. All these data have been used to derive a discrete solid phase (DSP) type C-S-H gel solubility model based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions in aqueous solution(SSAS). Features of the DSP type C-S-H gel solubility model include satisfactory predictions of pH values and Ca and Si concentrations for all molar Ca/Si ratios = 2.7  0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios
0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios  1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO
1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO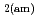 ) for Ca/Si ratios
) for Ca/Si ratios  0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
Kitamura, Akira; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mihara, Morihiro; Cowper, M.*; Kamei, Gento
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 298(1), p.485 - 493, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.40(Chemistry, Analytical)Solubility of thorium and americium in pore water squeezed from a cement paste was investigated by a batch method from oversaturation. The ordinary Portland cement was mixed with deionised water to prepare a cement paste from which the pore water was squeezed following solidification. Another batch of pore water was collected by the same method except that a superplasticiser was added to the deionised water used to prepare the cement paste. The aim was to investigate an effect of superplasticiser on solubility of thorium and americium in the squeezed cement porewaters. The obtained solubility values in the two squeezed pore waters (with and without superplasticiser present) were similar. Thermodynamic calculations were performed with the JAEA-TDB thermodynamic database and compared with the experimental data to verify their applicability. This result showed that superplasticisers after mixing with the cement paste did not have a significant effect on solubility of thorium and americium, and the thermodynamic calculations were applicable in the present system. Size distribution of colloidal species of thorium and americium was also investigated.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Mihara, Morihiro; Oda, Chie; Ichige, Satoru; Kurimoto, Yoshitaka; Hoshino, Seiichi; Akagi, Yosuke; Sato, Nobuyuki; Murakami, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-002, 82 Pages, 2011/03
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H20 (2008) Japanese fiscal year, which are (1) evaluation of long-term mechanical stability in the near-field including development of a creep mode of rock and analyses of mechanical behavior of TRU waste repository, (2) performance assessment of the disposal system including data acquisition and preparation on radionuclides migration, cementitious material alteration, bentonite and hostrock alteration with alkaline solution and nitrate effect, and (3) alternative technology development including decomposition of nitrate.
Hasegawa, Makoto; Kondo, Hitoshi; Kamei, Gento; Hirano, Fumio; Mihara, Morihiro; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Ueda, Hiroyoshi*; Oi, Takao*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-003, 47 Pages, 2011/02
In 2009, NUMO and JAEA set up a technical commission to investigate the reasonable TRU waste disposal following a cooperation agreement between these two organizations. In this report, the calculation result of radionuclide transport for a TRU waste geological disposal system was described, by using the TIGER code and the GoldSim code at identical terms. Comparing the calculation result, a big difference was not seen. Therefore, the reliability of both codes was able to be confirmed. Moreover, the influence on the disposal site design (Disposal capacity: 19,000 m ) was examined when 10% of the amount of TRU waste increased. As a result, it was confirmed that the influence of the site design was very little based on the concept of the Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan.
) was examined when 10% of the amount of TRU waste increased. As a result, it was confirmed that the influence of the site design was very little based on the concept of the Second Progress Report on Research and Development for TRU Waste Disposal in Japan.
Mihara, Morihiro
JAEA-Review 2009-060, 27 Pages, 2010/03
It is planned that JAEA-TDB has been developed modifying JNC-TDB released in 1999 by the end of FYJ 2009. The JAEA-TDB is planned to include thermodynamic data of compounds and complexes of metal elements with organic ligands which were not included in JNC-TDB. This report shows the selected thermodynamic data of compounds and complexes of metal elements with organic ligands which might be included in TRU waste in JAEA-TDB. Selected organics are oxalic acid, citric acid, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and iso-saccharinic acid (ISA) which were of interest in the OECD/NEA. The thermodynamic data evaluated by OECD/NEA were selected for JAEA-TDB. However, selected values by OECD/NEA are limited to evaluate the solubility calculation. Therefore, other published values and estimated values by LFER are also selected as tentative values for JAEA-TDB.