Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
-synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 11(4), p.e0151447_1 - e0151447_17, 2016/04
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:63.33(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Filamentous aggregates (amyloid fibrils) of the protein  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn) are related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. To understand the pathogenesis mechanism of this disease, the mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation of
-Syn) are related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. To understand the pathogenesis mechanism of this disease, the mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation of  -Syn must be elucidated. As a first step toward this ultimate goal, dynamical behavior of
-Syn must be elucidated. As a first step toward this ultimate goal, dynamical behavior of  -Syn in the monomeric and the fibril states was investigated using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). Analysis of the QENS spectra of solution samples of
-Syn in the monomeric and the fibril states was investigated using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). Analysis of the QENS spectra of solution samples of  -Syn shows that diffusive global motions are observed in the monomeric state but largely suppressed in the fibril state. However, the amplitude of the side chain motion is shown to be larger in the fibril state than in the monomeric state. This implies that significant solvent space exists within the fibrils, which is attributed to the
-Syn shows that diffusive global motions are observed in the monomeric state but largely suppressed in the fibril state. However, the amplitude of the side chain motion is shown to be larger in the fibril state than in the monomeric state. This implies that significant solvent space exists within the fibrils, which is attributed to the  -Syn molecules within the fibrils having a distribution of conformations. The larger amplitude of the side chain motion in the fibril state than in the monomeric state implies that the fibril state is entropically favorable.
-Syn molecules within the fibrils having a distribution of conformations. The larger amplitude of the side chain motion in the fibril state than in the monomeric state implies that the fibril state is entropically favorable.
 -dependence of spin exchange interactions in
-dependence of spin exchange interactions in  MnO
MnO (
( = Rare-Earth Ions)
= Rare-Earth Ions)梶本 亮一; 望月 秀記*; 吉澤 英樹*; 新谷 寛*; 木村 剛*; 十倉 好紀*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(9), p.2430 - 2433, 2005/09
被引用回数:39 パーセンタイル:79.79(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A型反強磁性秩序を示すPrMnO と長距離磁気秩序を示すTbMnO
と長距離磁気秩序を示すTbMnO のマグノン励起を中性子非弾性散乱実験によって調べた。LaMnO
のマグノン励起を中性子非弾性散乱実験によって調べた。LaMnO の結果(K. Hirota
の結果(K. Hirota  )も合わせて議論することで
)も合わせて議論することで イオンの違いによるスピン交換相互作用の系統的な変化を明らかにした。
イオンの違いによるスピン交換相互作用の系統的な変化を明らかにした。 イオンの半径が小さくなるにつれて
イオンの半径が小さくなるにつれて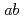 面内の最近接サイト間の交換相互作用は急激に減少し、TbMnO
面内の最近接サイト間の交換相互作用は急激に減少し、TbMnO では有限の次近接サイト間交換相互作用が存在する。対照的に
では有限の次近接サイト間交換相互作用が存在する。対照的に 軸方向の交換相互作用の
軸方向の交換相互作用の 依存性は非常に小さい。これらの結果は、
依存性は非常に小さい。これらの結果は、 MnO
MnO における磁気構造の変化は最近接サイト間相互作用と次近接サイト間相互作用の競合によって引き起こされるという説(T. Kimura
における磁気構造の変化は最近接サイト間相互作用と次近接サイト間相互作用の競合によって引き起こされるという説(T. Kimura  )と整合している。
)と整合している。
上出 英樹; 林 謙二; 軍司 稔; 林田 均; 西村 元彦; 飯塚 透; 木村 暢之; 田中 正暁; 仲井 悟; 望月 弘保; et al.
