Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Taruta, Yasuyoshi; Aratani, Kenta; Miyashita, Shinichi; Tomoda, Koichi; Fujiwara, Wataru
JAEA-Review 2024-002, 31 Pages, 2024/06
"Fugen Decommissioning Engineering Center", in planning and carrying out our decommissioning technical development, organizes "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning" which consists of the members well-informed, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened domestic and international, as the central place in research and development base of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report consists of presentation paper are "The current status of Fugen decommissioning", "Comparative consideration of dismantling method for fuel exchanger", "Status of consideration for installation of backup power supply equipment" and "Streamlining decommissioning operations by utilizing digital technology" which is presented in the 40th Technical Special Committee on Fugen Decommissioning.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.05001_1 - 05001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We measured ionization efficiencies of fermium, einsteinium, mendelevium, and lawrencium by using a newly developed gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of the elements have not been determined so far due to their low production rates and/or their short half-lives. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potentials of these actinide elements have been successfully determined.
Hamada, Takashi; Hasegawa, Shin; Fukasawa, Hideyuki*; Sawada, Shinichi; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Miyashita, Atsumi; Maekawa, Yasunari
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3(42), p.20983 - 20991, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:69.32(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
Nature, 520(7546), p.209 - 211, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:112 Percentile:97.06(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We successfully measured ionization efficiencies of lawrencium (Lr,  =103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
=103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
 gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; Towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)
gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; Towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1253 - 1257, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.39(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a surface-ionization ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr,
gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, 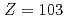 ). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of
). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of  Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Sato, Tetsuya; Sato, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 84(2), p.023304_1 - 023304_5, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.20(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed the surface ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system to measure the ionization potential of Lr atatom-at-a-time conditions. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time
gas-jet transport system to measure the ionization potential of Lr atatom-at-a-time conditions. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time  Lr ions by applying the present ion-source and the ISOL technique. The ionization efficiencies of Lr were estimated to be approximately 42% and 24% at 2600 K on Re and Ta surfaces, respectively. These values were higher than those of Lu in all of ionization condition. The results indicate that the ionization potential of Lr would be lower than that of Lu, 5.4 eV. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface ion-source is a promising apparatus tomeasure the first ionization potential of Lr. Using the present system, determination of the ionization potential of Lr is being performed.
Lr ions by applying the present ion-source and the ISOL technique. The ionization efficiencies of Lr were estimated to be approximately 42% and 24% at 2600 K on Re and Ta surfaces, respectively. These values were higher than those of Lu in all of ionization condition. The results indicate that the ionization potential of Lr would be lower than that of Lu, 5.4 eV. Therefore, it is concluded that the surface ion-source is a promising apparatus tomeasure the first ionization potential of Lr. Using the present system, determination of the ionization potential of Lr is being performed.
Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Li, Z.*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Miyashita, Sunao*; Mori, Tomotaka*; Suganuma, Hideo*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 84(9), p.903 - 911, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:49.57(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The cation-exchange behavior of element 104, rutherfordium (Rf), was investigated together with its lighter group-4 homologues Zr and Hf, and the tetravalent pseudo-homologue Th in HF/HNO mixed solution. The results demonstrate that distribution coefficients (
mixed solution. The results demonstrate that distribution coefficients ( ) of Rf in HF/0.10 M HNO
) of Rf in HF/0.10 M HNO decrease with increasing concentration of the fluoride ion [F
decrease with increasing concentration of the fluoride ion [F ], indicating the consecutive formation of fluorido complexes of Rf. We also measured the
], indicating the consecutive formation of fluorido complexes of Rf. We also measured the  values of Rf and the homologues as a function of the hydrogen ion concentration [H
values of Rf and the homologues as a function of the hydrogen ion concentration [H ]. The log
]. The log  values decrease linearly with an increase of log [H
values decrease linearly with an increase of log [H ] with slopes between -2.1 and -2.5. This indicates that these elements are likely to form the same chemical compounds: mixture of [MF]
] with slopes between -2.1 and -2.5. This indicates that these elements are likely to form the same chemical compounds: mixture of [MF] and [MF
and [MF ]
] (M = Rf, Zr, Hf and Th) in the studied solution. It is also ascertained that sequence in the fluoride complex formation is Zr
(M = Rf, Zr, Hf and Th) in the studied solution. It is also ascertained that sequence in the fluoride complex formation is Zr  Hf
Hf  Rf
Rf  Th.
Th.
Miyashita, Daisuke*; Takeda, Kazuya*; Oya, Shinichi*; Sano, Yuji*; Saito, Toshiyuki*; Akita, Koichi
Zairyo, 60(7), p.617 - 623, 2011/07
The surface residual stress relaxation under tensile loading occurred when the plastic-deformation started at the inside of material where the balancing tensile residual stress existed. Under the compressive loading, the surface residual stress relaxation started due to the plastic deformation beneath the surface where the maximum compressive residual stress existed. The plastic deformation at the inside of material caused the redistribution of the residual stress and resulted in the relaxation of the surface residual stress. For both tensile and compressive loading, the surface compressive residual stress relaxation occurred before the total stress (= (residual stress) + (applied stress)) at the surface reached to the yield condition. The conclusions of this study are thought to be able to apply to the behavior of the residual stress under the mechanical loading on metallic materials treated by any mechanical surface treatment.
