Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O
Kirishima, Akira*; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki*; Onishi, Takashi; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(6), p.958 - 966, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)A novel reprocessing process based on the selective sulfurization of fission products (FP) has been proposed, where FP and minor actinides (MA) are first sulfurized by CS gas, and then, dissolved by a dilute nitric acid solution. Consequently, the fuel elements are recovered as UO
gas, and then, dissolved by a dilute nitric acid solution. Consequently, the fuel elements are recovered as UO and PuO
and PuO . As a basic research of this new concept, the sulfurization and dissolution behaviors of U, Pu, Np, Am, Eu, Cs and Sr were investigated in this paper using
. As a basic research of this new concept, the sulfurization and dissolution behaviors of U, Pu, Np, Am, Eu, Cs and Sr were investigated in this paper using  Pu,
Pu,  Np,
Np,  Am,
Am,  Eu,
Eu,  Cs and
Cs and  Sr doped U
Sr doped U O
O sample by
sample by  ray and
ray and  spectrometries. The dependence of the dissolution ratio of each element on the sulfurization temperature was studied and reasonably explained by combining the information of the sulfide phase analysis and the chemical thermodynamics of the dissolution reaction. The sulfurization temperature ranging from 350 to 450
spectrometries. The dependence of the dissolution ratio of each element on the sulfurization temperature was studied and reasonably explained by combining the information of the sulfide phase analysis and the chemical thermodynamics of the dissolution reaction. The sulfurization temperature ranging from 350 to 450  C seems to be promising for the separation of FP and MA from U and Pu.
C seems to be promising for the separation of FP and MA from U and Pu.
Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.6), p.55 - 64, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to evaluate the transmutation behavior of americium under fast neutron spectra, two irradiated  Am samples (No.69, No.70) were analyzed by radiochemical methods. These samples were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO for 275 effective full power day by the fast neutron flux.
Am samples (No.69, No.70) were analyzed by radiochemical methods. These samples were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO for 275 effective full power day by the fast neutron flux. 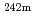 Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Pu to
Pu to  Pu and
Pu and  Cm to
Cm to  Cm were clearly observed. The isotopic composition of
Cm were clearly observed. The isotopic composition of 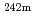 Am exceeded 1.01 at% for sample No.69 and 1.48 at% for No.70. It was suggested that this difference came from the different rates of neutron capture reaction.
Am exceeded 1.01 at% for sample No.69 and 1.48 at% for No.70. It was suggested that this difference came from the different rates of neutron capture reaction.
Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Proceedings of 9th OECD/NEA Information Exchange Meeting on Actinide and Fission Product Partitioning and Transmutation, p.509 - 518, 2007/00
In order to evaluate the transmutation behavior of americium under fast and thermal neutron spectra, two kinds of irradiated  Am oxide samples were analyzed by radiochemical methods in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. One is
Am oxide samples were analyzed by radiochemical methods in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. One is  Am encapsulated in a vanadium capsule which was irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO for 275 effective full power days (EFPD) under the fast neutron flux of 3
Am encapsulated in a vanadium capsule which was irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO for 275 effective full power days (EFPD) under the fast neutron flux of 3 10
10 c/cm
c/cm s. The other is
s. The other is  Am oxide pelletized with MgO which was irradiated in Japan Material Testing Reactor for 207 EFPD under the thermal neutron flux of 2
Am oxide pelletized with MgO which was irradiated in Japan Material Testing Reactor for 207 EFPD under the thermal neutron flux of 2 10
10 c/cm
c/cm s. After dissolution of these samples, americium, curium and plutonium were chemically separated and their isotope compositions were analyzed by alpha and
s. After dissolution of these samples, americium, curium and plutonium were chemically separated and their isotope compositions were analyzed by alpha and  -ray spectrometry and mass spectroscopy.
-ray spectrometry and mass spectroscopy.  Cs and
Cs and 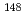 Nd were measured by
Nd were measured by  -ray spectrometry and mass spectroscopy, respectively, to determine the total fission events and burnup.
