Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niwa, Hideharu*; Saito, Makoto*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Moriya, Shogo*; Matsubayashi, Katsuyuki*; Nabae, Yuta*; Kuroki, Shigeki*; Ikeda, Takashi; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 223, p.30 - 35, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:50.94(Chemistry, Physical)To design non-platinum, inexpensive, but high performance carbon-based cathode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells, it is important to elucidate the active site for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). However, it is difficult to directly identify the active site by applying conventional structural or electronic probes to such complex systems. Here, we used C 1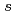 X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to observe electronic structure of carbon in iron phthalocyanine-based catalysts, and found a signature of edge exposure below the
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to observe electronic structure of carbon in iron phthalocyanine-based catalysts, and found a signature of edge exposure below the 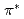 edge, whose intensity is well correlated with the ORR activity. These results demonstrate that C 1
edge, whose intensity is well correlated with the ORR activity. These results demonstrate that C 1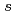 XAS can be used to characterize the ORR activity of carbon-based cathode catalysts in terms of the edge exposure.
XAS can be used to characterize the ORR activity of carbon-based cathode catalysts in terms of the edge exposure.
Kiuchi, Hisao*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Chokai, Masayuki*; Nabae, Yuta*; Kuroki, Shigeki*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Ikeda, Takashi; et al.
Electrochimica Acta, 82(1), p.291 - 295, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:34.42(Electrochemistry)We study the characteristics of oxygen adsorption on metal-free carbon-based cathode catalysts derived from nitrogen-containing polyamide (PA) and nitrogen-free phenolic resin (PhRs). Electrochemical analysis and Raman spectroscopy showed higher 2-electron oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and more defect sites in PA than PhRs. The increase in the amount of adsorbed oxygen in PA was also identified by oxygen adsorption isotherms.  X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveals that graphite-like nitrogen contributes to oxygen adsorption and C=O components are dominant in PA. These experimental results indicate that the adsorbed C=O components near the graphite-like nitrogen can be assigned as active sites for 2-electron ORR.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveals that graphite-like nitrogen contributes to oxygen adsorption and C=O components are dominant in PA. These experimental results indicate that the adsorbed C=O components near the graphite-like nitrogen can be assigned as active sites for 2-electron ORR.
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Saito, Makoto*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ofuchi, Hironori*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ikeda, Takashi; Koshigoe, Yuka*; Ozaki, Junichi*; et al.
Electrochimica Acta, 74, p.254 - 259, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:80.98(Electrochemistry)The electronic structure of the residual metal atoms in FePc-based carbon catalysts, prepared by pyrolyzing a mixture of FePc and phenolic resin polymer at 800 C, before and after acid washing have been investigated using XAFS spectroscopy to clarify the role of Fe in the ORR activity. The decomposition analyses for the XAFS spectra reveal that the composition ratio of each Fe component is unaltered by the acid washing, indicating that the residual Fe components were removed by the acid washing irrespective of their chemical states. Because the oxygen reduction potential was approximately unchanged by the acid washing, the residual Fe itself does not seem to contribute directly to the ORR activity. The residual Fe can act as a catalyst to accelerate the growth of the sp
C, before and after acid washing have been investigated using XAFS spectroscopy to clarify the role of Fe in the ORR activity. The decomposition analyses for the XAFS spectra reveal that the composition ratio of each Fe component is unaltered by the acid washing, indicating that the residual Fe components were removed by the acid washing irrespective of their chemical states. Because the oxygen reduction potential was approximately unchanged by the acid washing, the residual Fe itself does not seem to contribute directly to the ORR activity. The residual Fe can act as a catalyst to accelerate the growth of the sp carbon network during pyrolysis. The results imply that light elements are components of the ORR active sites in the FePc-based carbon catalysts.
carbon network during pyrolysis. The results imply that light elements are components of the ORR active sites in the FePc-based carbon catalysts.