PNC TN9410 96-279, 51 Pages, 1996/08
動力炉・核燃料開発事業団では「原子炉冷却系総合試験」として,高速炉の実用化を目指し,実証炉段階で採用される原子炉冷却系に係る新概念技術の確立を目的とし,原子炉容器から蒸気発生器までの1次,2次冷却系,水蒸気系,崩壊熱除去系を総合的に模擬した大型ナトリウム試験を計画している。実証炉の特徴であるトップエントリー配管システム,炉内冷却器を用い自然循環を積極的に活用した崩壊熱除去系,低温流体循環方式の炉容器壁保護系,一体貫流型蒸気発生器,再循環系を用いた崩壊熱除去運転などを含め配管短縮化,機器のコンパクト化,高信頼性崩壊熱除去システムなどについて熱流動上の課題,構造上の課題を設定し,それらを解決できる試験装置として特に原子炉容器ならびに1次冷却系の試験モデルの検討を行った。特に(1)実証炉の熱流動と構造上の課題に対する解決方策としての充足,(2)熱流動上の課題と構造上の課題のバランス,(3)総合試験として系統全体での複合現象,構成機器間の熱流動的および構造的相互作用の模擬を重視して,試験モデル候補概念の創出,予測解析を含む定量的な比較評価,モデルの選定を行った。さらに,選定モデル候補概念を元に,「原子炉冷却系総合試験」全体の試験装置概念を構築した。
 -synuclein and its relation to propensity for amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein and its relation to propensity for amyloid fibril formation藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
no journal, ,
A protein  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn), which is involved with pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease, forms amyloid fibrils. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We employed neutron scattering to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of
-Syn), which is involved with pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease, forms amyloid fibrils. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We employed neutron scattering to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of  -Syn at low and neutral pH, to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. We carried out the quasielastic neutron scattering experiments using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Analysis of the quasielasitc scattering spectra showed the increased flexibility of
-Syn at low and neutral pH, to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. We carried out the quasielastic neutron scattering experiments using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Analysis of the quasielasitc scattering spectra showed the increased flexibility of  -Syn at low pH. Since the increased flexibility is likely to arise from a wider distribution of conformational substates of
-Syn at low pH. Since the increased flexibility is likely to arise from a wider distribution of conformational substates of  -Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
-Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
 -synuclein; Implication for propensity for amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein; Implication for propensity for amyloid fibril formation藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
no journal, ,
A protein  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. This abnormal protein aggregation is related to pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of
-Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. This abnormal protein aggregation is related to pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. Propensity for amyloid fibril formation depends on environmental conditions such as pH. We carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments to investigate the "dynamic" behavior of  -Syn to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. The measurements on the solution samples of
-Syn to investigate the relationship between the dynamics and propensity for amyloid fibril formation. The measurements on the solution samples of  -Syn in different pH were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in flexibility of the protein were detected between the different conditions. Since the difference in flexibility is likely to arise from different distributions of conformational substates of
-Syn in different pH were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in flexibility of the protein were detected between the different conditions. Since the difference in flexibility is likely to arise from different distributions of conformational substates of  -Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
-Syn, the results obtained suggest an entropy-driven mechanism of the amyloid fibril formation.
 -synuclein detected by neutron scattering
-synuclein detected by neutron scattering藤原 悟; 荒木 克哉*; 松尾 龍人; 八木 寿梓*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 望月 秀樹*
no journal, ,
The protein,  -synuclein (
-synuclein ( -Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. Formation of amyloid fibrils is associated with the pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. In order to obtain insights into the role of the protein dynamics in the mechanism of amyloid fibril formation, we carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments and characterized the "dynamic" behavior of
-Syn) forms amyloid fibrils. Formation of amyloid fibrils is associated with the pathogenesis of a neuro-degenerative disorder, Parkinson's disease. In order to obtain insights into the role of the protein dynamics in the mechanism of amyloid fibril formation, we carried out quasielastic neutron scattering experiments and characterized the "dynamic" behavior of  -Syn. The measurements on the solution samples of
-Syn. The measurements on the solution samples of  -Syn in the monomeric and fibril states were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in the dynamical behavior of the protein were detected between the monomeric and fibril states. Analysis of the spectra obtained suggested an entropy-driven mechanism of amyloid fibril formation.
-Syn in the monomeric and fibril states were carried out using a high energy resolution near-backscattering spectrometer, BL02 (DNA), at MLF/J-PARC, Japan. Differences in the dynamical behavior of the protein were detected between the monomeric and fibril states. Analysis of the spectra obtained suggested an entropy-driven mechanism of amyloid fibril formation.