Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Miura, Akihiko; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.212 - 214, 2023/01
In the J-PARC linac, the bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is developed to precisely and rapidly measure the longitudinal beam profile at the front-end, towards the improvement of the beam matching. The graphite target having the good strength to the high-power beam, has been introduced in order to resist the heat loading of the high-intensity beam. The resolution and other uncertainties were evaluated for the BSM. The longitudinal Twiss parameters and emittance were measured using the BSM and the IMPACT, which was the 3D particle-in-cell simulation code. The precision of the longitudinal emittance measurement was improved, by implementing uncertainties related to the BSM into the calculation. In this presentation, we will report a series of the measurement result, the method of the beam diagnostics with the BSM at the front-end, and the comparison between the measurement and the beam simulation.
Kumagai, Tomohisa*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Miura, Naoki*; Marie, S.*; Almahdi, R.*; Mano, Akihiro; Li, Y.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Wada, Yoshitaka*; Hwang, J.-H.*; et al.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011509_1 - 011509_18, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.77(Engineering, Mechanical)To predict fracture behavior for ductile materials, some ductile fracture simulation methods different from classical approaches have been investigated based on appropriate models of ductile fracture. For the future use of the methods to overcome restrictions of classical approaches, the applicability to the actual components is of concern. In this study, two benchmark problems on the fracture tests supposing actual components were provided to investigate prediction ability of simulation methods containing parameter decisions. One was the circumferentially through-wall and surface cracked pipes subjected to monotonic bending, and the other was the circumferentially through-wall cracked pipes subjected to cyclic bending. Participants predicted the ductile crack propagation behavior by their own approaches, including FEM employed GTN yielding function with void ratio criterion, are FEM employed GTN yielding function, FEM with fracture strain or energy criterion modified by stress triaxiality, XFEM with J or delta J criterion, FEM with stress triaxiality and plastic strain based ductile crack propagation using FEM, and elastic-plastic peridynamics. Both the deformation and the crack propagation behaviors for monotonic bending were well reproduced, while few participants reproduced those for cyclic bending. To reproduce pipe deformation and fracture behaviors, most of groups needed parameters which were determined toreproduce pipe deformation and fracture behaviors in benchmark problems themselves and it is still difficult to reproduce them by using parameters only from basic materials tests.
Miura, Hiromi*; Watanabe, Chihiro*; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru*; Oba, Yojiro; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Yoshinaga, Naoki*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 833, p.142531_1 - 142531_12, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.27(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Hayashi, Naoki; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Miura, Akihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 7th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2018) (Internet), p.219 - 223, 2019/01
J-PARC is a multi-purpose facility. Accelerator stability is the one of important issues for users of this facility. To realize stable operation, we must collect data on interlocked events and analyze these data to determine the reasons for the occurrence of such events. In J-PARC Linac, data of interlocked events have been recorded using several some beam loss monitors and current monitors, and these data have been are analyzed and classified. In J-PARC RCS, new instrumentation is being introduced to obtain beam position. We discuss the present status and future plans related to this subject.
 laser stripping experiment in J-PARC RCS
laser stripping experiment in J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Okabe, Kota; Miura, Akihiko; Hayashi, Naoki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 6th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2017) (Internet), p.233 - 236, 2018/03
Hayashi, Naoki; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Miura, Akihiko; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.540 - 544, 2017/12
The J-PARC linac operation is stable, however, the numbers of interlocked events due to single beam loss monitor (BLMP) is increasing. Recently, the counts is comparable to the number of RFQ trip, and a measure has been required for improvement of the operation efficiency. Thus, every event data has been analyzed and classified into three categories. It is found that there are characteristic signal or pattern of BLMP for every categories. Although the linac BLMP detector is standard, its setting parameters are differ from those of other two synchrotrons in the J-PARC. To optimize time resolution, the input impedance of its pre-amplifier is selected to be 50  and interlock is defined in raw signal height and width not integral signal of BLMP. Some new parameters has been tried to reduce unnecessary interlock.
and interlock is defined in raw signal height and width not integral signal of BLMP. Some new parameters has been tried to reduce unnecessary interlock.
Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Miura, Akihiko
Proceedings of 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '17) (Internet), p.277 - 280, 2017/06
Multi-turn painting injection scheme is important for high intensity proton accelerators. At the J-PARC RCS, a transverse painting scheme was adapted by adding vertical painting magnets to the beam transport line before the injection point, with horizontal painting being performed by a set of dedicated pulse magnets in the ring. To establish a transverse painting condition, it is usual to base on the pulse magnet current pattern. However, it is more desirable to directly measure the beam orbit time variation for evaluation. A linac beam was chopped to match the ring RF bucket. We thought that it would be difficult to measure the position for each pulse; however, the average position could be extracted by introducing a particular device. For the beam injected into the ring, because the linac RF frequency component was diminished due to debunching quickly, one could determine its position in the beginning of the injection period. However, due to rebunching effect the position determination becomes difficult. This problem needs to be resolved.
Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Miura, Naoki*; Hoshino, Katsuaki*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 139(2), p.021203_1 - 021203_7, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to investigate the failure behavior of the pipes with local wall thinning subjected to multi-axial loads including the torsion, failure experiments were performed on 20 mm diameter carbon steel pipes with a local wall thinning. Based on the experimental results, the failure estimation method is investigated.
Hayashi, Naoki; Kato, Yuko; Miura, Akihiko; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 5th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2016) (Internet), p.368 - 371, 2017/03
It is important to understand why the beam loss occurs during user operation. It is understandable that the beam loss results from RF cavities failure. However, it would be still useful to study the beam loss detailed mechanism and to know which beam loss monitor (BLM) experiences the highest loss or is most sensitive. This may lead a reduction in the number of interlocked events and a more stable accelerator operation. The J-PARC Linac BLM has a simple data recorder that comprises multiple oscilloscopes. Although its functionality is limited, it can record events when an interlock is triggered. Of particular interest here are the events associated with only the BLM Machine Protection System (MPS). These may reveal hidden problems with the accelerator.
Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Miura, Naoki*; Hoshino, Katsuaki*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 139(1), p.011204_1 - 011204_10, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.08(Engineering, Mechanical)To investigate the failure behavior of cracked pipes subjected to multi-axial loads including the torsion moment, failure experiments were performed on 20 mm diameter stainless steel pipes with a circumferential surface crack or a through-wall crack under combined axial force, bending and torsion moments. Based on the experimental results, the failure estimation methods were investigated.
Miura, Akihiko; Hayashi, Naoki; Maruta, Tomofumi*; Liu, Y.*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Fukuoka, Shota*
Proceedings of 4th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2015) (Internet), p.386 - 389, 2016/02
We have used bunch shape monitors (BSMs) to measure the longitudinal bunch length of negative hydrogen ion beam in the J-PARC linac. In order to evaluate the measurement errors with peak beam current increasing, we observed waveforms with various beam current. As the result, an RMS bunch length depends on the peak beam current and the bending at the pulse head grows with the peak beam current. We also compared the data taken at an off-center beam to avoid the thermal stress with the ones at an on-center beam, because a target wire will be exposed to a higher peak beam current. In this paper, we introduced the peak beam current dependence of the bunch length waveforms, and an effect of on- /off-centering of the wire position. Finally the new buncher tuning method using one BSM have been discussed.
Miyao, Tomoaki*; Miura, Akihiko; Kawane, Yusuke; Tamura, Jun; Nemoto, Yasuo; Ao, Hiroyuki*; Hayashi, Naoki; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ouchi, Nobuo; Mayama, Minoru*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1338 - 1341, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawane, Yusuke; Tamura, Jun; Nemoto, Yasuo; Hayashi, Naoki; Fukuoka, Shota*; Mayama, Minoru*; Miura, Akihiko; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1246 - 1250, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Sawabe, Yuki; Maruta, Tomofumi*; Liu, Y.*; Miura, Akihiko; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hayashi, Naoki
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1202 - 1205, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Miura, Naoki*; Hoshino, Katsuaki*
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/07
The failure estimation method in ASME Code Section XI accounts for the bending moment and axial force due to pressure into account. The torsion moment is not considered. Recently, analytical investigations have been carried out by several authors on the limit load of cracked pipes considering multi-axial loads including torsion and two failure estimation methods for multi-axial loads including torsion moment with different ranges of values have been proposed. In this study, to investigate the failure behavior of cracked pipes subjected to multi-axial loads including the torsion moment and to provide experimental support for the failure estimation methods, failure experiments were performed on 20 mm diameter pipes with a circumferential surface crack or a through-wall crack under combined axial force and bending and torsion moments. Based on the experimental results, the proposed failure estimation methods were confirmed to be applicable to cracked pipes subjected to multi-axial loads.
Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Miura, Naoki*; Hoshino, Katsuaki*
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/07
Piping lines in nuclear power plants may experience multi-axial loads including tensile force, bending and torsion moments during operation. There is a lack of guidance for failure evaluation under the multi-axial loads including torsion moment. ASME B&PV Code Section XI Working Group is currently developing fully plastic failure evaluation procedures for pressurized piping items containing local wall thinning subjected to multi-axial loads. A failure estimation method for locally wall thinned pipes subjected to multi-axial loads including torsion moment has been proposed through numerical analyses. In this study, in order to investigate the failure behavior of the pipes with local wall thinning subjected to multi-axial loads including the torsion, failure experiments were performed on 20 mm diameter carbon steel pipes with a local wall thinning. Based on the experimental results, the proposed failure estimation method is confirmed to be applicable to pipes with local wall thinning.