Hou, Z.*; Wang, X.*; Ikeda, Takashi; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
Physical Review B, 85(16), p.165439_1 - 165439_9, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:130 Percentile:96.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand the interaction between nitrogen dopants and point defects in graphene, we have studied energetic stability of N-doped graphene with vacancies and Stone-Wales defect by performing the density functional theory calculations. Our results show that N substitution energetically prefers to occur at the carbon atoms near the defects, especially for those sites with larger bond shortening, indicating that the defect-induced strain plays an important role in the stability of N dopants. In the presence of mono-vacancy, the most stable position for N is the pyridine-like configuration while for other point defects studied N prefers a site in the pentagonal ring. While the N doping is endothermic in defect-free graphene, it becomes exothermic for defective one. Our results imply that the point defect and N dopant attract each other, which means that substitutional N dopants would increase the probability of point defect generation and vice versa.
Wang, X.*; Hou, Z.*; Ikeda, Takashi; Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Boero, M.*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
Physical Review B, 84(24), p.245434_1 - 245434_7, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:76.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structural and electronic properties of N-doped zigzag graphene ribbons with various ratios of di- to monohydrogenated edge carbons are investigated within the density functional theory framework. We find that the stability of graphitic N next to the edge, which is claimed to play important roles in the catalytic activity in our previous work, will be enhanced with increasing the concentration of di-hydrogenated carbons. Furthermore, the di-hydrogenated edge carbons turn out to be easily converted into mono-hydrogenated ones in the presence of oxygen molecules at room temperature. Based on our results, we propose a possible way to enhance the oxygen reduction catalytic activity of N-doped graphene by controlling the degrees of hydrogenation of edge carbons. The characteristic features in the X-ray absorption and emission spectra for each specific N site considered here will also be given.
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Horiba, Koji*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ofuchi, Hironori*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ikeda, Takashi; Koshigoe, Yuka*; Ozaki, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 196(20), p.8346 - 8351, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:67.33(Chemistry, Physical)The electronic structure of Co atoms in CoPc-based carbon catalysts, which were prepared by pyrolyzing a mixture of CoPc and phenol resin polymer up to 1000 C, has been investigated using XAFS analysis and HXPES. The Co K XAFS spectra show that most of the Co atoms are in the metallic state and small quantities of oxidized Co components are present in the samples even after acid washing to remove Co atoms. Based on the difference in probing depth between XAFS and HXPES, it was found that after acid washing, the surface region with the aggregated Co clusters is primarily composed of metallic Co. Since the electrochemical properties remain almost unchanged even after the acid washing process, the residual metallic and oxidized Co atoms themselves will hardly contribute to the ORR activity of the CoPc-based carbon cathode catalysts, implying that the active sites of the CoPc-based catalysts primarily consist of light elements such as C and N.
C, has been investigated using XAFS analysis and HXPES. The Co K XAFS spectra show that most of the Co atoms are in the metallic state and small quantities of oxidized Co components are present in the samples even after acid washing to remove Co atoms. Based on the difference in probing depth between XAFS and HXPES, it was found that after acid washing, the surface region with the aggregated Co clusters is primarily composed of metallic Co. Since the electrochemical properties remain almost unchanged even after the acid washing process, the residual metallic and oxidized Co atoms themselves will hardly contribute to the ORR activity of the CoPc-based carbon cathode catalysts, implying that the active sites of the CoPc-based catalysts primarily consist of light elements such as C and N.
 -edge X-ray absorption spectra of nanographene
-edge X-ray absorption spectra of nanographeneHou, Z.*; Wang, X.*; Ikeda, Takashi; Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Boero, M.*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115(13), p.5392 - 5403, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:72.35(Chemistry, Physical)Carbon  -edge X-ray absorption spectra of nanographene have been simulated by density functional theory calculations in order to obtain the information on the edge termination by hydrogen. Our results show that different edge terminations significantly affect the binding energy of 1s core-level of C atoms in the vicinity of edges because of the change in chemical bonding and the localized edge states. We find that a shoulder or a peak appears below the
-edge X-ray absorption spectra of nanographene have been simulated by density functional theory calculations in order to obtain the information on the edge termination by hydrogen. Our results show that different edge terminations significantly affect the binding energy of 1s core-level of C atoms in the vicinity of edges because of the change in chemical bonding and the localized edge states. We find that a shoulder or a peak appears below the 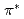 peak at relatively different positions with respect to the
peak at relatively different positions with respect to the 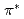 peak position in the theoretical spectra of zigzag graphene nano-ribbons, depending on the ratio of mono-hydrogen- to di-hydrogen-terminations. We also point out that the two additional features observed between the
peak position in the theoretical spectra of zigzag graphene nano-ribbons, depending on the ratio of mono-hydrogen- to di-hydrogen-terminations. We also point out that the two additional features observed between the 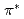 and
and 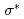 peaks of an ideal graphene originate from the
peaks of an ideal graphene originate from the 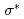 states of C-H bonding and C-H
states of C-H bonding and C-H bonding at the edges.
bonding at the edges.