-ray spectrometry and mass spectroscopy, respectively, to determine the total fission events and burnup. 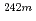 Am,
Am,  Am,
Am, 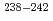 Pu and
Pu and 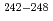 Cm were clearly observed. The total transmutation ratios of americium under the fast and thermal neutron spectra were about 10% and 80% in the irradiation conditions, respectively. The fission to capture cross-section ratios were evaluated in order to compare the transmutation behavior of americium. As the result, it is proved that the accumulation of even-even nuclei, such as
Cm were clearly observed. The total transmutation ratios of americium under the fast and thermal neutron spectra were about 10% and 80% in the irradiation conditions, respectively. The fission to capture cross-section ratios were evaluated in order to compare the transmutation behavior of americium. As the result, it is proved that the accumulation of even-even nuclei, such as  Cm and
Cm and 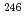 Cm, in the thermal neutron spectrum was remarkable than that under the fast neutron spectrum. It is expected that these results show the important aspect to discuss the transmutation concept by using several neutron reaction in the reactor. In this study, the fundamental analytical data could be obtained.
Cm, in the thermal neutron spectrum was remarkable than that under the fast neutron spectrum. It is expected that these results show the important aspect to discuss the transmutation concept by using several neutron reaction in the reactor. In this study, the fundamental analytical data could be obtained.
Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Czechoslovak Journal of Physics, 56(Suppl.D), p.D571 - D578, 2006/12
We have developed a sequential radiochemical separation method (SRCS) in order to isolate each trans-uranium element (TRU) contained in a TRU target (or fuel) irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. The chemical separation procedures for SRCS consist of the following steps. (1) Target dissolution with a 8M of HNO solution including hydrogen peroxides as a valence control reagents for Pu and Np to their tetravalent states. (2) Sequential elution of main fission products (FPs) including trivalent actinides (An(III)) and lanthanides (Ln(III)) by washing the anion exchange resin column with 8M HNO
solution including hydrogen peroxides as a valence control reagents for Pu and Np to their tetravalent states. (2) Sequential elution of main fission products (FPs) including trivalent actinides (An(III)) and lanthanides (Ln(III)) by washing the anion exchange resin column with 8M HNO . (3) Elution of U(VI) from the same column with 8M HNO
. (3) Elution of U(VI) from the same column with 8M HNO and the change the effluent to 11.6M HCl. (4) Elution of Pu(III) from the same column by reducing Pu(IV) to Pu(III) with 11.6M HCl-0.1M NH
and the change the effluent to 11.6M HCl. (4) Elution of Pu(III) from the same column by reducing Pu(IV) to Pu(III) with 11.6M HCl-0.1M NH I solution. (5) Group separation for Ln(III) and An(III) by using tertiary pyridine-type anion exchange resin embedded in silica bead. (6) Mutual separation of Am(III) and Cm(III), also for each lanthanide, by anion exchange resin. For the step 5 and 6, the effluent used was 3/7(v/v) mixture of methanol and HCl and 9/1(v/v) mixture of methanol and 0.013M HNO
I solution. (5) Group separation for Ln(III) and An(III) by using tertiary pyridine-type anion exchange resin embedded in silica bead. (6) Mutual separation of Am(III) and Cm(III), also for each lanthanide, by anion exchange resin. For the step 5 and 6, the effluent used was 3/7(v/v) mixture of methanol and HCl and 9/1(v/v) mixture of methanol and 0.013M HNO , respectively. The decontamination factor of Pu for the isolated Np was much higher than 10
, respectively. The decontamination factor of Pu for the isolated Np was much higher than 10 . The isotopic composition of isolated trans-uranium was determined mainly by thermal ionization mass spectroscopy. The SRCS sheet was applied to the analyses of MOX fuels irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. On the basis of isotope analysis, the transmutation and incineration behavior (T-I behavior) of trans-uranium nuclides were elucidated.
. The isotopic composition of isolated trans-uranium was determined mainly by thermal ionization mass spectroscopy. The SRCS sheet was applied to the analyses of MOX fuels irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. On the basis of isotope analysis, the transmutation and incineration behavior (T-I behavior) of trans-uranium nuclides were elucidated.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Ozaki, Takuo; Samadfam, M.*; Kozai, Naofumi; Yubuta, Kunio*; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki*; Kasama, Takeshi*; Francis, A. J.*
Chemical Geology, 220(3-4), p.237 - 243, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:70.55(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 32(7), p.635 - 650, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.8(Nuclear Science & Technology)Americium isotopes generated in the MOX fuel irradiated in the experimental fast reactor JOYO were analyzed by applying a sophisticated radiochemical technique. Americium was isolated from the irradiated MOX fuel by a combination method of anion-exchange chromatography and oxidation of Am. The isotopic ratio of americium and its content were determined by thermal ionization mass spectroscopy and alpha-spectrometry, respectively. The americium isotopic ratio was similar for all the specimens, but was significantly different from that of PWR-MOX. On the basis of present analytical results, the accumulation and transmutation behavior of americium nuclides in a fast reactor was discussed from viewpoints of neutron spectrum dependence and the isomeric ratio of  Am capture reaction Am for the capture reaction. The estimated isomeric ratio was about 87 %, which was close to recently evaluated value. A rapid estimation method of Am content by using
Am capture reaction Am for the capture reaction. The estimated isomeric ratio was about 87 %, which was close to recently evaluated value. A rapid estimation method of Am content by using  Pu to
Pu to  Pu index was adopted and was proved to be valid for the spent fuel irradiated in the fast reactor.
