Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Miwa, Shuhei
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 218, p.111433_1 - 111433_10, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) -CsOH
-CsOHRizaal, M.; Luu, V. N.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
 reaction system
reaction systemRizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Miwa, Shuhei
Proceedings of 11th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research Conference (ERMSAR 2024) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2024/05
 /MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditions
/MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditionsLiu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 37, p.101532_1 - 101532_5, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Katsumura, Kosuke*; Takagi, Junichi*; Hosomi, Kenji*; Miyahara, Naoya*; Koma, Yoshikazu; Imoto, Jumpei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Miwa, Shuhei; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Hidaka, Akihide*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(11), p.674 - 679, 2023/11
, 65(11), p.674 - 679, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Mohamad, A. B.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.215 - 222, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Miwa, Shuhei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kino, Chiaki*; Suzuki, Eriko; Imoto, Jumpei
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-022, 32 Pages, 2023/01
The improved model for cesium (Cs) chemisorption onto stainless steel (SS) in the fission product (FP) chemistry database named ECUME was incorporated into the severe accident (SA) analysis code SAMPSON for the more accurate estimation of Cs distribution within nuclear reactor vessels in the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The SAMPSON with the improved model was verified based on the analysis results reproducing the experimental results which were subjected to the modeling of Cs chemisorption behavior. Then, the experiment in the facility with the temperature gradient tube to simulate SA conditions such as temperature decrease and aerosol formation was analyzed to confirm availability of the improved model to the analysis of Cs chemisorption onto SS. The SAMPSON with the improved model successfully reproduced the experimental results, which indicates that the improved model and the analytical method such as setting a method of node-junction, models of aerosol formation and the calculation method of saturated CsOH vapor pressure can be applicable to the analysis of Cs chemisorption behavior. As the information on water-solubility of Cs deposits was also prerequisite to estimate the Cs distribution in the 1F because Cs can be transported through aqueous phase after the SA, the water-solubility of chemisorbed Cs compounds was investigated. The chemisorbed compounds on SS304 have been identified to CsFeO at 873 K to 973 K with higher water-solubility, CsFeSiO
at 873 K to 973 K with higher water-solubility, CsFeSiO at 973 K to 1273 K and Cs
at 973 K to 1273 K and Cs Si
Si O
O at 1073 K to 1273 K with lower water-solubility. From these results, the water-solubility of chemisorbed Cs compounds can be estimated according to the SA analysis conditions such as temperature in the reactor and the CsOH concentration affecting the amount of chemisorbed Cs.
at 1073 K to 1273 K with lower water-solubility. From these results, the water-solubility of chemisorbed Cs compounds can be estimated according to the SA analysis conditions such as temperature in the reactor and the CsOH concentration affecting the amount of chemisorbed Cs.

 atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)
atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)Yamamoto, Takeshi; Fujita, Manami; Gogami, Toshiyuki*; Harada, Takeshi*; Hayakawa, Shuhei*; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ishikawa, Yuji*; Kamata, K.*; Kanauchi, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.03001_1 - 03001_5, 2022/11
Liu, J.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Shirasu, Noriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.484 - 490, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Miwa, Shuhei
2022-Nendo Renkei Juten Kenkyu Seika Hokokusho (Internet), 7 Pages, 2022/00
no abstracts in English
Rizaal, M.; Miwa, Shuhei; Suzuki, Eriko; Imoto, Jumpei; Osaka, Masahiko; Gou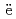 llo, M.*
llo, M.*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(48), p.32695 - 32708, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.61(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Miwa, Shuhei; Miyahara, Naoya*; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Imoto, Jumpei; Suzuki, Eriko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(12), p.825 - 829, 2021/12
, 63(12), p.825 - 829, 2021/12
In the BWR severe accident, it was indicated that the control material boron significantly influences chemical behavior and transition behavior of cesium, which is important from the viewpoint of exposure, and it causes great uncertainty in the prediction of environmental release and distribution in the reactor. Therefore, in order to elucidate the important chemistry to be considered in severe accident analysis, we have developed the experimental setup that enables the evaluation of chemistry during transportation in the reactor, and evaluated cesium chemistry. Based on the results, we developed the chemistry database named ECUME composed of datasets and models that are the basis of chemical reaction analysis so that chemical behavior could be evaluated by severe accident analysis code.
