Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi; Sagawa, Masato*; Koyama, Keiichi*; Miyazaki, Terunobu*
no journal, ,
Sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets consist of Nd Fe
Fe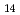 B main phase with about 5
B main phase with about 5 m diameter and Nd-rich grain boundary phase. It is well known that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets is highly dominated by this Nd-rich phase, which is reported to change from discontinuous to continuous arrangement by a low temperature annealing around 500
m diameter and Nd-rich grain boundary phase. It is well known that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets is highly dominated by this Nd-rich phase, which is reported to change from discontinuous to continuous arrangement by a low temperature annealing around 500 600
600 C. We have shown that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets can be further increased by applying a high magnetic field during the annealing. We found that such a coercivity enhancement phenomenon occurred only when a small amount of Cu is added, and when the annealing temperature is around 500
C. We have shown that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets can be further increased by applying a high magnetic field during the annealing. We found that such a coercivity enhancement phenomenon occurred only when a small amount of Cu is added, and when the annealing temperature is around 500 C or 550
C or 550 C. In this paper, we report on the results of interface nanostructure analysis by DSC and Small Angle Neutron Scattering experiments to investigate the reason magnetic field effect occurs only in Cu-containing samples at specific annealing temperatures.
C. In this paper, we report on the results of interface nanostructure analysis by DSC and Small Angle Neutron Scattering experiments to investigate the reason magnetic field effect occurs only in Cu-containing samples at specific annealing temperatures.