Pu index was adopted and was proved to be valid for the spent fuel irradiated in the fast reactor.
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(9), p.907 - 914, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)Curium isotopes formed in irradiated MOX fuel in the experimental fast reactor JOYO were analyzed by applying a sophisticated radiochemical technique. Curium was isolated from the irradiated fuel by anion ion-exchange chromatography using a mixed medium of nitric acid and methanol. The isotopic ratio of curium and its content were determined by thermal ionization mass spectroscopy and alpha-spectrometry, respectively. U, Pu, Am and Nd were also isolated and analyzed for the determination of the curium content and burnup. The curium content was less than 0.004 at.% even at a burnup of 120 GWd/t, which is much smaller than that of PWR-MOX at 60 GWd/t. On the basis of the present analytical results, the transmutation behavior of curium isotopes in a fast reactor was discussed from various viewpoints. Transmutation rates of curium isotopes were estimated; the rate for 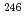 Cm, which is known to be a key nuclide in the transmutation of curium, was larger than the previously reported val
Cm, which is known to be a key nuclide in the transmutation of curium, was larger than the previously reported val
Osaka, Masahiko; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Global 2003; International Conference on Atoms for Prosperity: Upda, 0 Pages, 2003/00
Cm isotopes formed in irradiated MOX fuel in the experimental fast reactor JOYO were analyzed by applying a sophisticated radiochemical technique. Cm was isolated from the irradiated fuel by anion ion-exchange chromatography using a mixed medium of nitric acid and methanol. The isotopic ratio of Cm and its content were determined by thermal ionization mass spectroscopy and alpha-spectrometry, respectively. U, Pu, Am and Nd were also isolated and analyzed for the determination of the Cm content and burnup. The Cm content was less than 0.004 at.%, which is much smaller than that of PWR-MOX at 60 GWd/t. On the basis of the present analytical results, the transmutation behavior of Cm isotopes in a fast reactor was discussed from various viewpoints. Transmutation speeds of Cm isotopes were estimated; the speed for 246Cm, which is known to be a key nuclide in the transmutation of Cm, was smaller than the previously reported value. Transmutation behavior of each Cm isotope was also eval
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 4(1), 0 Pages, 2003/00
None
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Morozumi, Katsufumi; Namekawa, Takushi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(10), p.912 - 914, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
 Np reaction amount by chemical analysis of Neptunium sample irradiated at experimental fast reactor "JOYO"
Np reaction amount by chemical analysis of Neptunium sample irradiated at experimental fast reactor "JOYO"Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Morozumi, Katsufumi; Namekawa, Takashi
JNC TN9400 2001-016, 54 Pages, 2000/08
The chemical analysis technique was established to determine the nuclide generated in Neptunium (Np) sample with a high accuracy, to contribute to evaluation of transmutation characteristics of  Np in the fast reactor. (1)Establishment of chemical analysis technique The chemical analysis technique containing determination technique of fission amount of
Np in the fast reactor. (1)Establishment of chemical analysis technique The chemical analysis technique containing determination technique of fission amount of  Np, which was consist of Vanadium (V) of capsule material removal and Neodymium (Nd) recovery at high efficiency, was established with optimization of experimental conditions. Four Np saples irradiated in "JOYO" were analyzed using this technique. Results were as follows. (a)
Np, which was consist of Vanadium (V) of capsule material removal and Neodymium (Nd) recovery at high efficiency, was established with optimization of experimental conditions. Four Np saples irradiated in "JOYO" were analyzed using this technique. Results were as follows. (a) Np were determined with high accuracy (relative error was 2.2% at maximum). (b)Errors of fission amount monitoring nuclides
Np were determined with high accuracy (relative error was 2.2% at maximum). (b)Errors of fission amount monitoring nuclides 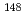 Nd were half less than that of
Nd were half less than that of  Cs. (c)Small amount of
Cs. (c)Small amount of  Pu was able to determined. (2)Evaluation of
Pu was able to determined. (2)Evaluation of  Np reaction amount The reaction amount of capture, fission and (n,2n) reactions were evaluated using analyzed values. Transmutation characteristics of
Np reaction amount The reaction amount of capture, fission and (n,2n) reactions were evaluated using analyzed values. Transmutation characteristics of  Np were evaluated using reaction amount. Evaluated results were as follows. (a)The ratio of capture or fission amount to unirradiated
Np were evaluated using reaction amount. Evaluated results were as follows. (a)The ratio of capture or fission amount to unirradiated  Np amount were 6.1
Np amount were 6.1 25.5 at%, 0.7
25.5 at%, 0.7 3.6 at%, respectively. (b)The
3.6 at%, respectively. (b)The  Np (n,2n)
Np (n,2n) 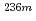 Np reaction amount was 7.0
Np reaction amount was 7.0 10
10 times of
times of  Np amount at maximum. (c)The dependences of
Np amount at maximum. (c)The dependences of  Np reaction amount to neutron energy spectrum were revealed from the fact such as linearity of fission to capture reaction amount ratio against fast neutron ratio in same fuel assembly.