Akita, Koichi; Miyashita, Daisuke*; Takeda, Kazuya*; Oya, Shinichi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Sano, Kenji*; Saito, Toshiyuki*
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-44-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.46 - 50, 2010/07
Relaxation process of surface compressive residual stress during tensile or compressive loading on a laser peened aluminum alloy was investigated. The residual stress was measured by X-ray, synchrotron and neutron diffractions and analyzed by a finite element method. The relaxation process clarified in this study was described as follows. When the tensile loading was increased, plastic deformation was occurred at the tensile residual stress region that existed inside of the material to be balanced with the surface compressive residual stress. On the other hand, when the compressive loading was applied, the plastic deformation was started at the maximum compressive residual stress region located just beneath the surface. Because the plastic deformation of the inside of the material induced the redistribution of the residual stress in the sample, the surface compressive residual stress was relaxed prior to the surface yielding.
Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Tome, Hayato; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Miyashita, Sunao*; Mori, Tomotaka*; Suganuma, Hideo*; et al.
Chemistry Letters, 37(3), p.288 - 289, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:55.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated cation-exchange behavior of Rf together with the lighter homologues of the group-4 elements Zr and Hf, and the tetravalent pseudo-homologue Th, in HF/HNO solution using Automated Ion exchange separation apparatus coupled with the Detection system for Alpha spectroscopy (AIDA). The
solution using Automated Ion exchange separation apparatus coupled with the Detection system for Alpha spectroscopy (AIDA). The 
 values of Zr, Hf, Th and Rf in HF/0.1 M HNO
values of Zr, Hf, Th and Rf in HF/0.1 M HNO were decreased with increasing the concentration of the fluoride ion [F
were decreased with increasing the concentration of the fluoride ion [F ], indicating the formation of the fluoride complexes. The sequence of the fluoride complexation strength is Zr
], indicating the formation of the fluoride complexes. The sequence of the fluoride complexation strength is Zr  Hf
Hf  Rf
Rf  Th.
Th.
Sato, Tetsuya; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sonoda, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the first ionization potential (IP) of lawrencium (Lr, Z=103), we have developed a surface ionization type ion-source coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the JAEA-ISOL. We measured ionization efficiencies of
gas-jet transport system for the JAEA-ISOL. We measured ionization efficiencies of  Lr and various short-lived lanthanide isotopes by applying the ion-source. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time
Lr and various short-lived lanthanide isotopes by applying the ion-source. We successfully ionized and mass-separated for the first time  Lr ions. From a correlation between the IPs and ionization efficiencies of the short-lived lanthanide isotopes, we estimated the IP of Lr in this work.
Lr ions. From a correlation between the IPs and ionization efficiencies of the short-lived lanthanide isotopes, we estimated the IP of Lr in this work.
 =103) by a surface ionization technique
=103) by a surface ionization techniqueSato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
We have newly developed a surface ionization ion-source coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system for JAEA-ISOL in order to determine the first ionization potential of the heaviest actinide element, lawrencium (
gas-jet transport system for JAEA-ISOL in order to determine the first ionization potential of the heaviest actinide element, lawrencium (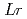 ,
,  =103). In this work, we successfully ionized
=103). In this work, we successfully ionized  Lr produced in the reaction of
Lr produced in the reaction of  Cf and
Cf and  B with the ionization efficiency of about 37% with the present apparatus. And we evaluated the first ionization potential of Lr from a correlation between effective ionization potentials and ionization efficiencies of short-lived lanthanide isotopes for the first time.
B with the ionization efficiency of about 37% with the present apparatus. And we evaluated the first ionization potential of Lr from a correlation between effective ionization potentials and ionization efficiencies of short-lived lanthanide isotopes for the first time.
Kaneya, Yusuke*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Tomitsuka, Tomohiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hirose, Kentaro; Osa, Akihiko; et al.
no journal, ,
To study the influence of the valence 7p electronic orbital on chemical properties of lawrencium, a measurement of the adsorption enthalpy of lawrencium was carried out. A new method using a surface ionization technique coupled to an on-line isotope separator was developed, which enabled one to measure temperature dependence of lawrencium surface adsorption on a metallic tantalum surface at high temperature up to 2800 K. The temperature dependences of adsorption of lawrencium as well as various lanthanide elements were investigated with this method, and the adsorption enthalpy of lawrencium was successfully extracted.
electronic orbital on chemical properties of lawrencium, a measurement of the adsorption enthalpy of lawrencium was carried out. A new method using a surface ionization technique coupled to an on-line isotope separator was developed, which enabled one to measure temperature dependence of lawrencium surface adsorption on a metallic tantalum surface at high temperature up to 2800 K. The temperature dependences of adsorption of lawrencium as well as various lanthanide elements were investigated with this method, and the adsorption enthalpy of lawrencium was successfully extracted.