Niwa, Hideharu*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Horiba, Koji*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ikeda, Takashi; Koshigoe, Yuka*; Ozaki, Junichi*; Miyata, Seizo*; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 196(3), p.1006 - 1011, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:91.52(Chemistry, Physical)We report on the electronic structure of three different types of N-containing carbon-based cathode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells observed by hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. C 1s spectra show the importance of 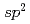 carbon network formation for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity. Samples having high oxygen reduction reaction activity in terms of oxygen reduction potential contain high concentration of graphite-like nitrogen. Based on a quantitative analysis of our results, the oxygen reduction reaction activity of the carbon-based cathode catalysts will be improved by increasing concentration of graphite-like nitrogen in a developed
carbon network formation for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity. Samples having high oxygen reduction reaction activity in terms of oxygen reduction potential contain high concentration of graphite-like nitrogen. Based on a quantitative analysis of our results, the oxygen reduction reaction activity of the carbon-based cathode catalysts will be improved by increasing concentration of graphite-like nitrogen in a developed 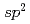 carbon network.
carbon network.
Ikeda, Takashi; Boero, M.*; Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ozaki, Junichi*; Miyata, Seizo*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114(19), p.8933 - 8937, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:83.04(Chemistry, Physical)Carbon Alloy Catalysts (CACs) have been attracting a growing interest as potential Pt-free electrode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cell. In this computational study, we inspect possible oxygen adsorption and reduction processes on various models for exposed edges of these catalysts via first principles molecular dynamics. Our simulations suggest that the codoping of boron and nitrogen in CACs is a promising route to further enhancement of their catalytic activity with respect to both stability and reactivity.
Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ozaki, Taisuke*; Ikeda, Takashi; Boero, M.*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ozaki, Junichi*; Miyata, Seizo*
Physical Review B, 80(23), p.235410_1 - 235410_12, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:168 Percentile:97.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Recent studies suggest that the carbon-alloy catalyst with doped nitrogen may be a powerful candidate for cathode catalyst of fuel cell. In this paper, we aim to clarify the microscopic mechanisms of the enhancement in the catalyst activity caused by nitrogen doping using a simple graphene cluster model. We analyze modifications in the electronic structures and the energetical stability for some different configurations of N doping. We extend the analysis to the case of co-doping of nitrogen and boron and propose two possible scenarios explaining the further enhancement of catalytic activity by N and B co-doping.
Niwa, Hideharu*; Horiba, Koji*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ikeda, Takashi; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ozaki, Junichi*; Miyata, Seizo*
Journal of Power Sources, 187(1), p.93 - 97, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:434 Percentile:99.8(Chemistry, Physical)The electronic structure of nitrogens introduced in various carbon-based cathode catalysts for a polymer electrolyte fuel cell (PEFC) has been investigated using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The profile of the 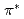 peaks at the pre-edge of the N 1s XAS spectra is used to determine the chemical states of nitrogens, which can be a marker of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity; it is found that catalysts that have relatively high amount of graphite-like nitrogen exhibit higher ORR activity than those having relatively high amount of pyridine-like nitrogen. We propose that effective doping of graphite-like nitrogen is a practical guideline for the synthesis of active carbon alloy catalysts.
peaks at the pre-edge of the N 1s XAS spectra is used to determine the chemical states of nitrogens, which can be a marker of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity; it is found that catalysts that have relatively high amount of graphite-like nitrogen exhibit higher ORR activity than those having relatively high amount of pyridine-like nitrogen. We propose that effective doping of graphite-like nitrogen is a practical guideline for the synthesis of active carbon alloy catalysts.
Ikeda, Takashi; Boero, M.*; Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ozaki, Junichi*; Miyata, Seizo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Takashi; Hou, Z.*; Wang, X.*; Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Takashi; Hou, Z.*; Wang, X.*; Huang, S.-F.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Takashi; Hou, Z.*; Wang, X.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English