Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ssbauer isomer shifts using second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess Hamiltonian
ssbauer isomer shifts using second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess HamiltonianKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Hyperfine Interactions, 239(1), p.20_1 - 20_10, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:80.85(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We optimized a mixing ratio of exchange energy between pure DFT and exact Hartree-Fock using TPSS exchange-correlation functional to estimate the accurate coordination bonds in f-block complexes by numerically benchmarking with the experimental data of M ssbauer isomer shifts for
ssbauer isomer shifts for  Eu and
Eu and  Np nuclides. Second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess Hamiltonian with segmented all-electron relativistically contracted basis set was employed to calculate the electron densities at Eu and Np nuclei, i.e. contact densities, for each five complexes for Eu(III) and Np(IV) systems. We compared the root mean square deviation values of their isomer shifts between experiment and calculation by changing the mixing ratio of Hartree-Fock exchange parameter from 0 to 100 % at intervals of 10 %. As the result, it was indicated that the mixing ratio of 30 and 60 % for Eu and Np benchmark systems, respectively, gives the smallest deviation values. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the covalency in the metal-ligand bonds for both Eu and Np complexes decreases with increasing the Hartree-Fock exchange admixture.
Np nuclides. Second-order Douglas-Kroll-Hess Hamiltonian with segmented all-electron relativistically contracted basis set was employed to calculate the electron densities at Eu and Np nuclei, i.e. contact densities, for each five complexes for Eu(III) and Np(IV) systems. We compared the root mean square deviation values of their isomer shifts between experiment and calculation by changing the mixing ratio of Hartree-Fock exchange parameter from 0 to 100 % at intervals of 10 %. As the result, it was indicated that the mixing ratio of 30 and 60 % for Eu and Np benchmark systems, respectively, gives the smallest deviation values. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the covalency in the metal-ligand bonds for both Eu and Np complexes decreases with increasing the Hartree-Fock exchange admixture.
Kimura, Taiki*; Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 47(42), p.14924 - 14931, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.16(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We demonstrated density functional calculations of Eu(III) and Am(III) complexes with pnictogen-donor (X) ligands, CH )
) X-CH
X-CH -CH
-CH -X(CH
-X(CH )
) (X = N, P, As and Sb). We investigated the optimized structures of the cmoplexes and the Gibbs energy differences in the complex formation reactions. Those results indicated that the N- and P-donor ligands have Am(III) ion selectivity over Eu(III) ion, especially, the P-donor ligand showed the highest selectivity. The tendency of the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity by the pnictogen-dono ligands was found to be comparable to that of soft acid classification in hard and soft acids and bases rule. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the bonding property between the metal ion and the pnictogen atoms correlated with the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity. In particular, the participation of f-orbital electrons of the metal ion in the covalency was indicated to have an important role for the selectivity.
(X = N, P, As and Sb). We investigated the optimized structures of the cmoplexes and the Gibbs energy differences in the complex formation reactions. Those results indicated that the N- and P-donor ligands have Am(III) ion selectivity over Eu(III) ion, especially, the P-donor ligand showed the highest selectivity. The tendency of the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity by the pnictogen-dono ligands was found to be comparable to that of soft acid classification in hard and soft acids and bases rule. Mulliken's spin population analysis indicated that the bonding property between the metal ion and the pnictogen atoms correlated with the Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity. In particular, the participation of f-orbital electrons of the metal ion in the covalency was indicated to have an important role for the selectivity.

 /
/ values by benchmark study of the M
values by benchmark study of the M ssbauer Isomer shifts for Ru, Os complexes using relativistic DFT calculations
ssbauer Isomer shifts for Ru, Os complexes using relativistic DFT calculationsKaneko, Masashi; Yasuhara, Hiroki*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.36_1 - 36_9, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.16(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We aim to evaluate the validity of density functional calculations to the bonding property for Ru and Os complexes. We performed the benchmarking of theoretical computational method with  Ru,
Ru, 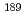 Os M
Os M ssbauer isomer shifts. As the result, the computational values of the electron densities at nucleus position correlated with the experimental M
ssbauer isomer shifts. As the result, the computational values of the electron densities at nucleus position correlated with the experimental M ssbauer isomer shifts.
ssbauer isomer shifts.
