Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cu
Cu O
O containing inclined columnar defects
containing inclined columnar defectsIshikawa, Norito; Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Miyahara, K.*; Kisu, T.*
Physica C, 357-360(Part.1), p.505 - 508, 2001/09
no abstracts in English
Miyahara, H.*; Narita, N.*; Ikeda, Keiichi*; Kato, Y.*; Fujiki, K.*; Momose, Takumaro; Tasaki, Takashi; Kurihara, Osamu; Hayashi, Naomi
JNC TY8400 2001-002, 81 Pages, 2001/07
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu Oy under magnetic field
Oy under magnetic fieldIshikawa, Norito; Sueyoshi, T.*; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Fujiyoshi, T.*; Miyahara, K.*; Kisu, T.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 284-288(Part1), p.873 - 874, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O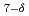 thin films with columnar defects
thin films with columnar defectsFujiyoshi, T.*; Sueyoshi, T.*; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kisu, T.*; Miyahara, K.*
Advances in Superconductivity XI, 1, p.597 - 600, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O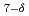 thin film
thin filmSueyoshi, T.*; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kisu, T.*; Fujiyoshi, T.*; Miyahara, K.*
Advances in Superconductivity XI, 1, p.593 - 596, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Tschiersch, J.*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Spielmann, V.*; Hurkamp, K.*; Iijima, Kazuki; Shinonaga, Taeko*; Miyahara, Kaname
no journal, ,
Inhalation dose depends on the kind and amount of inhaled radionuclides, but also on the size of radioactive particles and the solubility of the radionuclides in the lungs. Initial measurements during decontamination provide experimental data of the main parameters. These are particle size distribution with activity median aerodynamic diameter (AMAD) and geometric standard deviation and the solubility in the lungs. The dose assessment is performed according ICRP lung model using the computer code IMBA professional. Doses determined from measured parameters are compared to those using ICRP default values. Variability is studied and the range of potential inhalation dose is assessed.
Tschiersch, J.*; Spielmann, V.*; Shinonaga, Taeko*; Hurkamp, K.*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Okura, Takehisa; Iijima, Kazuki; Miyahara, Kaname
no journal, ,