Sato, Tetsuya; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Osa, Akihiko; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hirose, Kentaro; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Our experimental results on the first ionization potential measurement of lawrencium (Lr, element 103) have strongly suggested that the Lr atom has a [Rn]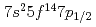 configuration as a result of the influence of strong relativistic effects. The configuration is different from that expected from the lanthanide homologue, lutetium (Lu). According to a semi-empirical consideration, it is expected that the change of the electronic configuration leads higher volatility of Lr than that of Lu. In this work, adsorption behaviors of Lr and various short-lived rare earth isotopes on a tantalum surface were investigated via observation of their surface ionization efficiencies. It was found that Lr would behave like low volatile rare earth elements such as Lu contrary to the semi-empirical expectation.
configuration as a result of the influence of strong relativistic effects. The configuration is different from that expected from the lanthanide homologue, lutetium (Lu). According to a semi-empirical consideration, it is expected that the change of the electronic configuration leads higher volatility of Lr than that of Lu. In this work, adsorption behaviors of Lr and various short-lived rare earth isotopes on a tantalum surface were investigated via observation of their surface ionization efficiencies. It was found that Lr would behave like low volatile rare earth elements such as Lu contrary to the semi-empirical expectation.
 /HF mixed solution, 2
/HF mixed solution, 2Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Miyashita, Sunao*; Mori, Tomotaka*; Suganuma, Hideo*; et al.
no journal, ,
Chemical properties of rutherfordium (Rf, the element 104) in HNO /HF mixed solutions have been investigated using cation-exchange chromatography. Distribution coefficients of Rf on the cation-exchange resin as a function of hydrofluoric-acid and nitric-acid concentrations have been measured precisely, and it was found that the strength of the fluoride complex formation of Rf is much weaker than those of lighter group 4 homologs Zr and Hf. The same result was obtained through the anion-exchange chromatography. These results enabled us to quantitatively account for the fluoride complexation of Rf.
/HF mixed solutions have been investigated using cation-exchange chromatography. Distribution coefficients of Rf on the cation-exchange resin as a function of hydrofluoric-acid and nitric-acid concentrations have been measured precisely, and it was found that the strength of the fluoride complex formation of Rf is much weaker than those of lighter group 4 homologs Zr and Hf. The same result was obtained through the anion-exchange chromatography. These results enabled us to quantitatively account for the fluoride complexation of Rf.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Vascon, A.*; Sakama, Minoru*; Sato, Daisuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
Sato, Tetsuya; Sonoda, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Miyashita, Sunao; Osa, Akihiko; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, Z=103), we have developed an appropriate surface-ionization type ion source as a part of the JAEA-ISOL setup, which is coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system. The new ion source is an improved version based on our previously used ion source, which already had a good ionization efficiencies for lanthanide. To achieve higher ionization efficiencies of low volatility elements like Lr, an additional filament was newly installed. We report, here, on the development and performance of our new gas-jet coupled surface-ionization ion source, and on the first successful ionization and mass separation of 27-s
gas-jet transport system. The new ion source is an improved version based on our previously used ion source, which already had a good ionization efficiencies for lanthanide. To achieve higher ionization efficiencies of low volatility elements like Lr, an additional filament was newly installed. We report, here, on the development and performance of our new gas-jet coupled surface-ionization ion source, and on the first successful ionization and mass separation of 27-s  Lr produced in the
Lr produced in the  Cf +
Cf +  B reaction.
B reaction.
Yamamoto, Takashi; Matsuo, Hidehiko; Miyashita, Shinichi
no journal, ,
Fugen is a heavy water-moderated, boiling light water-cooled, pressure tube-type reactor with the electrical power of 165 MW. It had been operated for 25 years from March 1979 to March 2003. After ceasing its operation, decommissioning project started 2008. Currently, FUGEN is the second phase of decommissioning (Reactor Periphery Facilities Dismantling Period). Fugen in decommissioning has the risk decreased than in operation. Therefore, it have been rationalizing maintenance continuously. At the paper, report on the rationalization and improvements of the maintenance in decommissioning. After ceasing the operation, all of the spent fuels were removed from reactor to the spent fuel pool. And now, the spent fuels has low heat generation and it is not necessary to remove the heat. Therefore, we are continuing to rationalize the maintenance plan depending on the situation of decommissioning.
 /HF solution
/HF solutionIshii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Miyashita, Sunao*; Mori, Tomotaka*; Suganuma, Hideo*; et al.
no journal, ,
The cation-exchange behavior of rutherfordium(Rf) in HNO /HF solution has been studied based on an atom-at-a-time scale. In the symposium, we will discuss the fluoride complexation of rutherfordium in comparison with that of Zr, Hf and Th.
/HF solution has been studied based on an atom-at-a-time scale. In the symposium, we will discuss the fluoride complexation of rutherfordium in comparison with that of Zr, Hf and Th.
Nonoue, Kazuki; Kubota, Shintaro; Iekura, Takeshi; Ando, Koji; Miyashita, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English