 ssbauer isomer shifts with density functional calculations
ssbauer isomer shifts with density functional calculationsKaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Radioisotopes, 66(8), p.289 - 300, 2017/08
Scalar-relativistic density functional calculations applied to some trivalent europium complexes. Five Eu(III) complexes whose  Eu M
Eu M ssbauer isomer shifts vary from -1.8 to 0.5 mm/s are referred by previously reported results. Geometrical optimizations of their complexes reproduces the experimental coordination structures. Single-point calculations are applied to their optimized geometries at three density functionals, namely, BP86, B3LYP, and B2PLYP, to obtain their electron densities at Eu nucleus. A comparison of the linearity between the electron densities and the corresponding
ssbauer isomer shifts vary from -1.8 to 0.5 mm/s are referred by previously reported results. Geometrical optimizations of their complexes reproduces the experimental coordination structures. Single-point calculations are applied to their optimized geometries at three density functionals, namely, BP86, B3LYP, and B2PLYP, to obtain their electron densities at Eu nucleus. A comparison of the linearity between the electron densities and the corresponding  Eu M
Eu M ssbauer isomer shifts reveals that B2PLYP functional shows the best linearity. Electron population and bond analyses indicate that d- and f-orbital electrons of Eu ion in the complexes are found to be correlated to the experimental
ssbauer isomer shifts reveals that B2PLYP functional shows the best linearity. Electron population and bond analyses indicate that d- and f-orbital electrons of Eu ion in the complexes are found to be correlated to the experimental  Eu M
Eu M ssbauer isomer shifts. This indicates that the d- and f-orbital electrons are involved in the covalent interaction of the coordination bond between the Eu ion and the ligands.
ssbauer isomer shifts. This indicates that the d- and f-orbital electrons are involved in the covalent interaction of the coordination bond between the Eu ion and the ligands.
Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 17, p.9 - 15, 2017/03
Density functional calculations were applied to the complexation of Eu(III) and Am(III) ions with phosphinic acid (O-donor) and dihiophosphinic acid (S-donor) from the viewpoint of the bonding nature of valence orbitals in metal ion. Two and four conformers for S-donor and O-donor complexes, respectively were optimized. Their stabilization energies by complex formation toward [M(H O)
O) ]
] were estimated. As the result, the energies reproduced the experimental Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity that O-donor ligand preferably coordinates to Eu(III) ion, whereas S-donor ligand selectively coordinates to Am(III) ion. Focused on the bonding natures of d and f-orbital electrons, it was indicated that the d-orbital electrons in both Eu and Am complexes participate in the covalency as bonding-type nature and have the almost same contribution. Meanwhile, the contribution of the f-orbital electrons was different between Eu and Am complexes and indicated that in the case of S-donor complex, non-bonding type and bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively and in the case of O-donor complex, bonding type and anti-bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively. This result suggested that the bonding natures of d-orbital electrons contribute to the geometrical similarity of molecular structures for Eu and Am complexes and the bonding natures of f-orbital electrons contribute to the difference in the selectivity of Eu and Am ions.
were estimated. As the result, the energies reproduced the experimental Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity that O-donor ligand preferably coordinates to Eu(III) ion, whereas S-donor ligand selectively coordinates to Am(III) ion. Focused on the bonding natures of d and f-orbital electrons, it was indicated that the d-orbital electrons in both Eu and Am complexes participate in the covalency as bonding-type nature and have the almost same contribution. Meanwhile, the contribution of the f-orbital electrons was different between Eu and Am complexes and indicated that in the case of S-donor complex, non-bonding type and bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively and in the case of O-donor complex, bonding type and anti-bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively. This result suggested that the bonding natures of d-orbital electrons contribute to the geometrical similarity of molecular structures for Eu and Am complexes and the bonding natures of f-orbital electrons contribute to the difference in the selectivity of Eu and Am ions.
Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:71.09(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.05001_1 - 05001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We measured ionization efficiencies of fermium, einsteinium, mendelevium, and lawrencium by using a newly developed gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of the elements have not been determined so far due to their low production rates and/or their short half-lives. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potentials of these actinide elements have been successfully determined.
 and W(CO)
and W(CO)
Usoltsev, I.*; Eichler, R.*; Wang, Y.*; Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 104(3), p.141 - 151, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:94.04(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Conditions of the production and decomposition of hexacarbonyl complexes of short-lived Mo and W isotopes were investigated to study thermal stability of the heaviest group 6 hexacarbonyl complex Sg(CO) . A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO)
. A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO) and W(CO)
and W(CO) , indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO)
, indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO) could be determined with this technique.
could be determined with this technique.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
Nature, 520(7546), p.209 - 211, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:115 Percentile:97.06(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We successfully measured ionization efficiencies of lawrencium (Lr,  =103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
=103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
Even, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(3), p.2457 - 2466, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.55(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid In situ synthesis of metal carbonyl complexes has been demonstrated using short-lived isotopes produced in nuclear fission and fusion reactions. The short-lived isotopes with high recoil energy directly react with carbon-monoxides and form carbonyl complexes. Only highly volatile complexes were fast transported in a gas stream to counting and chemistry devices. Short-lived Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, W, Re, Os, and Ir were found to form volatile carbonyl complexes, while no volataile complex of Hf and Ta were detected. This technique has been applied to a chemical investigation of the superheavy element Sg (atomic number 106), and will be applicable to various fields of nuclear science with short-lived transition metal isotopes.
 gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; Towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)
gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; Towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1253 - 1257, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.87(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a surface-ionization ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr,
gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, 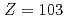 ). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of
). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of  Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.92(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 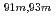 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
Science, 345(6203), p.1491 - 1493, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:83.10(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A new superheavy element complex, a seaborgium carbonyl, has been successfully synthesized, and its adsorption property has been studied using a cryo-thermochromatography and  -detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived
-detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived  Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of
Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of  50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO)
50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO) . This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
. This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
Sato, Tetsuya; Sato, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 84(2), p.023304_1 - 023304_5, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:57.94(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed the surface ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system to measure the ionization potential of Lr atatom-at-a-time conditions. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time
gas-jet transport system to measure the ionization potential of Lr atatom-at-a-time conditions. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time  Lr ions by applying the present ion-source and the ISOL technique. The ionization efficiencies of Lr were estimated to be approximately 42% and 24% at 2600 K on Re and Ta surfaces, respectively. These values were higher than those of Lu in all of ionization condition. The results indicate that the ionization potential of Lr would be lower than that of Lu, 5.4 eV. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface ion-source is a promising apparatus tomeasure the first ionization potential of Lr. Using the present system, determination of the ionization potential of Lr is being performed.
Lr ions by applying the present ion-source and the ISOL technique. The ionization efficiencies of Lr were estimated to be approximately 42% and 24% at 2600 K on Re and Ta surfaces, respectively. These values were higher than those of Lu in all of ionization condition. The results indicate that the ionization potential of Lr would be lower than that of Lu, 5.4 eV. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface ion-source is a promising apparatus tomeasure the first ionization potential of Lr. Using the present system, determination of the ionization potential of Lr is being performed.
Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Li, Z.*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Miyashita, Sunao*; Mori, Tomotaka*; Suganuma, Hideo*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 84(9), p.903 - 911, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:49.45(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The cation-exchange behavior of element 104, rutherfordium (Rf), was investigated together with its lighter group-4 homologues Zr and Hf, and the tetravalent pseudo-homologue Th in HF/HNO mixed solution. The results demonstrate that distribution coefficients (
mixed solution. The results demonstrate that distribution coefficients ( ) of Rf in HF/0.10 M HNO
) of Rf in HF/0.10 M HNO decrease with increasing concentration of the fluoride ion [F
decrease with increasing concentration of the fluoride ion [F ], indicating the consecutive formation of fluorido complexes of Rf. We also measured the
], indicating the consecutive formation of fluorido complexes of Rf. We also measured the  values of Rf and the homologues as a function of the hydrogen ion concentration [H
values of Rf and the homologues as a function of the hydrogen ion concentration [H ]. The log
]. The log  values decrease linearly with an increase of log [H
values decrease linearly with an increase of log [H ] with slopes between -2.1 and -2.5. This indicates that these elements are likely to form the same chemical compounds: mixture of [MF]
] with slopes between -2.1 and -2.5. This indicates that these elements are likely to form the same chemical compounds: mixture of [MF] and [MF
and [MF ]
] (M = Rf, Zr, Hf and Th) in the studied solution. It is also ascertained that sequence in the fluoride complex formation is Zr
(M = Rf, Zr, Hf and Th) in the studied solution. It is also ascertained that sequence in the fluoride complex formation is Zr  Hf
Hf  Rf
Rf  Th.
Th.
Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Tome, Hayato; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Miyashita, Sunao*; Mori, Tomotaka*; Suganuma, Hideo*; et al.
Chemistry Letters, 37(3), p.288 - 289, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:55.20(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated cation-exchange behavior of Rf together with the lighter homologues of the group-4 elements Zr and Hf, and the tetravalent pseudo-homologue Th, in HF/HNO solution using Automated Ion exchange separation apparatus coupled with the Detection system for Alpha spectroscopy (AIDA). The
solution using Automated Ion exchange separation apparatus coupled with the Detection system for Alpha spectroscopy (AIDA). The 
 values of Zr, Hf, Th and Rf in HF/0.1 M HNO
values of Zr, Hf, Th and Rf in HF/0.1 M HNO were decreased with increasing the concentration of the fluoride ion [F
were decreased with increasing the concentration of the fluoride ion [F ], indicating the formation of the fluoride complexes. The sequence of the fluoride complexation strength is Zr
], indicating the formation of the fluoride complexes. The sequence of the fluoride complexation strength is Zr  Hf
Hf  Rf
Rf  Th.
Th.