Liu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 26, p.100916_1 - 100916_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Miwa, Shuhei
2021-Nendo Renkei Juten Kenkyu Seika Hokokusho (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/00
no abstracts in English
Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Gou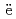 llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1287 - 1296, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:65.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to clarify the cesium iodide (CsI) transport behavior with a focus on the mechanisms of gaseous iodine formation in the reactor coolant system of LWR under a severe accident condition, a reproductive experiment of CsI transport behavior was conducted using a facility equipped with a thermal gradient tube. Various analyses on deposits and airborne materials during transportation could elucidate two mechanisms for the gaseous iodine formation. One was the gaseous phase chemical reaction in Cs-I-O-H system at relatively high-temperature region, which led to gaseous iodine transport to the lower temperature region without any further changes in gas species due to the kinetics limitation effects. The other one was the chemical reactions related to condensed phase of CsI, namely those of CsI deposits on walls with surface of stainless steel to form Cs CrO
CrO compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Chikashi; Rizaal, M.; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Osaka, Masahiko
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.253 - 260, 2020/12
We have proceeded the fundamental study for the improvement of the evaluation of fission product (FP) chemistry and the treatment of fine space resolution which are main issues for the evaluation of FP behaviors in a severe accident (SA). We have been developing FP chemistry database named ECUME for the improvement of SA analysis codes. We prepared thermodynamic data for Cs compounds which is no experimental data available by computational approach. Regarding the space resolution issue, we have been developing analysis tool named CHASER based on 3D-CFD code with the model for FP chemistry. More accurate evaluation of FP behavior can be achieved by incorporating ECUME to the CHASER.
Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miyahara, Naoya; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Liu, J.; Miradji, F.; Imoto, Jumpei; Afiqa, B. M.; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00537_1 - 19-00537_11, 2020/06
We constructed the fission product (FP) chemistry database named ECUME for LWR severe accident. This version of ECUME is equipped with dataset of the chemical reactions and their kinetics constants for the reactions of cesium(Cs)-iodine(I)-boron(B)-molybdenum(Mo)-oxygen(O)-hydrogen(H) system in gas phase, the elemental model for the high temperature chemical reaction of Cs with stainless steel applied as the structural material in a reactor, and thermodynamic data for CsBO vapor species and solids of Cs
vapor species and solids of Cs Si
Si O
O and CsFeSiO
and CsFeSiO for these chemical reactions. The ECUME will provide estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
for these chemical reactions. The ECUME will provide estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Miwa, Shuhei; Takase, Gaku; Imoto, Jumpei; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Miyahara, Naoya; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.291 - 300, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:66.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the evaluation of transport behavior of control material boron in a severe accident of BWR from the viewpoint of chemical effects on cesium and iodine behavior, boron chemistry during transportation in the high temperature region above 400 K was experimentally investigated. The heating tests of boron oxide specimen were conducted using the dedicated experimental apparatus reproducing fission product release and transport in steam atmosphere. Released boron oxide vapor was deposited above 1,000 K by the condensation onto stainless steel. The boron deposits and/or vapors significantly reacted with stainless steel above 1,000 K and formed the stable iron-boron mixed oxide (FeO) BO
BO . These results indicate that released boron from degraded BWR control blade in a severe accident could remain in the high temperature region such as a Reactor Pressure Vessel. Based on these results, it can be said that the existence of boron deposits in the high temperature region would decrease the amount of transported cesium vapors from a Reactor Pressure Vessel due to possible formation of low volatile cesium borate compounds by the reaction of boron deposits with cesium vapors.
. These results indicate that released boron from degraded BWR control blade in a severe accident could remain in the high temperature region such as a Reactor Pressure Vessel. Based on these results, it can be said that the existence of boron deposits in the high temperature region would decrease the amount of transported cesium vapors from a Reactor Pressure Vessel due to possible formation of low volatile cesium borate compounds by the reaction of boron deposits with cesium vapors.
Liu, J.; Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Takano, Masahide; Hidaka, Akihide; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 527, p.151819_1 - 151819_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To evaluate the effect of each constituent element on the evaporation rate of ruthenium (Ru) from fission-produced alloy precipitates, the oxidation and evaporation behaviors of metallic Ru, molybdenum (Mo), palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh) and Mo-Ru-Pd-Rh alloy powders were investigated by thermogravimetric analysis under oxidizing atmospheres from 1473 to 1723 K. The findings led to the following conclusions: (1) The quick oxidation of Mo into condensed Mo oxides can effectively suppress the oxidation and evaporation of Ru in alloy powders; (2) After the complete evaporation of Mo, the evaporation loss rate of Ru would be directly influenced by the Ru activity in the Ru-Pd-Rh alloys, which is determined by the composition of alloys.
Miwa, Shuhei; Miyahara, Naoya; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Liu, J.; Miradji, F.; Imoto, Jumpei; Afiqa, B. M.; et al.
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
We constructed the first version of fission product (FP) chemistry database named ECUME for LWR severe accident. The first version of ECUME is equipped with dataset of the chemical reactions and their kinetics constants for the reactions of cesium(Cs)-iodine(I)-boron(B)-molybdenum(Mo)-oxygen(O)-hydrogen(H) system in gas phase, the elemental model for the high temperature chemical reaction of Cs with stainless steel, and thermodynamic data for CsBO vapor species and solids of Cs
vapor species and solids of Cs Si
Si O
O and CsFeSiO
and CsFeSiO . The ECUME will provide more accurate estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
. The ECUME will provide more accurate estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.