Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hamase, Erina; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Yasutomo*; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113738_1 - 113738_12, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To enhance the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors, the natural circulation (NC) decay heat removal systems with a dipped-type direct heat exchanger (D-DHX) have been investigated. During the D-DHX operation, since the core-plenum interaction occurs, the reactor vessel model using a computational fluid dynamics code (RV-CFD) is required to be established. Previously, the CFD model based on the subchannel analysis was developed. In this study, to achieve lower computational cost maintaining the prediction accuracy, the coarse-mesh subchannel CFD (CMSC) model was developed, and was incorporated into the core of RV-CFD. As a result of PLANDTL-1 test analysis, the RV-CFD with the CMSC model can reproduce the core-plenum interaction under NC conditions.
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakajima, Toru; Ogata, Manabu; Uchida, Mao; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Tanaka, Kiriha; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-035, 29 Pages, 2024/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2024. The objectives and contents of this research are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Hamase, Erina; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Yasutomo*; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2024-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2024/09
In a design study of sodium-cooled fast reactors, we have developed the practical reactor vessel thermal-hydraulic analysis method (RV-CFD) that had a low computational cost about the thermal-hydraulics in the core to evaluate the core-plenum interactions occurred in the natural circulation decay heat removal during the dipped-type direct heat exchanger operation. In this study, the non-equilibrium thermal model which considered the thermal inertia of fuel pins was developed and incorporated into the core of RV-CFD. Through the transient analysis simulating the power reduction due to reactor scram, the applicability of RV-CFD to the transient analysis was confirmed.
Hamase, Erina; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Yasutomo*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
We have been developed a thermal-hydraulic analysis model in the reactor vessel using the computational fluid dynamics code with a low computational cost to evaluate core-plenum interactions during a natural circulation decay heat removal using a dipped-type direct heat exchanger in a design of sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, we investigate the coarse mesh modeling of interwrapper gap (IWG) using correlations for the purpose of the development of a practical model which can reduce the computational cost maintaining the prediction accuracy. An influence of combinations of the coarse mesh and the correlation for pressure loss in the IWG on the thermal-hydraulics and the core temperature distribution is revealed through the numerical analysis of a sodium experiment.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3445 - 3450, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Deng, Y.*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Manabe, Seiya*; Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Abe, Shinichiro; Tampo, Motonobu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 71(4, Part 2), p.912 - 920, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)With the miniaturization of semiconductors and the decrease in operating voltage, there is a growing interest and discussion in whether the muons in cosmic rays may be the source of single event upsets (SEUs). In the case of neutron-induced SEUs, it was reported that the irradiation side has the impact on SEU cross sections. Here, to investigate the impact of irradiation direction on muon-induced SEUs, we have measured and simulate muon-induced SEUs in 65-nm bulk SRAMs with different muon irradiation directions. It was found that the peak SEU cross section for the package side irradiation is about twice large as that for the board side irradiation. We also revealed that the difference in observed SEU cross sections between the package side and the board side irradiation is caused by differences in energy straggling due to changes in penetration depth depending on the incident direction.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Chiu, I.-H.; Kudo, Takuto*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Sentoku, Sawako*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.1797_1 - 1797_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The amount of C in steel, which is critical in determining its properties, is strongly influenced by steel production technology. We propose a novel method of quantifying the bulk C content in steel non-destructively using muons. This revolutionary method may be used not only in the quality control of steel in production, but also in analyzing precious steel archaeological artifacts. A negatively charged muon forms an atomic system owing to its negative charge, and is finally absorbed into the nucleus or decays to an electron. The lifetimes of muons differ significantly, depending on whether they are trapped by Fe or C atoms, and identifying the elemental content at the muon stoppage position is possible via muon lifetime measurements. The relationship between the muon capture probabilities of C/Fe and the elemental content of C exhibits a good linearity, and the C content in the steel may be quantitatively determined via muon lifetime measurements. Furthermore, by controlling the incident energies of the muons, they may be stopped in each layer of a stacked sample consisting of three types of steel plates with thicknesses of 0.5 mm, and we successfully determined the C contents in the range 0.20 - 1.03 wt% depth-selectively, without sample destruction.
