Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.78(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 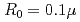 m.
m.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Inagaki, Manabu; Miyasaka, Iku*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1193, p.375 - 380, 2009/05
The scenario analysis was performed for microbial effect on the performance assessment (PA) of high level radioactive waste disposal system based on recent literature review. The consideration for PA with these effects was clarified and important FEPs were selected in the point of safety function under various uncertainties for microbe information. It is clear that the biological effect on groundwater components evolution, which is caused by the microbial redox reaction, is one of the most important issues to assess on PA. And we developed a biological parameter database which has growth and metabolism data for interactive six microbial groups. The database composed some significant data like specific growth rate, maximum growth rate, constant decay rate, and experimental condition for model assessment.
JRR-2 Control Office; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Kohayakawa, Toru; Morozumi, Minoru; Kambayashi, Yuichiro; Shitomi, Hajimu; Kokanezawa, Takashi; et al.
JAERI 1027, 57 Pages, 1962/09
no abstracts in English
Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Haginoya, Kinichi; Kohayakawa, Toru; Yamaki, Jikei; Yokota, Mitsuo; Horiki, Oichiro; Yuhara, Shunichi; et al.
JAERI 1023, 120 Pages, 1962/09
no abstracts in English
JRR-2 Operations Office; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Haginoya, Kinichi; Kohayakawa, Toru; Yamaki, Jikei; Yokota, Mitsuo; Horiki, Oichiro; et al.
JAERI 1024, 79 Pages, 1962/08
no abstracts in English
JRR-2 Critical Experiments Group; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Kohayakawa, Toru; Morozumi, Minoru; Kambayashi, Yuichiro; Shitomi, Hajimu; Kokanezawa, Takashi; et al.
JAERI 1025, 62 Pages, 1962/03
no abstracts in English
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Miyasaka, Iku*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asano, Takahiro; Ishii, Kosuke*; Miyasaka, Iku*; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yui, Mikazu; Miyasaka, Iku*
no journal, ,
To evaluation of safety assessment for high-level radioactive waste disposal, it is considered that microbial effect is very important. The effects of microbes on groundwater chemistry is evaluated with the numerical code "MINT", using data collected from the borehole HDB-10 in the Horonobe underground research laboratory (URL) in Japan.
Miyasaka, Iku*; Fukunaga, Sakae*; Kanno, Takeshi*; Tochigi, Yoshikatsu; Namba, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Kosuke*; Miyasaka, Iku*; Fukunaga, Sakae*; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Miyasaka, Iku*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
We developed a method to measure microbial activity by using hydrogen consumption without organic-matter addition. It was applied to shallow and deep groundwaters at Horonobe, which contained little biodegradable-organic matter, and revealed microbial adaptation to an anaerobic environment. The result would contribute to answer a question whether consideration for microbes is needed in studying groundwater at a site. The research was carried out as a part of "Project for Assessment Methodology Development of Chemical Effects on Geological Disposal System" funded by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan.
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Ishii, Kosuke*; Miyasaka, Iku*; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Ishii, Kosuke*; Miyasaka, Iku*; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English