 Db
DbAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao; Oe, Kazuhiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
 -
- spectroscopy of
spectroscopy of  Db, the element 105, was performed for the first time, and the first experimental information on the proton configuration of the ground state of
Db, the element 105, was performed for the first time, and the first experimental information on the proton configuration of the ground state of  Db was obtained. Non observation of
Db was obtained. Non observation of  and X rays following its
and X rays following its  decay indicates that the
decay indicates that the  decay of
decay of  Db directly populates the 7/2
Db directly populates the 7/2 [514] ground state or the 1/2
[514] ground state or the 1/2 [521] isomeric state in the daughter nucleus
[521] isomeric state in the daughter nucleus  Lr, and does not populate the 9/2
Lr, and does not populate the 9/2 [624] excited state. This result indicates that the proton configuration of the ground state of
[624] excited state. This result indicates that the proton configuration of the ground state of  Db should not be the theoretically predicted 9/2
Db should not be the theoretically predicted 9/2 [624], but the 7/2
[624], but the 7/2 [514] or 1/2
[514] or 1/2 [521].
[521].
Miyashita, Sunao; Oe, Kazuhiro; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
no journal, ,
For the experiments of the redox potentials of Sg, rapid separation between different oxidation states of Sg is needed. In this study, solvent extraction of hexavalent Mo and W, as the lighter homologues of Sg, from 1.0 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution into di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (HDEHP), 1-phenyl-3-metyl-4-benzoyl-5-pyrazolone (PMBP), N-benzoyl-N-pheny-hydroxylamine (BPHA) and 4-isopropyl-tropolone (HT) in toluene was carried out. When HDEHP and PMBP were used as extractant, extraction equilibrium of  W was achieved within 5 and 1 hours respectively. On the other hand, when BPHA and HT were used, extraction equilibrium of
W was achieved within 5 and 1 hours respectively. On the other hand, when BPHA and HT were used, extraction equilibrium of  W was quickly achieved within 1 minute in both extractants. Extraction kinetics of
W was quickly achieved within 1 minute in both extractants. Extraction kinetics of 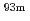 Mo using BPHA and HT was examined. Extraction kinetics of Mo was slower than that of W. Extraction equilibrium of Mo was achieved within 10 by BPHA and 3 minutes by HT. We concluded that HT is a suitable extractant for the Sg reduction experiment.
Mo using BPHA and HT was examined. Extraction kinetics of Mo was slower than that of W. Extraction equilibrium of Mo was achieved within 10 by BPHA and 3 minutes by HT. We concluded that HT is a suitable extractant for the Sg reduction experiment.
Miyashita, Sunao; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
del, M.; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
no journal, ,
For determination of the redox potentials of seaborgium (Sg), we plan to carry out rapid continuous experiments using a new system combined with a flow electrolytic column and the rapid liquid-liquid extraction apparatus SISAK. For the experiments of redox potentials of Sg, fast separation between different oxidation states of Sg is required. In this study, solvent extraction of W and Mo, as the lighter homologues of Sg, from 0.10 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution into di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (HDEHP), 1-phenyl-3-metyl-4-benzoyl-5-pyrazolone (PMBP) and 3-isopropyl-tropolone (HT) in toluene was investigated. A synergistic effect by tributylphosphate (TBP) was also examined.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao; Oe, Kazuhiro; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
del, M.; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We plan to determine the redox potential of seaborgium (Sg) in continuous experiments with a flow electrolytic column and a continuous solvent extraction SISAK. In this study, reduction experiments of its lighter homologues, Mo and W, were performed using the flow electrolytic column apparatus. After 200  L of the
L of the  W radiotracer in 0.1 M HCl was introduced into the apparatus, 1000
W radiotracer in 0.1 M HCl was introduced into the apparatus, 1000  L of 0.1 M HCl was fed into the electrode on which an potential was applied between -0.8 and 0.6 V. 1000
L of 0.1 M HCl was fed into the electrode on which an potential was applied between -0.8 and 0.6 V. 1000  L was taken from the effluent from the electrode and was then mixed with 10
L was taken from the effluent from the electrode and was then mixed with 10 M hinokitiol in toluene with the same volume. After shaking for 1 min and then centrifuging for 30 s, 800
M hinokitiol in toluene with the same volume. After shaking for 1 min and then centrifuging for 30 s, 800  L was taken from each phase, which was then separately subjected to
L was taken from each phase, which was then separately subjected to  -ray spectrometry. As a result, the extraction yield of
-ray spectrometry. As a result, the extraction yield of  W was constant against the variation of the applied potential. It seems that once reduced W was again oxidized to the +6 state in the extraction procedure.
W was constant against the variation of the applied potential. It seems that once reduced W was again oxidized to the +6 state in the extraction procedure.