Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:97.1(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 Cs and
Cs and  Cs radioactivity measurements
Cs radioactivity measurementsMalins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Takahashi, Junko*; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 226, p.106456_1 - 106456_12, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.04(Environmental Sciences)Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Miura, Katsuya*; Sugano, Ryoko*; Ichimura, Masahiko*; Hayakawa, Jun*; Ikeda, Shoji*; Ohno, Hideo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review B, 84(17), p.174434_1 - 174434_7, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yoshikawa, Hideki; Miura, Masahiko*; Sato, Tomofumi*; Matsubara, Masaaki*
no journal, ,
A characterization for SRB biofilm and Cs sorption experiment with the film were carried out.
 ; A Model for astrobiological studies
; A Model for astrobiological studiesHorikawa, Daiki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Abe, Wataru*; Koshikawa, Shigeyuki*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Iwata, Kenichi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Higashi, Seigo*; et al.
no journal, ,
We report the first successful rearing of the herbivorous tardigrade,  , by supplying a green alga
, by supplying a green alga  as a food. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle, from eggs, to juveniles, and to adults. Reared adults, while in an anhydrobiotic state, were tolerant to temperatures -196
as a food. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle, from eggs, to juveniles, and to adults. Reared adults, while in an anhydrobiotic state, were tolerant to temperatures -196 C and 100
C and 100 C. Furthermore, they were shown to be tolerant to the exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile, 1 GPa of hydrostatic pressure, or 5000 Gy of He ion radiation. We will report the details of these results, along with the description of their life history. Due to the observed tolerance to such extreme environmental conditions, we propose R. varieornatus to be included as a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
C. Furthermore, they were shown to be tolerant to the exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile, 1 GPa of hydrostatic pressure, or 5000 Gy of He ion radiation. We will report the details of these results, along with the description of their life history. Due to the observed tolerance to such extreme environmental conditions, we propose R. varieornatus to be included as a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
Do, V. K.; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Miura, Katsue; Iwasaki, Maho; Sato, Soichi
no journal, ,
Technical support for environmental restoration of Fukushima and decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) are the most important mission of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In this presentation, we outline Okuma Analysis and Research Center and our mission on technical development for analyzing rubble and wastes from the decommissioning of 1F. Novel analytical methods are being developed at the center for determining difficult-to-measure nuclides. In addition, some analytical techniques based on liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry, a novel optically spectroscopic method, for measuring elemental composition of highly active liquid wastes is reported.
Malins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Malins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
We analyzed changes in ambient dose equivalent rates (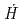 *(10)) between 2011 and 2017 in forests in Fukushima Prefecture. PHITS was used to calculate the effects of changes in the distribution of
*(10)) between 2011 and 2017 in forests in Fukushima Prefecture. PHITS was used to calculate the effects of changes in the distribution of 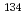 Cs and
Cs and 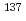 Cs within forests on
Cs within forests on 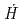 *(10). The transfer of radiocesium from the crowns of evergreen coniferous trees to the forest floor appeared to cause slower decreases in
*(10). The transfer of radiocesium from the crowns of evergreen coniferous trees to the forest floor appeared to cause slower decreases in 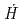 *(10) at 1 m height in early years than expected by the rate of
*(10) at 1 m height in early years than expected by the rate of 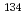 Cs and
Cs and 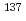 Cs decay.
Cs decay.
Malins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Nagano, Takuya*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kaida, Atsushi*; Nojima, Hitomi*; Yoshimura, Ryoichi*; Miura, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
In radiotherapy, metals placed close to oral tumors are often irradiated together. To date, physical calculations and dosimetry have confirmed dose enhancement around metals; however, the biological effects remain unclear. In this study, using gold as a dental material and lead which is a high atomic number similar to gold, we investigated the biological effects of tumor cells placed close to metals after therapeutic X-rays. As a result of the cell experiment, the sensitizing effect ratios of the lead plate with 2 mm and 3 mm thicknesses at 1% survival endpoint were 1.41 and 1.27, respectively, and the ratio for the 2-mm gold plate was 1.44. Meanwhile, the PHITS simulation shows that the dose enhancement ratio with and without the metal plate was approximately 1.11, which was equivalent to the measured sensitization effect ratio. In the future, we will measure the DNA damage responses for various metal thicknesses and further elucidate the mechanism of the sensitizing effects from standpoints of a hybrid approach combined with PHITS simulation.
Nagano, Takuya*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kaida, Atsushi*; Nojima, Hitomi*; Furuta, Takuya; Sato, Kaoru; Yoshimura, Ryoichi*; Miura, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
A dental prosthesis such as a metal crown exists in radiation field when performing head and neck cancer radiotherapy. In our previous studies, we have evaluated the sensitizing effect ratio (SER) of the radiobiological effects around metal crowns by in vitro analysis. However, it is uncertain how much SER is actually expected in complex geometry in clinical practice. Here, we simulated the treatment plan using a head phantom with a metal crown, and evaluated the dose distributions around the metal crown in a realistic patient system by simulation. The simulation results using PHITS agree well with the SER values obtained in vitro. It has been known that localized mucositis occurs around metal crowns during radiotherapy, and this outcome is expected to provide a precise understanding of the mechanism on inflammation in tissues around metals.