Yamamoto, Masato*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Valo, M.*; Lambrecht, M.*; Viehrig, H.-W.*; Miura, Naoki*; Soneda, Naoki*
Small Specimen Test Techniques; 6th Volume (ASTM STP 1576), p.53 - 69, 2015/05
In order to ensure the robustness of the Master Curve technique, round-robin tests were performed using 0.16 inch-thick Mini-CT specimens by different investigators to see if consistent 
 values can be obtained. All the specimens used were machined and pre-cracked by one fabricator from unique Japanese RPV material. Seven institutes participated in this exercise, and obtained valid
values can be obtained. All the specimens used were machined and pre-cracked by one fabricator from unique Japanese RPV material. Seven institutes participated in this exercise, and obtained valid 
 values according to the ASTM E1921 standard. The scatter of
values according to the ASTM E1921 standard. The scatter of 
 values obtained was well within the uncertainty range defined in the standard, indicating the robustness of the Mini-CT specimen test technique. Throughout this activity, we could obtain 182
values obtained was well within the uncertainty range defined in the standard, indicating the robustness of the Mini-CT specimen test technique. Throughout this activity, we could obtain 182 
 for a single material. We investigated the statistics of this large database, and found that there is no remarkable difference not only in the
for a single material. We investigated the statistics of this large database, and found that there is no remarkable difference not only in the 
 values but also in the fracture toughness distribution between the Mini-CT specimen and the standard size 1T-C(T) specimen results.
values but also in the fracture toughness distribution between the Mini-CT specimen and the standard size 1T-C(T) specimen results.
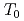 under various selections of temperature conditions
under various selections of temperature conditionsYamamoto, Masato*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Viehrig, H.-W.*; Miura, Naoki*; Soneda, Naoki*
Proceedings of 2014 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2014) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
The Master Curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness reference temperature To is expected to be a powerful tool to ensure the reliability of long-term used RPV steels. In order to get sufficient number of data for the MC approach related to the present surveillance program for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is important. The test technique for the miniature specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick had been verified the basic applicability of MC approach by means of Mini-CT for the determination of fracture toughness of typical Japanese RPV steels. A round robin (RR) program was organized to assure the robustness of the technique. As the third step of RR program, blinded tests were carried out. Precise material information was not provided to the participants. From the results obtained, the scatter range in 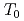 was within the acceptable scatter range specified in the testing standard. The selection of testing temperature seems to give limited effect like that in larger specimens.
was within the acceptable scatter range specified in the testing standard. The selection of testing temperature seems to give limited effect like that in larger specimens.
Yamamoto, Masato*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Naoki*
Proceedings of 2013 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
Master Curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness evaluation is expected to be a powerful tool to assess the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In order to get sufficient number of reliable data by the MC approach from used specimens of surveillance tests for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is necessary. For this purpose, a round robin test program on the miniature compact tension specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick for the MC approach was launched with the participation of academia, industries and a research institute in Japan. The program aims to verify the reliability of experimental data from Mini-CT, and to pick out technical issues to be solved. As the second step of this program, the effect of loading rate (d /d
/d ) was evaluated based on enlarged database. Despite of the difference in d
) was evaluated based on enlarged database. Despite of the difference in d /d
/d , no specific difference in scatter band of
, no specific difference in scatter band of 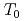 was found in d
was found in d /d
/d -
- 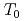 relationships. D
relationships. D /d
/d seems not to be sensitive on scatter band of To in the present results.
seems not to be sensitive on scatter band of To in the present results.
Yamamoto, Masato*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Chiba, Atsushi*; Hirano, Takashi*; Sugihara, Takuji*; Sugiyama, Masanari*; Miura, Naoki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2012 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2012) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2012/07
Master curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness evaluation is expected to be a powerful tool to assess the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In order to get sufficient number of reliable data for the MC approach from broken halves of surveillance test specimens for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is necessary. For this purpose, a round robin test program on the miniature compact tension specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick for the MC approach of a Japanese RPV steel has been launched with the participation of academia, industries and a research institute in Japan. The program aims to verify the reliability of experimental data from Mini-CT, and to pick out further investigation items to be solved. As the first step of this program, four institutes carried out MC testing and evaluation using common test procedure and specimens. Valid reference temperature T was successfully obtained in each institute. However, the T
was successfully obtained in each institute. However, the T values showed large differences with maximum of 34
values showed large differences with maximum of 34 C. It was indicated on the reason of difference that there is a strong correlation between the T
C. It was indicated on the reason of difference that there is a strong correlation between the T values and loading rate, which was selected by each institute per test standard.
values and loading rate, which was selected by each institute per test standard.