Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mishima, Ria; Inaba, Yusuke*; Tachioka, Sotaro*; Harigai, Miki*; Watanabe, Shinta*; Onoe, Jun*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Takeshita, Kenji*
Chemistry Letters, 49(1), p.83 - 86, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.18(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Separation of platinum group metals (PGMs) from high-level liquid waste generated from the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels is important to produce good quality vitrified glass for final disposal. A new sorbent, Aluminum hexacyanoferrate (AlHCF), was synthesized and the general sorption behavior of PGMs from concentrated nitric acid was examined. Nitric acid caused substantial elution of AlHCF but the sorption of Pd stabilized the structure. Consequently, Rh was sorbed in the presence of Pd, whereas single Rh sorption caused complete dissolution of AlHCF. Relation between sorbed mount of Pd vs eluted Al and Fe revealed that the elution ratio of Al and Fe was not the same as molar ratio of synthesized AlHCF, indicating the re-sorption of Fe resulted in formation of new structure. The sorption mechanism of PGMs by this new sorbent, AlHCF, not only the simple ion exchange, but also oxidation reduction reaction as well as kinetics play important rule. Understanding the general sorption and dissolution behavior will help improve the sorption performance of PGMs by AlHCF.
Kotake, Shoji; Sakamoto, Yoshihiko; Mihara, Takatsugu; Kubo, Shigenobu*; Uto, Nariaki; Kamishima, Yoshio*; Aoto, Kazumi; Toda, Mikio*
Nuclear Technology, 170(1), p.133 - 147, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:91.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is now executing "Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT)" project in cooperation with the Japanese electric utilities. In the FaCT project, both the conceptual design study for Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) and the developments of innovative technologies to be adopted to JSFR are now implemented with paying attention to the consistency between the design and the innovative technologies. The current target is that the development will be accomplished around 2015, after that a licensing procedure for the demonstration JSFR will be launched. This paper describes design requirements, design characteristics of JSFR and evaluation on the performances for economic competitiveness. Furthermore, the current status of the key technology development for JSFR is briefly introduced.
Kondo, Masaaki; Sekita, Kenji; Emori, Koichi; Sakaba, Nariaki; Kimishima, Satoru; Kuroha, Misao; Noji, Kiyoshi; Aono, Tetsuya; Hayakawa, Masato
JAEA-Testing 2006-002, 55 Pages, 2006/07
The leakage rate test for the reactor containment vessel of HTTR is conducted in accordance with the absolute pressure method provided in Japan Electric Association Code(JEAC4203). Although leakage test of a reactor containment vessel is, in general, performed in condition of reactor coolant pressure boundary to be opened in order to simulate an accident, the peculiar test method to HTTR which use the helium gas as reactor coolant has been established, in which the pressure boundary is closed to avoid the release of fission products into the environment of the reactor containment vessel. The system for measuring and calculating the data for evaluating the leakage rate for containment vessel of HTTR was developed followed by any modifications. Recently, the system has been improved for more accurate and reliable one with any useful functions including real time monitoring any conditions related to the test. In addition, the configuration of containment vessel boundary for the test and the calibration method for the detectors for measuring temperature in containment vessel have been modified by reflecting the revision of the Code mentioned above. This report describes the method, system configuration, and procedures for the leakage rate test for reactor containment vessel of HTTR.
Nariai, Hideki*; Sugiyama, Kenichiro*; Kataoka, Isao*; Mishima, Kaichiro*; *; Monde, Masanori*; Sugimoto, Jun; ; Hidaka, Akihide; *; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(9), p.739 - 752, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Mishima, Ria; Tachioka, Sotaro*; Inaba, Yusuke*; Harigai, Miki*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Watanabe, Shinta*; Onoe, Jun*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
no journal, ,
In Japan, the final disposal of high level liquid waste (HLLW) will be done after vitrification into borosilicate glass and then disposed into deep underground. In this vitrification process, there are some concerns. The first concern is precipitation of platinum group metals (PGMs) in the melter due to their low solubility into borosilicate glass. The second concern is the formation of yellow phase caused by Mo content. The final concern is the generation of huge number of vitrified glasses and the requirement of wide space needed for final disposal. Among many kinds of extractants and adsorbents for separation of such metal ions, metal hexacyanoferrate (HCFs) were reported to have an ability to adsorb PGMs. The objective of this study is to elucidate the adsorption behavior of aluminum hexacyanoferrate (AlHCF) for various metal ions and understand the relation between elution and adsorption. The effect of synthetic and workup conditions on PGM and Mo adsorption from simulated HLLW (sHLLW) was surveyed. Also, the relationship between adsorption of metal ions and elution of the AlHCF was studied. The synthesized AlHCF showed adsorption performance for PGMs and Mo in simulated HLLW. As a result of an adsorption test with a Pd single component solution to investigate the adsorption mechanism, the eluted element ratio was Fe:Al = 1:4 in the Pd adsorption test. However, the element ratio was Fe:Al = 3:4 in the original AlHCF. Therefore, it was suggested the existence of not only Pd adsorption, but also resorption and stabilization mechanisms.
Mishima, Ria; Tachioka, Sotaro*; Inaba, Yusuke*; Harigai, Miki*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Watanabe, Shinta*; Onoe, Jun*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
no journal, ,
In Japan, the final disposal of high level liquid waste (HLLW) will be done after vitrification into borosilicate glass and then disposed into deep underground. In this vitrification process, there are some concerns. The first concern is precipitation of platinum group metals (PGMs) in the melter due to their low solubility into borosilicate glass. The second concern is the formation of yellow phase caused by Mo content. The final concern is the generation of huge number of vitrified glasses and the requirement of wide space needed for final disposal. Among many kinds of extractants and adsorbents for separation of such metal ions, metal hexacyanoferrate (HCFs) were reported to have an ability to adsorb PGMs. The objective of this study is to elucidate the adsorption behavior of aluminum hexacyanoferrate (AlHCF) for various metal ions and understand the relation between elution and adsorption. The effect of synthetic and workup conditions on PGM and Mo adsorption from simulated HLLW (sHLLW) was surveyed. Also, the relationship between adsorption of metal ions and elution of the AlHCF was studied. The synthesized AlHCF showed adsorption performance for PGMs and Mo in simulated HLLW. As a result of an adsorption test with a Pd single component solution to investigate the adsorption mechanism, the eluted element ratio was Fe:Al = 1:4 in the Pd adsorption test. However, the element ratio was Fe:Al = 3:4 in the original AlHCF. Therefore, it was suggested the existence of not only Pd adsorption, but also resorption and stabilization mechanisms.
 Zr
Zr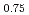 N with Pd
N with PdMishima, Ria; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Hayashi, Hirokazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Zr
Zr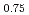 N with Pd, 2; Temperature dependence of the reaction product composition
N with Pd, 2; Temperature dependence of the reaction product compositionMishima, Ria; Sato, Takumi; Hayashi, Hirokazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English