Np reaction amount to neutron energy spectrum were revealed from the fact such as linearity of fission to capture reaction amount ratio against fast neutron ratio in same fuel assembly.
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Morozumi, Katsufumi; Namekawa, Takashi
JNC TN9400 2000-058, 49 Pages, 2000/04
The analytical technique for Cm contained in a MOX FUEL was developed and analysis of Cm contained in irradiated fuel of experimental fast reactor "JOYO" was carried out, to contribute to evaluation of transmutation characteristics of MA nuclide in the fast reactor. The procedure of ion-exchange separation of Cm with nitric acid-methanol mixed media essential for the isotopic analysis in irradiated MOX fuel was adopted considering for being rapid and easy. The fundamental test to grasp separation characteristics of this procedure, such as Cm elution position and separation capacity between Cm and Am or Eu, was carried out. ln applying this procedure to the analysis of Cm contained in actual specimen, separation condition was evaluated and optimized, and the procedure consist of impurity removal and Am removal process was devised. This procedure resulted in high recovery rate of Cm and high removal rate of Am and impurity which becomes a problem in sample handling and mass-spectrometry such as Eu and Cs. The Cm separation test from irradiated MOX fuel was carried out using this technique, and Cm isotopic ratio analysis was enabled. The analytical technique for Cm contained in irradiated MOX fuel was established using the procedure of ion-exchange separation with nitric acid-methanol mixed media. The analysis of Cm contained in irradiated MOX fuel of experimental fast reactor "Joyo" was carried out. As a result, it was revealed from measured data that Cm content rate was 1.4 4.0
4.0 lO
lO atom%, small amount of
atom%, small amount of 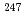 Cm was generated and Cm isotopic ratio was constant above burn-up 60GWd/t.
Cm was generated and Cm isotopic ratio was constant above burn-up 60GWd/t.
*; Takasu, Aki*; *; Kimura, Hideo; Sato, Seichi*; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Nakayama, Shinichi; Niibori, Yuichi*; *; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki*; et al.