 symmetry for anisotropic
symmetry for anisotropic 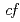 hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi
hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Higashiya, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165121_1 - 165121_10, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chiu, I.-H.; Terada, Kentaro*; Osawa, Takahito; Park, C.*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*
Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 58(9), p.1333 - 1344, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Hamase, Erina; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Yasutomo*; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2023-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/09
In sodium-cooled fast reactors, decay heat removal systems under natural circulation with a dipped-type direct heat exchanger (D-DHX) have been investigated. During the D-DHX operation, the cold sodium from the D-DHX flows into the assemblies and the interwrapper gap (IWG) between them. To evaluate such phenomena in design studies, the reactor vessel thermal-hydraulic analysis method (RV-CFD) which has the accuracy required for design studies while reducing the computational cost is required. In this study, with the aim of developing the practical RV-CFD with a low computational cost, the influence of the combination of the mesh number in the IWG and the pressure loss coefficient on the core temperature distribution was investigated through the numerical analysis of a sodium experimental apparatus named PLANDTL-1.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ezure, Toshiki; Hamase, Erina
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The numerical analysis model for the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code for the design study is developed to evaluate the thermal-hydraulics in the core under the core-plenum interaction (CPI) during the decay heat removal using the dipped type direct heat exchanger (D-DHX). To judge the adequacy of the numerical results for a validation study with the sodium experiment results conducted at PLANDTL-2 facility, the degree of difference (DoD) between the numerical and experimental results must be measured by using the area validation metrics (AVM). Through the examinations, the applicability of the AVM and MAVM based on the p-box method was confirmed.
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:72.47(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Chiu, I.-H.; Terada, Kentaro*; Osawa, Takahito; Park, C.*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012004_1 - 012004_6, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:71.57(Physics, Applied)In the last decade, non-destructive elemental analysis using negative muon beams advanced significantly. This method can be used to determine the elemental composition of bulk materials without causing damage. In this study, we performed a negative muon irradiation experiment for a Northwest Africa 482 lunar meteorite (NWA482), which was installed in a stainless steel analysis chamber. The analysis chamber was filled with helium gas to suppress the background signals caused by air-scattering muons. The muonic X-rays from Al, Fe, Ca, Mg, Si, and O in the samples were detected using six high-purity germanium semiconductor detectors arranged around the analysis chamber. To correct the X-ray self-absorption effect of the samples, a Monte-Carlo simulation using Geant4 toolkit was used. Based on the quantitative analysis for muonic X-ray measurement with the correction application from the simulation, we successfully investigated the analytical sensitivity of each element in meteorites based on the NWA482 data.
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Hamase, Erina; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Yasutomo*; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/09
To enhance the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors, the natural circulation (NC) decay heat removal systems with a dipped-type direct heat exchanger (D-DHX) have been investigated. During the D-DHX operation, since the core-plenum interaction occurs, development of the reactor vessel model including the more model by using a computational fluid dynamics code (RV-CFD) is required. Previously, the CFD model based on the subchannel analysis was developed. In this study, to achieve much lower computational cost maintaining the prediction accuracy, the coarse-mesh subchannel CFD (CMSC) model has been developed and was incorporated into the core of RV-CFD. As a result of PLANDTL-1 test analysis, the RV-CFD with the CMSC model can reproduce the radial heat transfer under NC conditions.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Hamase, Erina; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Yasutomo*; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 9(4), p.21-00438_1 - 21-00438_15, 2022/08
To enhance the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors, a dipped-type direct heat exchanger (D-DHX) has been investigated in a natural circulation decay heat removal system. During the D-DHX operation, the core-plenum interactions occurs and the thermal-hydraulics in the reactor vessel (RV) is complicated, the establishment of thermal-hydraulic analysis model in the RV for computational fluid dynamics code (RV-CFD) is required to simulate the thermal stratification in the upper plenum and thermal-hydraulics in the core. In this study, in terms of using RV-CFD for design study, the subchannel CFD model with low computational cost was adopted to the core of RV-CFD and the numerical simulation was carried out in comparison with the measured data in the sodium test facility named PLANDTL-1. As the result, the calculated sodium temperature in the core had good agreement with the experimental result and the applicability of the RV-CFD for the core-plenum interactions was confirmed.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Tsuji, Mitsuyo; Kobayashi, Jun; Kurihara, Akikazu; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Nakane, Shigeru*; Ishida, Katsuji*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/04
In sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), optimizing the design and operate decay heat removal systems (DHRSs) is important for safety enhancement against severe accidents that could lead to core melting. The natural circulation phenomena in a reactor vessel during operating a DHRS were clarified by conducting water experiments using a 1:10 scale experimental facility (PHEASANT) simulating the reactor vessel of loop-type SFRs. In this study, we investigated the natural circulation phenomena under conditions of operating the dipped-type DHX and RVACS using the results of temperature and particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements, respectively. Furthermore, the effects of temperature fluctuation on the PIV measurement were quantitatively evaluated.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.