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 5(1), p.3 - 19, 1998/08
no abstracts in English
Koyama, Shinichi; ; ; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Morozumi, Katsufumi;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 35(6), 406 Pages, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:70.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
 Np transmutation characteristics with chemical analysis of neptunium dosimeter irradiated in "Joyo"
Np transmutation characteristics with chemical analysis of neptunium dosimeter irradiated in "Joyo"Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Otsuka, Yuko; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Namekawa, Takashi; Konno, Koichi
PNC TN9410 98-020, 70 Pages, 1997/12
The purpose of this study is to evaluate transmutation characteristics such as dependence of  Np transmutation rate to neutron energy spectrum and neutron fluences. Analysis of the Neptunium dosimeter, in which was irradiated in the experimental fast reactor "Joyo", was carried out by applying the technique for analysis of minor actinide nuclides in irradiated MOX fuel. It is necessary to remove Vanadium before analysis of Neptunium dosimeter because NpO
Np transmutation rate to neutron energy spectrum and neutron fluences. Analysis of the Neptunium dosimeter, in which was irradiated in the experimental fast reactor "Joyo", was carried out by applying the technique for analysis of minor actinide nuclides in irradiated MOX fuel. It is necessary to remove Vanadium before analysis of Neptunium dosimeter because NpO powder was enclosed in Neptunium dosimeter that was made of Vanadium capsule. The result of analysis and evaluations are as follows. (1)In order to recover Neptunium sample completely, sample was dissolved with capsule before removing the Vanadium from sample solution. Sample treatment method of whole capsule dissolution for chemical analysis of Neptunium dosimeter was established. (2)
powder was enclosed in Neptunium dosimeter that was made of Vanadium capsule. The result of analysis and evaluations are as follows. (1)In order to recover Neptunium sample completely, sample was dissolved with capsule before removing the Vanadium from sample solution. Sample treatment method of whole capsule dissolution for chemical analysis of Neptunium dosimeter was established. (2) Np, Plutonium isotopes,
Np, Plutonium isotopes,  Am and
Am and  Cs in the dosimeter were analyzed using the method of whole capsule dissolution, alpha spectrometry, gamma spectrometry and isotopic dilution mass spectrometry. Transmutation rate of
Cs in the dosimeter were analyzed using the method of whole capsule dissolution, alpha spectrometry, gamma spectrometry and isotopic dilution mass spectrometry. Transmutation rate of  Np was calculated using the analyzed value. Tendency of transmutation rate was certified, which is higher fission ratio at the center and higher capture ratio at both upper and lower end. (3)Transmutation rate with error was evaluated by neutron fluences considering the neutron energy spectrum, and calculated value by "MAGI" code was agreed well with analysis value. Dependence of transmutation rate of
Np was calculated using the analyzed value. Tendency of transmutation rate was certified, which is higher fission ratio at the center and higher capture ratio at both upper and lower end. (3)Transmutation rate with error was evaluated by neutron fluences considering the neutron energy spectrum, and calculated value by "MAGI" code was agreed well with analysis value. Dependence of transmutation rate of  Np to neutron energy spectrum was certified.
Np to neutron energy spectrum was certified.
Koyama, Shinichi; ; Osaka, Masahiko; ; ; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
Proceedings of International Conference on Future Nuclear Systems (Global'97), Vol.2, 0 Pages, 1997/10
no abstracts in English
Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Konno, Koichi; Kajitani, Yukio
PNC TN9410 97-054, 44 Pages, 1997/04
For analysis of a small quantity of americium, it is necessary to separate from curium which has similar chemical property. As a chemical separation method for americium, and curium, the oxidation of americium with pentavalent bismuth and subsequent co-precipitation of trivalent curium with BIPO were applied to analyze americium in irradiated MOX fuels which contained about 3Owt% plutonium and 0.9wt%
were applied to analyze americium in irradiated MOX fuels which contained about 3Owt% plutonium and 0.9wt%  Am before irradiation and were irradiated up to 26.2GWd/t in the experimental fast reactor Joyo. The purpose of this study is to measure isotopic ratio of americium and to evaluate the change of isotopic ratio with irradiation. Following results are obtained in this study, (1)The isotopic ratio of americium (
Am before irradiation and were irradiated up to 26.2GWd/t in the experimental fast reactor Joyo. The purpose of this study is to measure isotopic ratio of americium and to evaluate the change of isotopic ratio with irradiation. Following results are obtained in this study, (1)The isotopic ratio of americium ( Am,
Am,  Am and
Am and  Am) can be analyzed in the MOX fuels by isolating americium. The isotopic ratio of
Am) can be analyzed in the MOX fuels by isolating americium. The isotopic ratio of 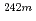 Am and
Am and  Am increases up to 0.62at% and 0.82at% at maximum burnup, respectively. (2)The results of isotopic analysis indicates that the contents of
Am increases up to 0.62at% and 0.82at% at maximum burnup, respectively. (2)The results of isotopic analysis indicates that the contents of  Am decreases, whereas
Am decreases, whereas  Am,
Am,  Am increase linearly with increasing burnup.
Am increase linearly with increasing burnup.
Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Otsuka, Yuko; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Konno, Koichi; Kajitani, Yukio
PNC TN9410 96-297, 79 Pages, 1996/11
As a part of evaluation of irradiation behavior and burnup characteristics of MA nuclides such as Np, Am and Cm in MA containing MOX fuel, we are studying the quantitative analysis techniques for MA nuclides in irradiated fuel. In this study, we studied the mutual separation method for Am and Cm to establish the analysis method for Am and Cm following Np analysis by alpha spectrometry. The measurements of Am and Cm are difficult to analyze quantitatively because the amounts of some nuclides are too small and the number of nuclides are large, whose energies of the alpha radioactive rays are almost same. Therefore we selected to analyze the trace amount of Am and Cm isotopes using mass spectrometry, and have studied the techniques for mutual separation of Am and Cm using oxidation method of Am by NaBiO for standard samples. We have also evaluated the availability of this method for irradiated fuel. Results are as follows. (1)Through the mutual separation tests, we have found the most suitable conditions for separation of both Am and Cm from each other element. The method obtaining Am which contains no Cm is used water for precipitation washing solution, containing Cm is achicved that the remaining ratio of Am (ratio of radioactivity of
for standard samples. We have also evaluated the availability of this method for irradiated fuel. Results are as follows. (1)Through the mutual separation tests, we have found the most suitable conditions for separation of both Am and Cm from each other element. The method obtaining Am which contains no Cm is used water for precipitation washing solution, containing Cm is achicved that the remaining ratio of Am (ratio of radioactivity of  Am/
Am/ Cm against before separation) were reduced less than 1/10 for Cm. (2)Applying of this method to irradiated fuel, the coordinate remaining ratio and the chemical yield of Am and Cm were almost same as them in the separation tests. This method to apply various irradiated MOX Fuel is therefore possible. (3)The isotope ratio
Cm against before separation) were reduced less than 1/10 for Cm. (2)Applying of this method to irradiated fuel, the coordinate remaining ratio and the chemical yield of Am and Cm were almost same as them in the separation tests. This method to apply various irradiated MOX Fuel is therefore possible. (3)The isotope ratio  Am,
Am,  Am and
Am and  Am measured by mass spectrometry, which could not be analyzed by radioactive ray spectrometry causing less than detection limit, were 98.55% : 0.62% : 0.83%. We also measured zero of the mass number of 240 and 244 on the specimens and then certified no contamination of Cm to Am.
Am measured by mass spectrometry, which could not be analyzed by radioactive ray spectrometry causing less than detection limit, were 98.55% : 0.62% : 0.83%. We also measured zero of the mass number of 240 and 244 on the specimens and then certified no contamination of Cm to Am.
 Am content and evaluation of burnup dependence in Am containing MOX fuel pin
Am content and evaluation of burnup dependence in Am containing MOX fuel pinKoyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Otsuka, Yuko; Konno, Koichi; Kajitani, Yukio; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki
PNC TN9410 96-301, 61 Pages, 1996/10
We are studying quantitative analysis of Minor Actinides (Np, Am, Cm) in irradiated fuels as a part of the PNC research project for advanced nuclear fuel recycle system. In alpha-gamma section, irradiation behavior of MOX fuel and burning characteristic evaluation research of the MA nuclide which contain the minor actinide species are carrying out. We measured  Am content of the MOX fuel pin which contained
Am content of the MOX fuel pin which contained  Am of about 0.9wt% before irradiation and were irradiated up to 26.2GWd/t in the JOYO reactor. The results are as follows. Burn-up dependence of the
Am of about 0.9wt% before irradiation and were irradiated up to 26.2GWd/t in the JOYO reactor. The results are as follows. Burn-up dependence of the  Am content in this samples was not observed. The
Am content in this samples was not observed. The  Am content showed the fixed value of about 1% in the range from 0 to 28GWd/t. This reason is assumed that Am produced by
Am content showed the fixed value of about 1% in the range from 0 to 28GWd/t. This reason is assumed that Am produced by  -decay of
-decay of  Pu for cooling times between each cycles valances it in disappearance under irradiated in JOYO based on the calculated value by ORIGEN-II code.
Pu for cooling times between each cycles valances it in disappearance under irradiated in JOYO based on the calculated value by ORIGEN-II code.
 Am sample irradiated in Japan Material Testing Reactor
Am sample irradiated in Japan Material Testing ReactorKoyama, Shinichi; Tanaka, Kenya; Mitsugashira, Toshiaki; Sato, Isamu*; Hara, Mitsuo*; Suto, Mitsuo*; Hanami, Akira*
no journal, ,
Radiochemical analysis of  Am sample irradiated in JMTR was performed. After mutual separation of Am, Cm and Pu from the irradiated
Am sample irradiated in JMTR was performed. After mutual separation of Am, Cm and Pu from the irradiated  Am sample, the isotopic composition was analyzed by mass spectroscopy.
Am sample, the isotopic composition was analyzed by mass spectroscopy.